The frailty, characterized by reduced physiological function is closely related to a fall, disability, institutionalization, hospitalization, and mortality in the elderly. A reduced physical fitness is a major phenotype of the frailty. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship among pre-frailty, physical activity (PA) and functional fitness in the community dwelling elderly women. The study participants were elderly women (n=338, 70.6±4.2years) aged over 65 who took part in the Korean Healthy Fitness Criteria study for the National Fitness Award Project in 2015. The pre-frailty was defined using the Cardiovascular Health Study frailty criteria. PA was assessed using the International PA Questionnaire (IPAQ). The participants were classified as regular PA participants if they meet the World Health Organization (WHO) PA recommendation for the elderly. Functional fitness was assessed using the composite of the National Fitness Award fitness testing for the elderly. Quality of life was evaluated using EuroQoL visual analogue scale and WHO quality of life assessment. As the results, the pre-frail elderly women were significantly older and obese (body mass index, percent body fat, waist circumference) than the healthy elderly. The pre-frail elderly presented significant decreases in walking, moderate intensity, and total PA compared to the healthy elderly even after adjusted for age and percent body fat. However, no significant difference was found in vigorous-intensity activity between the pre-frail and healthy elderly. Also, the pre-frail elderly women showed the decrease in functional fitness and quality of life compared to the healthy elderly. Regular PA was associated with high levels of muscular endurance and coordination in healthy and pre-frail elderly. In pre-frail elderly, high levels of cardiorespiratory endurance was associated with PA. In conclusion, regular PA is inversely associated with fitness decline in healthy and pre-frail community-dwelling elderly women. Regular PA might attenuate fitness decline in pre-frail elderly women.
PURPOSE This study assessed Taekwondo’s impact on functional fitness and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in older women from South Korean multicultural families. METHODS Through purposive sampling, 16 participants were divided into an experimental group that underwent a 12-week Taekwondo training program and a control group without this intervention. RESULTS Pre- and post-intervention assessments showed that the Taekwondo group experienced significant improvements in both functional fitness and HRQoL. These findings suggest that Taekwondo could be an effective physical activity for enhancing the well-being of older women in multicultural families, advocating for inclusion of culturally sensitive physical activities in health promotion programs targeting this demographic. CONCLUSIONS This study contributes to the growing body of evidence supporting physical activity’s benefits for elderly populations, particularly in multicultural family dynamics.
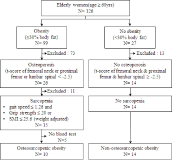
Purpose The purpose of this study were to assess physiological and biochemical characteristics in elderly women with osteosarcopenic obesity (OSO), and to analyze relationships among irisin, adipokines and bone metabolism markers. Methods 126 elderly women were selected and among them 10 women were classified into OSO group (76.9±5.2 yrs) and 14 women were classified as a NOSO group (72.9±5.6 yrs). Physique, body composition and bone mineral density were measured. Senior fitness tests were 30-s chair stand, 30-s arm curl, chair sit-and-reach, back scratch, 8-foot up-and-go, grip strength, and 2-min step test. Isokinetic muscle strength was measured by isokinetic dynamometer (Cybex 770, USA). Nutrition intake and physical activity were administered. Biochemical parameters including irisin, FNDC-5, leptin, adiponectin, CTx, 25(OH)D, osteocalcin, and PTH were measured. All data were analyzed by SAS 9.4. Independent t-test was applied to compare between OSO and NOSO groups. Multiple regression analysis was used. The level of significance was set at .05. Results The results of the study showed that there were significantly high for waist circumference, hip circumference, WHR, and BMI in OSO group compared to those of NOSO group. Higher results were also obtained for fat tissue and percent body fat but significantly low for lumbar bone mineral density. OSO group showed significant lower results for grip strength and 2-min step test compared to NOSO group. Peak torque, and relative peak torque at 60° were significantly lower for left and right knee flexion in OSO group. Protein intake was significantly low in OSO group, but no difference was obtained in level of physical activity between two groups. Irisin was significantly related to adiponectin, FNDC-5 and osteocalcin in explaining 35.2%, 81.5% and 92.1% of the variance, respectively. Conclusions This study shows that elderly women with OSO have higher results for physique and body composition parameters except body height. However, lower values were obtained for functional fitness, and isokinetic muscle strength. OSO may have more risks for metabolic syndrome, bone fractures, fall, lack of daily physical activity and limit of locomotion due to the imbalance of quadriceps and biceps femoris in non dominant leg. This study suggests that criteria and mechanism of OSO should be clarified by follow-up study.


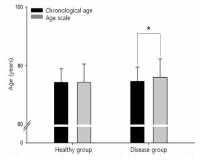
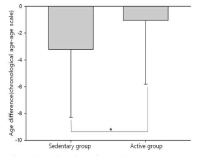
Purpose Evaluating the aging of senior and providing optimal sevices are important things for successful aging. This study identified functional fitness related with heath of aged 65 years or older and developed an age scale (longevity fitness age) for assessing their aging. Methods Participants were 458 older people (166 male, 292 female). They were divided into healthy group and disease group. Healthy group was used for the development of the longevity age equation and disease group was for investigating the validity of the equation. Participants completed 13 function fitness variables. The first principal component obtained from a principal component analysis was used to compute the equation. All variables except for grip strength and carrying beans were correlated with chronological aged. Grip strength and variables related lower functional fitness had differences between healthy group and disease group. Finally, 4 variables were selected for the equation. Results It was the following: longevity fitness age=0.942*X1+2, 185*X2+0.673*X3+0.051*X4+0.588*chronological age+58.401, where X1=standing up from a supine position, sec (s), X2=maximum walking (s), X3=standing up and sitting down a chair (s), X4=one leg balance with eyes open (s). The longevity fitness age of healthy group do not have a difference compared to their chronological age but disease group had a difference significantly. Age difference (chronological age-longevity fitness age) of sedentary group in disease group was significantly bigger than its active group. Longevity fitness age could assess an aging of senior. Conclusion We suggest that it can use as the tool for early detecting senior who need the health care service.

PURPOSE This study aims to investigate the effects of a 12-week equipment-based Pilates training on physical fitness, cardiovascular function, and vascular endothelial function in obese middle-aged women. METHODS Twenty-four women, aged 30-40 years with a body mass index ≥ 25 and percent body fat ≥ 30% were randomly assigned to one of two groups: the Pilates training group (TR; n=12); and control group (CON; n=12). The TR participants underwent three 50-minute equipmentbased Pilates training sessions per week for 12 weeks. Participants in the CON maintained their normal life patterns for the same intervention period. Variables regarding physical fitness, cardiovascular function, and vascular endothelial function were measured and compared pre-test and post-test u a two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. RESULTS The main results of the study were as follows: 1) Regarding physique and body composition, participants’ body weight, body mass index, fat mass, percent body fat, waist circumference, hip circumference, and waist-to-hip ratio decreased significantly in the TR. 2) Regarding physical fitness, muscle strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, and cardiorespiratory endurance increased significantly in the TR. 3) Regarding cardiovascular response, SV increased significantly in the TR. 4) Regarding vascular endothelial function, blood vessel diameter at rest and during vasodilation as well as blood flow volume during vasodilation decreased significantly in the CON, resulting in a significant interaction between group and test in FMD percentage. CONCLUSIONS It was concluded that the 12-week equipment-based Pilates program improved the physical fitness and vascular endothelial function in obese middle-aged women.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 8 weeks of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation on a body composition, physical fitness, insulin resistance, liver function, blood pressure, and heart rate. Fifty-one elderly women were randomly assigned to aerobic training group (EX: n=12), resveratrol supplementation group (R: n=13), combined aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation group (EX+R: n=12), and control group (CON: n=14). The subjects in EX group exercised three sessions per week, 40 minutes per session for 8 weeks, the subjects in R group took 500 mg of resveratrol per day for 8 weeks, and the subjects in EX+R group received both treatments. The subjects in CON group were asked to maintain normal daily life pattern without any treatment for the same period of intervention. Body composition, physical fitness, insulin resistance, liver function, blood pressure, and heart rate were measured at pre- and post-test and the data were compared among groups and between tests by utilizing two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Physique and body composition did not change significantly in all groups. 2) Muscular endurance increased significantly in EX+R group, whereas the other physical fitness-related variables showed no significant changes in all groups. 3) Fasting glucose, fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, and HbA1c tended to be improved in EX+R group. 4) AST, ALT, and γ·GT showed no significant changes in all groups. 5) Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure increased significantly in CON group. Heart rate tended to be decreased in EX+R group and EX group. It was concluded that the 8 weeks of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation had positive effects on muscular endurance, insulin resistance, and blood pressure in T2DM elderly women. Research investigating the effects of a longer period of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation on the same variables would be warranted in the future.
This study was designed to investigate the effects of increment of physical activity for 12 weeks through aerobic exercise training or change from own vehicle to public transportation for commuting on physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function in middle-aged men. Forty-four subjects, aged 30-50 yrs, were randomly assigned to either one of three groups, i.e., aerobic exercise training group (TR: n=14), change to public transportation group (PT: n=15), or control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR performed aerobic exercise for 30 min per sessions, three sessions per week, subjects in PT changed from their own vehicle to public transportation for commuting, and subjects in CON maintained their life patterns during the same intervention period. Physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function were measured at pre- and post-test, and the data were analyzed by repeated two-way ANOVA. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables related to physical fitness improved significantly in TR. Right grip strength, standing long jump, side step test, and sit-and-reach improved significantly in PT. 2) Although there were no significant changes in all variables related to insulin resistance, the variables tended to be improved in TR and PT. 3) TNF-α decreased significantly in TR and PT. IL-6 and CRP tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. 4) ALT decreased significantly in PT. AST and γ-GT tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. It was concluded that the 12 weeks of change to public transportation as well as aerobic exercise training would be beneficial for physical fitness and inflammatory markers. These interventions also would be possible to improve insulin resistance and liver function. The increment of physical activity through change from own vehicle to public transportation was found to be equally beneficial for health promotion compared to aerobic exercise.

The primary purpose of the study was to identify the characteristics of Korean national youth soccer players’ functional movements. The secondary purpose was to examine whether certain tests of Functional Movement Screen (FMS) meaningfully achieve goodness-of-fit for the soccer-specific movements. Korean national youth soccer players (30 male players, 18.37 ± 0.67 yrs, 178.7±7.09 cm, 70.2±6.46 kg), performed FMS tests [deep squat (DS), hurdle step (HS), in-line lunge (IL), shoulder mobility (SM), active straight leg raise (ASLR), trunk stability push-up (TSP), and rotary stability (RS)]. The mean (±SD) FMS composite score and each test score were calculated. Rasch analysis, which was used to determine the goodness-of-fit for the tests, was applied to examine the item difficulty of the FMS tests. The mean FMS composite score was 10.2± 1.79; the mean DS, HS, IL, SM, ASLR, TSP, and RS score were 1.13±0.35, 1.27±0.45, 1.4±0.56, 1.6±0.77, 2.07±0.69, 1.43±0.82, and 1.3±0.47 respectively. According to the results of Rasch analysis, 4 tests (DS, IL, ASLR, and RS) were shown to be within the acceptable range (infit & outfit > 0.5 ~ < 1.5). The other 3 tests (HS, SM, and TSP) were shown to be out of acceptable range. The additional analysis revealed the DS (logit = 2.08) as the most difficult test and ASLR (logit = -3.16) the least. The results of the study showed that the players’ FMS composite score was lower (< 14) than the cut-off points used by previous studies for different athletes. The further study is warranted to examine the relationships between the scores of the tests appeared to be soccer-specific in the present study and the level of performance variables.

PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of different resistance training structures on basic physical fitness, 1-repetition maximum (1RM), and isokinetic shoulder and knee muscle functions in male college students. METHODS Forty college students were divided into four groups: control group (CG, n=10), compound set training group (CSG, n=10), pyramid set training group (PSG, n=10), and superset training group (SSG, n=10). Excluding CG, each group performed a different resistance exercise method at an intensity of 60~80% 1RM for 60~90 min, three times a week for eight weeks. To compare the effects of resistance training structures, we confirmed body composition, basic physical fitness, 1RM, as well as isokinetic shoulder and knee functions. RESULTS Results indicated that the PSG exhibited the most significant improvement in relative peak torque in isokinetic shoulder and knee testing compared to the other groups. Additionally, all exercise groups positively affected back strength, 40m sprint, and 1RM compared to the CG, although no significant differences were observed among exercise groups. CONCLUSIONS The findings suggest scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of pyramidal resistance training in improving isokinetic shoulder and knee muscle functions in male college students.
Frailty in older adults is related to an increased risk for poor health outcomes including falls, disability, hospitalization and mortality. The purpose of this study was to determine the thresholds of a functional fitness associated with frailty for community-dwelling woman aged 65 or older. In this study, the National Fitness Award(NFA) items for elderly were utilized as the physical function and fitness testing for korean elderly women. The total of 444 community-dwelling woman completed the testings. Frailty status was classified by the Japan LTCI system ‘Kihon Checklist’ in the study. The prevalence of the frailty was 19.1% in the study. The frail elderly were older and showed higher obesity index such as weight, body mass index (BMI), percent body fat and waist circumference than the normal elderly. After adjusting for age and BMI which was related to frailty, fitness testing items were compared depending on frailty. As the result, the frail elderly showed significantly lower fitness levels in grip strength, 30-second chair stand test, timed up and go, figure-of-8 walk around two cones, and 2-minute step test than the normal elderly. When the fitness cut-off values were analyzed using the ROC curve, also, grip strength: 34.13%, 30-second chair stand test: 14 reps, timed up and go: 7.09 seconds, figure-of-8 walk around two cones: 30.88 seconds, and 2-minute step test: 93 reps. In addition, based on the cut-off values of each fitness item, the group with a low fitness level showed a 1.86 to 3.09 higher odds ratio of frailty than the group with a high fitness level, even after age and BMI were adjusted. In conclusion, these findings indicate that the fitness cut-off values in this study are fitness levels for preventing frailty of Korean elderly women and there will be a need for a large-scale study including subdivided fitness cut-off values for each age group and targets elderly men as well.