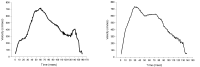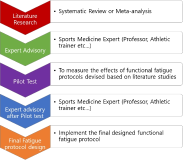
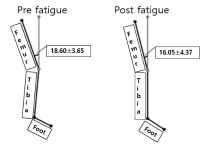
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of a functional fatigue protocol on lower extremity dynamic and static postural control. Methods A total of 20 physically active collegiate students participated in this study (ten males, ten females; age 22.5±2.7 years; mass 67.0±13.0 kg; height 168.0±8.9 cm). A unilateral stance with eyes closed for 10 seconds was performed to test static postural control using a balance force plate and single-leg drop landing on 30cm box was performed as a dynamic postural control test and captured using VICON motion analysis system. Results The results of this study showed an average heart rate of 176.3 beats/minute, an 18 rating on the perceived exertion scale, significant differences in blood lactate, and a static postural control deficit after fatigue as compared with before fatigue(p<.05). Dynamic postural control after fatigue changed landing strategy in the form of stiff landing. Knee flexion was decreased at initial contact and at peak vertical ground reaction force, also, both decreased valgus and internal rotation of knee joint. Conclusions This protocol may use for enhancing fatigue-endurance training as well as for inducing fatigue. Further, to ascertain a landing strategy, it is recommended to increase landing height to clearly observe changes in landing strategy.








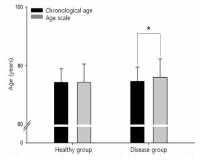
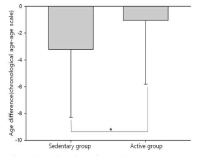
Purpose Evaluating the aging of senior and providing optimal sevices are important things for successful aging. This study identified functional fitness related with heath of aged 65 years or older and developed an age scale (longevity fitness age) for assessing their aging. Methods Participants were 458 older people (166 male, 292 female). They were divided into healthy group and disease group. Healthy group was used for the development of the longevity age equation and disease group was for investigating the validity of the equation. Participants completed 13 function fitness variables. The first principal component obtained from a principal component analysis was used to compute the equation. All variables except for grip strength and carrying beans were correlated with chronological aged. Grip strength and variables related lower functional fitness had differences between healthy group and disease group. Finally, 4 variables were selected for the equation. Results It was the following: longevity fitness age=0.942*X1+2, 185*X2+0.673*X3+0.051*X4+0.588*chronological age+58.401, where X1=standing up from a supine position, sec (s), X2=maximum walking (s), X3=standing up and sitting down a chair (s), X4=one leg balance with eyes open (s). The longevity fitness age of healthy group do not have a difference compared to their chronological age but disease group had a difference significantly. Age difference (chronological age-longevity fitness age) of sedentary group in disease group was significantly bigger than its active group. Longevity fitness age could assess an aging of senior. Conclusion We suggest that it can use as the tool for early detecting senior who need the health care service.


The purpose of this study was a investigate the endothelial function of prehypertensive during dynamic exercise. Hypothesis of this study was to impair the endothelial function in prehypertensive compared to normtensive during dynamic handgrip exercise. Eleven healthy prehypertension (24±2 yrs) and ten healthy normotensive (25 ± 2 yrs) were recruited in this study. Participants were performed dynamic handgrip exercise in one contraction per second at 30% of maximum voluntary contraction for three minutes. Vascular (blood vessel diameter, blood flow) and cardiar response (stroke volume, heart rate and cardiac output) were measured at rest and during exercise. Flow mediated dilation (FMD) was decrease significantly in prehypertensive less than normotensive (p<0.05) at rest, and vasodilation of prehypertensive was reduced significantly less than normitensive during exercise (p<0.05). All the cardiovascular responses were aot significantly different at rest and during exercise between prehypertensive and normotensive. These results suggest that endothelial function is impaired in prehypertensive compared to in normotensive


The objective of this study was to reveal the characteristics of lower extremity motions of middle-aged women in accordance with their walking speed, and also to suggest elements of improving functions of walking-shoe for the improvement of gait stability. Total 30 healthy middle-aged women were asked to walk in their preferred speed and also speed 20% faster than that. Using the 3D motion capture system and the plantar pressure measuring system, the characteristics of lower extremity motions were measured. For the analysis on differences in motions between preferred and faster speeds, the paired t-test was performed. At this time, the significance level was set up as α=.05. The walking in faster speed showed the greater ground contact angle than walking in preferred speed while its gait stability was low. Also, the faster walking showed the bigger plantar pressure, and especially, the pressure on the great toe was high. It would be necessary to improve functions of shoes for the gait stability and dispersion of pressure on feet while fast walking.




The purpose of this study was to analyze and confirm whether the items used in final paper and pencil test was determined to DIF when school sports clubs in each school operated by discriminatory curriculum in accordance with gender. Participants were 8th middle school students(male=135, female=141). They joined in school sports club every week from freshman to sophomore 1st semester. At that time, boys of them participated in soccer and basketball, and girls played dodge ball. They studied soccer unit at sophomore 1st semester, and had a final examination consisting of 5 soccer items. Using the data, differentially functioning item by the population difference between male and female were analysed quantitatively and qualitatively. The results showed that Mantel-Haenszel method(using classical test theory), comparison of item characteristic curve and likelihood ratio test(using IRT) determined item number 4 and 5 to differentially functioning item. Finally, item number 4 were identified differentially functioning item in favor of male students in intensive qualitative analyses. That item have low content validity and application-level of cognitive behavior classification. The result provides that application-level item can be functioning differentially to female students with little sports experience than male students in paper and pencil test of PE.





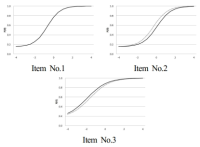

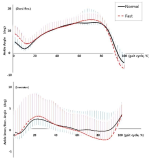
The primary purpose of the study was to identify the characteristics of Korean national youth soccer players’ functional movements. The secondary purpose was to examine whether certain tests of Functional Movement Screen (FMS) meaningfully achieve goodness-of-fit for the soccer-specific movements. Korean national youth soccer players (30 male players, 18.37 ± 0.67 yrs, 178.7±7.09 cm, 70.2±6.46 kg), performed FMS tests [deep squat (DS), hurdle step (HS), in-line lunge (IL), shoulder mobility (SM), active straight leg raise (ASLR), trunk stability push-up (TSP), and rotary stability (RS)]. The mean (±SD) FMS composite score and each test score were calculated. Rasch analysis, which was used to determine the goodness-of-fit for the tests, was applied to examine the item difficulty of the FMS tests. The mean FMS composite score was 10.2± 1.79; the mean DS, HS, IL, SM, ASLR, TSP, and RS score were 1.13±0.35, 1.27±0.45, 1.4±0.56, 1.6±0.77, 2.07±0.69, 1.43±0.82, and 1.3±0.47 respectively. According to the results of Rasch analysis, 4 tests (DS, IL, ASLR, and RS) were shown to be within the acceptable range (infit & outfit > 0.5 ~ < 1.5). The other 3 tests (HS, SM, and TSP) were shown to be out of acceptable range. The additional analysis revealed the DS (logit = 2.08) as the most difficult test and ASLR (logit = -3.16) the least. The results of the study showed that the players’ FMS composite score was lower (< 14) than the cut-off points used by previous studies for different athletes. The further study is warranted to examine the relationships between the scores of the tests appeared to be soccer-specific in the present study and the level of performance variables.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of an eye movement exercise intervention on cognitive function and prefrontal cortex connectivity in the elderly with mild cognitive impairment. METHODS Ten older adults with mild cognitive impairment participated in eye movement exercise consisting of saccadic eye movement, pursuit eye movement, vestibular-ocular eye movement, and vergence eye movement for 4 weeks. Cognitive function (MoCA-K), reaction time during stroop task, and prefrontal cortex connectivity were measured using the functional near-infrared spectrometric analyzer (fNIRS) before and after the intervention. RESULTS First, cognitive function of the elderly with mild cognitive impairment showed significant improvement after the eye movement exercise (p < .05). Second, reaction time decreased significantly from 1.16 to 0.91 ms after eye movement exercise. Third, the strength of prefrontal cortex connectivity (left OFC - right FPC, right OFC - right FPC) increased after the intervention in the older adults with mild cognitive impairment. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study suggest that eye movement exercise is an effective intervention for improving cognitive function through improvement of brain functional connection in the elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment.
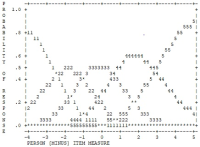
Purpose The purpose of this study was to determine item goodness-of-fit and the optimal categorization of an instrument measuring Korean elite young soccer player’s self-esteem using a two-facets Rasch model (item parameters and person parameters). Methods 10-item Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale (RSES) with five response categories was administered to 366 elite young soccer players from the Korea football association. The Rasch analysis was conducted by WINSTEPS 3.65. Results First, the model fit the data well. Second, 5-category rating scale did function well. Third, a item-person map illustrated the distribution of RSES items and person’s level of self-esteem. Fourth, the separation reliability of the items and person was shown to be an acceptable degree of confidence, respectively. Lastly, there was statistically significant difference in self-esteem between starting players and bench players, which supported the known-difference evidence of validity. Conclusion These findings provided additional support for the suitability of the RSES in assessing self-esteem of Korean elite young soccer players.


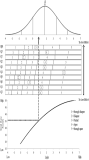
Purpose The purpose of this study was to find out the physical characteristics of Wushu athletes by comparing the differences on the results of physical fitness between the male athletes of the Wushu national team Taolu and the Sanda group. Methods Measurement of basic and professional fitness based on muscle function, targeting 37 men Wushu national team players (24 taolu, 13 Sanda) in the selection and evaluation contests twice in 2018 and 2019. Body composition, isometric muscle strength, flexibility and equilibrium, anaerobic power, and isokinetic muscle strength. The fitness factors were divided into two groups, Taolu and Sanda. Results First, body fat rate of the Sanda athlete group was significantly lower than that of the taolu athlete group (p<.01). Second, in the isometric muscle strength category(back muscle strength, grip strength), the Sanda athlete group had higher muscle strength than Taolu athlete group, but there was a statistically significant difference only in the left grip strength (p<.01). Third, in terms of flexibility and equilibrium, the taolu players were significantly higher in all items(p<.001). Fourth, in the anaerobic power, the taolu athlete group had higher both the peak power and the mean power, and there were a significant differences(peak power: p<.01, mean power: p<.001). Fifth, isokinetic muscle strength was significantly higher in the right knee flexion of the taolu athlete group (p<.01), and lumbar extensor muscle was significantly higher in the Sanda athlete group (p<.05). Sixth, in the isokinetic strength ratio, the knee flexion ratio of the Sanda athlete group were significantly higher on the left and right knee flexion and extensor ratios (p<.05). In addition, in the lumbar flexor and extensor ratios, the group of Sanda athlete group were significantly higher on the lumbar extensor(p<.05). Seventh, there was no significant difference between two groups in isokinetic muscle power. Conclusions The results of this study can be used as basic data to improve the efficiency of technical and physical training through the analysis of the characteristics of Taolu and Sanda. The effectiveness of this training will help to improve the performance.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of coupled high frequency rTMS and prism illusion in elderly stroke patients, based on the result of previous studies which discovered the effect of bilateral training, mirror rehabilitation treatment, and rTMS. Methods This is a case study of 4 stroke patients who were homogeneous on the basis of selection criteria such as brain injury area, duration of onset, degree of upper limb movement function. A total of 24 rehabilitation sessions were conducted three times a week during the training period, and TMS(transcranial magnetic stimulator), EMG, motion analysis system, and prism optical glasses were used for apparatus. Results The results of the study were as follows: Combined rehabilitation exercises were found to be beneficial to restore upper limb function in stroke patients. Particularly, the maximum speed of stretching and JTT(Jebsen-taylor Test) performance showed improvement after training. The amount of total map volume and MEP(megnetic evoked potential) increased in evaluation of neurophysiology. Conclusion The upper limb dysfunction of stroke patients could be restored by combine rehabilitation exercises.