Purpose The valuable impacts of exercise-intervention in diverse type of cancer patients were rationally well-prescribed, though many experimental and review researches already performed in this fields. Generally, cancer-related fatigue and pain remains one of the most prevalent problems for cancer populations. Therefore, exercise has become increasingly significant in cancer prevention and progression. The purpose of this recent study was to analyze the combined exercise program on cancer-related fatigue, pain, quality of life and cancer prognosis in diverse type of cancer patients. This study analyses the safety and feasibility of exercise intervention in diverse stages of cancer patients such as early stage, advanced stage and even metastatic periods in cancer populations. we also wanted to know the impacts of dose-response trial of aerobic and resistance exercise on quality of life in cancer survivors. Methods we conducted a comprehensive PubMed/MEDILINE electronic database from Jan 2015 to August 2020. The reference lists of eligible experimental research articles and relevant systemic review articles were checked. Inclusion criteria were adult cancer survivors from randomized controlled trials performing well-tailored exercise intervention programs to diverse type of cancer patients, Using predefined search items ‘exercise-intervention, cancer & immunology’. Based on reference search, more than 100 articles were identified whereas 30 research papers met the inclusion criteria and were well connected with exercise-intervention and cancer progression. we analyzed the connections between physical exercise and cancer intervention in the main text. Results Moderate to vigorous exercise (aerobic and resistance exercise) revealed to decreased level of cancer-related fatigue, pain, and cancer-related symptoms, however increased level of sleep quality, activities of daily living, exercise performance and health- related quality of life. Exercise intervention reduced pro-inflammatory markers and oxidative stress as well as insomnia, fatigue, pain symptoms whereas it enhanced the antioxidant systems and immune functions. In addition, home-based aerobic physical exercise might enhance muscular strength and quality of life in many types of cancer survivors. Psychological intervention also effective for reducing cancer-related fatigue and pain during and after cancer treatment. they might be the much better intervention than available pharmaceutical options. we believe that it is the related mechanisms of immune cell mobilization and activation such as NK cells which is induced by the activation of sympathetic system during and after physical exercise. Conclusion According to the aforementioned results, it was concluded that implementation of exercise intervention appear to be the best non-pharmaceutical interventions for cancer populations, and also revealed to be safe and feasible in early and advanced stages, although not in the metastatic periods. Sometimes, psychological intervention such as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) might be useful in reducing anxiety, depression, fatigue, pain and enhancing quality of life, quality of sleep for cancer populations. we can conclude, exercise-intervention might not just be prevention effect but might be therapeutics, however more studies are urgently needed to confirm the exercise intervention on the NK-receptors activation and immune connection of cancer populations.

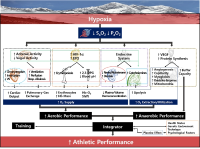
Purpose The purpose of this study is to emphasize the need for the establish and the use of altitude training center via examining exercise training method in natural or artificial altitude environment that is applied to various elite athletes in various advanced countries to maximize exercise performance and its effectiveness. Results Altitude training in natural or artificial altitude environment enhances aerobic and anaerobic exercise performance baesd on the hematological and nonhematological adaptations to hypoxic conditions. These altitude training methods can be classified into living high training high (LHTH), living high training low (LHTL), and living low training high (LLTH). LHTH (i.e., developed since the 1968 Mexico Olympics) and LHTL (i.e., developed in the 1990s by Levine and Stray-Gundersen) improve exercise performance via hematologic changes through erythropoiesis such as increased hemoglobin mass and erythrocyte volume. On the other hand, LLTH (i.e., has been developed variously since the 2000s) is composed continuous hypoxic training (CHT), intermittent hypoxic training (IHT) and repeated sprint training in hypoxia (RSH), and the altitude environment is constructed using a vacuum pump and a nitrogen generator. In general, LLTH method dose not induce hematological change in a short time within 3 hours. However, CHT and IHT enhance aerobic exercise capacity by improved exercise economy, supply and utilization of blood to tissues, capillary and mitochondrial densities, and oxidative enzyme activity through various biochemical and structural changes in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. RSH enhances anaerobic power and repetitive sprint performance by improving glycolytic enzyme, glucose transport, and pH control. In Korea, however, there are almost no facilities for altitude training that is applied to enhance athletic performance in advanced sports countries and recognition of the need for altitude training is also very poor. Conclusions Therefore, it is very urgent to develop altitude training for maximizing athletic performance in Korea and a lot of support and efforts are needed from the government and local governments.


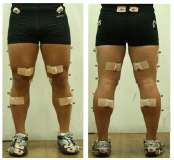
The purpose of this research is to investigate the factors affecting the performance capability of lunge movements by performing lunge movements which are commonly used as a method of instant physical movement in sports with a kinetic analysis including an EMG analysis. This research targeted 14 skilled fencers and made the subjects perform kick-lunges which allow them to go farthest from their positions and performed an analysis on such, applying a 3D motion analysis system and an EMG system. The subjects performed kick-lunges in two movements; one with a preliminary movement and the other without it and those are performed with both dominant leg and non-dominant leg. The result of this research is as follows. The lunges with a preliminary movement showed higher performance capability than those without it. Furthermore, as the level of skills gets higher, the length of lunges gets longer, and it seemed that a tactical mechanism shortening exercise performance times was used as a mechanism to control the impulse coming from such lengthened lunges. In addition, a difference appeared in mechanical factors such as moment and power in a dominant leg movement and it seemed to result from a difference in an functional capability using muscles.




Purpose The aim of this study is to find how the pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise effect on the body composition, exercise performance ability, blood factor and obesity related hormone, and to verify the effect of pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise as an effective substance for obesity improvement. Methods This study selected 20 obese men in their twenties who has more BMI than 25kg/m2, and are applicable in 25% of the body fat, and randomly sampled group of 10 people for pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise (PYA), and 10 people for placebo intake and aerobic exercise (PLA). Intake of pyruvate and placebo was implemented for 10 weeks, 6 g a day, and aerobic exercise, treadmill exercise in the intensity of 50 ~ 60%’s target heart rate, was conducted for 10 weeks, 3 times a week, 60 minutes a day. To demonstrate the effect of pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise, all of the body composition, exercise performance ability, Lactate, and blood factor and hormone related to obesity were measured before and after the test in the same manner. Results The main results from this study are as follow; 1) In the case of body composition, in PYA, weight(p < .01), BMI(p < .05), body fat percentage(p < .01), and body weight without fat(p < .001) are reduced meaningfully. 2) In the exercise performance ability increased significantly in both PYA(p < .01) and PLA(p < .001) for V˙O2max, Also, in the case of distance during the exercise, PYA(p < .01) and PLA(p < .05) increased significantly in 15 minutes and PYA(p < .01) and PLA(p < .05) 30 minutes, but only in PYA from 45 minutes(p < .01) to 60 minutes(p < .05) 3) In case of Lactate, the significant decrease in PYA during stabilization and the significant increase in PYA after 30 minutes of exercise was not seen after 45 minutes 4) In the case of blood factor, HDL-C showed a meaningful decrease in PLA(p < .05) and Leptin showed a meaningful decrease in PYA(p < .001). Conclusions To sum up these results, it was more effective for the group of PYA which ingested pyruvate in improving obesity, even when the same aerobic exercise is conducted.
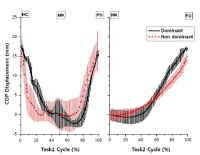
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to compare the dynamic postural control of youth athletes with and without a history of lateral ankle sprains. METHODS Twenty-eight youth athletes (14 lateral ankle sprain, 14 healthy control) participated in this study. All participants answered the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure questionnaire and were subject to the Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT) for dynamic postural control evaluation to collect the joint angles of the lower extremity, a center of pressure (COP) path, and COP velocity. Independent sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U-test were performed to analyze the difference between the groups. RESULTS The lateral ankle sprain group (LAS) was found to have a long experience in participating in sports, and low Foot and Ankle Ability Measure scores were identified when compared to the healthy control (CON; p<0.05). LAS was observed with a short reach distance, less hip flexion, and dorsiflexion angles during the anterior direction of SEBT when compared to CON (p<0.05). Furthermore, LAS showed a slower anteroposterior and mediolateral center of pressure velocities in the posteromedial aspect of SEBT and a slower anteroposterior COP velocity in the posterolateral aspect of SEBT when compared to that of CON (p<0.05). There were no differences between the groups with respect to the other variables (p>0.05). CONCLUSIONS Based on these results, decreased anterior reach distance of SEBT may be affected by changing the dynamic posture control strategy of the lower extremity joint on the sagittal plane in LAS.

Purpose This study was to investigate the effect of various motor leaning techniques which were applied on the youth soccer training program. Methods 12 elementary soccer players and the director of R youth soccer team have participated in the study. The expertise level of youth soccer team were ranged from beginner to advance. To investigate the effect of new soccer training program we adopted a methodology of action research. We first analyzed the problems of original youth soccer program and reconstructed the training program considering of individualized characteristics. The 3 main problems of original soccer program (1. feedback provisions 2. difficulty of task level 3. time distribution of training) have been reconstructed by four motor learning experts. For the data analysis, several qualitative analyze techniques were conducted to observe player’s improvements. Results First, participants had a better understanding on proper motion of shooting and lifting skills from the guidance techniques. Second, utilizing the personal skills and team cohesion have been improved by the modified rules and space competition. Third, the ability of active problem solving have been improved from the self-learning environment. Forth, the player’s confidence level have been improved by eliminating performance outcome. Conclusions From the aspects of variety circumstances in sport education field, the comprehensive motor learning program should be developed and applied.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of regular vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) level, aging- and lifestyle disease-related blood components in middle-aged women. Methods The participants were recruited from a total of 19 physically healthy people aged 50-59 years, and were randomly divided into vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise (VIAE, n = 10) and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (MIAE, n = 9) group. The participants were performed vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise three times a week for eight weeks, and body composition measurement, graded exercise test, blood collection were performed before and after. Results Mean exercise time was significantly longer in the MIAE group than in the VIAE group. The V̇O2max was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. Body weight, BMI, and body fat percentage were significantly lower than pre both groups. The BDNF concentration was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. The dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-s) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentration were significantly higher than pre both groups. The free fatty acid and triglyceride concentrations were significantly lower than pre both groups, and HDL-C concentrations were significantly higher than pre both groups. Conclusions Vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise not only increases maximal oxygen uptake and blood BDNF level in middle-aged women, but also induces positive changes in aging-related hormones and lifestyle-related blood variables.
Impact of 9-week strength training of racing cyclist candidate during training camp on body composition, racing cyclist specific fitness, and racing cycle performance was examined. Two by two (cyclist experience, y/n and strength training (ST) participation, y/n) experiment design was employed. A total of 20 candidates participated and divided evenly into four groups; 1) experienced cyclist participating ST (CST), 2) non-experience cyclist participating ST (nCST), 3) experienced cyclist no participating ST (CnST), and 4) non-experience cyclist no participating ST (nCnST). Two programs were introduced; 1) non ST containing, pre-existing program emphasizing on sprint and acceleration training and 2) new-program containing ST and sprint and acceleration training. CST and nCST participated the latter program. Before and after the 9-week training, body composition, racing cyclist specific fitness, and racing cycle performance was tested. After 9 weeks, all groups decreased body weight(p<0.05), body fat content(p<0.05), body mass index, and CST and nCST increased lean body mass(p<0.05). Muscular strength measures such as grip strength, low back strength, 1RM of bench press, 1RM of squat, and anaerobic capacity improved after 9 weeks in all groups(p<0.05). The magnitude of changes was greater in order of CST, nCST, CnST, nCnST. Time trial of 200 meter sprint was faster after 9 weeks in all groups except CnST while 500 meter sprint was improved only in nCnST(p<0.05). After 9 weeks, regardless of previous cyclist experience, those who participated in ST ranked high places at racing cycle competition. Both training programs for the candidates improved body composition and racing cyclist specific fitness. When strength training was added to pre-existing training program emphasized on sprint and acceleration, the racing cycle performance was enhanced. Strength training for racing cyclist is highly recommended to improve their racing performance.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the factors for setting proper training duration of frequency that can guarantee the student athletes' right to study and performance, and to derive the ranks of setting proper training duration of frequency of student athletes by school level. Consequently, to provide basic data for the development of training guidelines for the growth period of Korean student athletes. Methods Delphi and Analytic Hierarchical Process(AHP) techniques were used. The Delphi survey was conducted in three phases, and collected data through Delphi survey were computed by SPSS win ver. 22.0 and Excel, using the mean, standard deviation, median, and coefficient of variation. Using the AHP technique, we classified the factors for setting proper training duration of frequency derived through Delphi survey, and calculated the importance by using Microsoft Excel 2010. Conclusion First, elementary students should be guaranteed regular class participation, have basic after school training, and be provided with adequate rest so that they do not lose interest in the exercise. Second, middle school students are required to decide whether to continue exercise based on their ability to exercise and abundant experience. Therefore, when abandoning the exercise, students should be able to faithfully carry out their academic performance. Third, high school students are directly related to college entrance and employment, so they have to concentrate on performance rather than on academic performance.
PURPOSE This study was conducted to estimate the tendency of psychological factors influencing cycling performance by analyzing the characteristic factors of athlete reputation in the news big-data. METHODS To explore the psychological factors influencing cycling performance, an open questionnaire was conducted on 82 cyclists, and Inductive Content Analyses was performed. Overall, 89,520 news articles were collected through BIGKinds, and forming factors of athlete reputation were derived through LDA topic modeling analysis and inductive categorization. Through regression analysis, time series tendency of the factors of athlete reputation was calculated. Finally, the tendency of psychological factors to influence cycling performance was estimated based on the previously derived results in this study. RESULTS The psychological factors influencing cycling performance were found to be; emotion control, trust capital, cognitive control, motivation and communications with the coach. The forming factors of athlete reputation was found to be; reporting of the sports event, infrastructure creation, analysis to performance, moral issue, social environmental changes and sports gossip. The time series tendency of the forming factors of athlete reputation was found to include the categories of Hot, Warm, Cool and Cold. The psychological factors influencing cycling performance are estimated to expand to exercise performance and moral intelligence. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study suggest that the discussion of psychological factors influencing cycling performance extends not only to exercise performance, but also to moral intelligence, reflecting the socio-cultural context in the discussion of performance.