
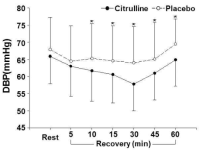
It has well known that post-exercise hypotension (PEH) after a bout of aerobic exercise was a major mechanism to reduce blood pressure though exercise training, and that citrulline supplementation reduced blood pressure by increasing nitric oxide in vivo. However, the effects of citrulline supplementation on PEH have not been fully elucidated yet. This study was designed to examine the effects of citrulline supplementation on PEH after a bout of aerobic exercise in prehypertensive and normotensive 20s males. The effects of a four-day citrulline or placebo treatment on blood pressure, cardiovascular function, and blood lactate concentration measured at rest and during recovery phase after a bout of exercise performed for 30 min at 70% VO2max were compared and analyzed. All subjects participated in a citrulline trial and a placebo trial repeatedly according to a counter-balanced order. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and mean arterial pressure measured at 10-60 min of recovery phase in citrulline trial were significantly lower than placebo trial. Rate-pressure product measured at 30 min and 45 min of the recovery phase in citrulline trial was significantly lower than placebo trial. 2) No significant differences were found in heart rate (HR), cardiac output (CO), and total peripheral resistance (TPR) measured during the recovery phase between two trials. There were significant differences in HR, stroke volume, CO, and TPR among times within a trial. 3) No significant difference was found in blood lactate concentration measured at rest and during the recovery phase between two trials. The results would be summarized that the PEH was augmented by the citrulline supplementation, and that burden to cardiac muscle as well as cardiovascular function were not affected by the citrulline supplementation. It was concluded that the short-term citrulline supplementation would be very effective to augment the PEH. A research investigating the effects of citrulline supplementation on the PEH in pre-hypertensive and/or hypertensive individuals would be warranted. In addition, a study examining the effects of citrulline supplementation during long-term exercise training on the blood pressure in hypertensive patients also would be warranted in near future.

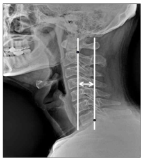
This study was designed to investigate the effects of combined treatment of chiropractic and PNF exercise on musculoskeletal function in forward head posture patients. Thirty patients volunteered to participate in the study as subjects, and they were divided into one of three groups, i.e., chiropractic group (n=10), PNF exercise group (n=10), and combined treatment of chiropractic and PNF exercise group (C+P group; n=10). Subjects in three groups went through each program for 25 min/session, three times/wk for eight weeks. Cervical alignment, cervical muscular strength and endurance, and cervical range of motion were measured and compared among groups and between pre- and post-test utilizing two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables regarding cervical alignment increased significantly in all three groups. The changes in C+P group were more significant than other two groups. 2) All variables regarding cervical muscular strength and endurance increased significantly in all three groups. 3) All variables regarding cervical range of motion increased significantly in all three groups. The changes in ROM regarding flexion and extension in C+P group were more significant than other two groups. It was concluded that all three treatments applied in this study would be effective for functional recovery of the musculoskeletal function in forward head posture patients. Especially, combination of chiropractic and PNF pattern exercise would be the most effective intervention for the patients.


The primary purpose of the study was to compare cardiovascular function, mental health indices, stress-related variables according to body mass index (BMI) and percent body fat (%BF) in 20s females. Sixty-eight women, aged 20-29 yrs, participated in the study as subjects. There were three groups, i.e., normal group (BMI<24 kg·m-2 and %BF<25%; n=25), normal weight obese group (BMI<24 kg·m-2 and 28%<%BF<40%; n=19), and obese group (BMI>26 kg·m-2 and 28%<%BF<40%; n=24). Cardiovascular function, mental health indices, stress-related blood variables were measured and compared among three groups. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) SBP, DBP, mean arterial pressure, and RPP were significantly higher in obese group than normal group. 2) There were no significant differences in mental health indices among three groups. 3) Fasting plasma insulin, fasting plasma glucose, and CRP were significantly higher in obese group than normal weight obese group and normal group. It was concluded that there would be abnormal cardiovascular function, insulin resistance, and inflammation in general obese individuals in 20s females, not normal weight obese and normal individuals.
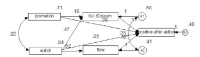
The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship among service quality, psychological experiment, and positive feedback including the moderating effect of motivation at Formula One World Championship. Therefore, the proposed research model was divided and compared by the level of motivation. By using questionnaire method, we found the following results. First, high motivation group indicated a higher-level of service quality, psychological experiment, and positive feedback than low motivation group's. Second, service quality had an influence on positive feedback directly and indirectly with the psychological experiment as a mediator. Third, it would be more effective for high motivation group that driving positive feedback through promotion while both promotion and watch is effective for low motivation group to drive positive feedback. Thus, promotion is considered as an important factor in both high and low motivation group and the watch needs to be strengthened in high motivation group.

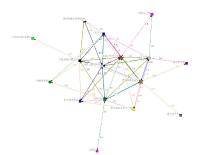
The purpose of this study was to investigate structural characteristics and participants` roles & functions of sport policy network in Korea, by social network analysis on structural characteristics of sport policy network and AHP analysis on participants` roles and functions. For that, 21 executive officers from 19 organizations and agencies related to sports policy were selected as study subjects, and, the materials collected from whole twice surveys on them were analysed by Ucinet 6 and Expert Choice 2000 program. As the results, the governmental organizations like the Blue House and Ministry of CultureㆍSports and Tourism composed the central position group of sport policy network of Korea, and took the main functions of planing and arrangement within their main roles of policy agenda formation and policy decision, so, sport policy network of Korea could be called centralized network by government. And, in cases of private agencies, Korea Sports Council composed the central position group only in policy network of professional sport, Korea Council of Sport for All of sport for all, and Korea Sports Association for the Disabled of disability sport, and, each of them took the main roles and functions of policy execution in their fields, so, it was obvious that the private agencies were divided into their own sport policy areas.

PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate how a 10-week online live Pilates training held during the COVID-19 pandemic affected body composition, cardiovascular function, and physical fitness in sedentary middle-aged obese women. METHODS Thirty obese women, aged 30 to 49 years (BMI : 25kg/m2 or more; waist circumference: 85cm or more) who were leading a sedentary lifestyle for more than 8 hours a day were assigned to one of two groups—that is, the Pilates training group (TR) and the control group (CON). Four participants were dropped from the study during the intervention period. Participants in the TR group (n=13) performed online live mat Pilates exercises (3 sessions per week; 60 minutes per session for 10 weeks, whereas participants in the CON group (n=13) were asked to maintain their normal lifestyles during the same intervention period. Independent variables related to body composition, cardiovascular function, venous function in the lower body, physical fitness, and 1-RM (repetition maximum) were measured at pre-test and post-test, and data were compared between the two groups and between the two tests. RESULTS 1) Regarding body composition, body weight, body mass index, fat mass, and waist circumference decreased significantly in the TR group. 2) Regarding cardiovascular function, stroke volume and cardiac output increased significantly in the TR group, and total peripheral resistance decreased significantly in the TR group. 3) Regarding venous function in the lower body, blood flow velocity and blood flow volume of the parenchyma area increased significantly in the TR group. 4) Regarding physical fitness, cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular endurance, flexibility, and balance improved significantly in the TR group. 5) 1RM of biceps curl, lat pull-down, leg curl, and leg extension increased significantly in the TR group. CONCLUSIONS It was concluded that the 10-week online live Pilates training had positive effects on the body composition, cardiovascular function, venous function in the lower body, and physical fitness of middle-aged obese women leading sedentary lifestyles.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 8-week aerobic exercise and polyphenol intake on body composition, cardiovascular response, vascular endothelial function, and physical fitness at rest and during exercise in prehypertensive men. METHODS The study included twenty-eight males in their 20-30 years of age with prehypertension. Participants in the aerobic exercise + polyphenol intake group (EX + PP; n = 14) performed aerobic exercise three sessions/week, 30 min/session, at 65% of the heart rate reserve, and consumed polyphenol (grape seed extract 300 mg) for 8 weeks. Participants in the aerobic exercise + placebo intake group (EX + PL; n = 14) performed the same aerobic exercise; however, they consumed placebo instead of polyphenol. All independent variables were measured at pre-test and post-test, and the data were analyzed. RESULTS The main results of the study were as follows: 1) SBP and MAP at rest decreased significantly in EX + PP, while MAP decreased significantly in EX + PL group. 2) In the EX + PP group, CO increased significantly, whereas DBP, MAP, and TPR decreased significantly during the hand grip exercise. In contrast, CO decreased significantly, while DBP and TPR increased significantly in the EX + PL group during the hand grip exercise. 3) Regarding vascular endothelial function, % FMD increased significantly in EX + PP group. 4) Sit-up increased significantly in both EX + PP and EX + PL groups; however, sit-and-reach in EX + PP group was significantly higher than that in EX + PL group at post-test. CONCLUSIONS The findings of this study showed that the 8-week aerobic exercise would have positive effects on body composition, cardiovascular response, and physical fitness at rest and during exercise in hypertensive men. Additionally, polyphenol intake would contribute more towards reduction of blood pressure at rest and during exercise and improvement of vascular endothelial function.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of trunk stabilization exercise (TSE) with abdominal expansion maneuver (AEM) that lasted for 8 weeks on postural stability and functional movement in college athletes. METHODS Twenty college athletes participated in the program (AEM=9, Control=11) and were subjected to 8-week TSE. The AEM group performed exercise by applying AEM techniques during TSE, and control group performed TSE without breathing-related instructions. Both groups measured postural stability with lower-quarter Y-balance test (LQYBT) and functional movement with functional movement screen (FMS) before and after applying TSE to verify the interaction before and after this study with the two groups. Two-way repeated analysis of variance was performed to evaluate the differences between groups and time for an absolute value of LQYBT and FMS, followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests for post-hoc analysis. RESULTS As a result of the left and right LQYBT, there was a significant difference between the time x group (p=.041, p=.033), and post-hoc analysis indicated that there was a significant difference between the AEM and control groups (p=.000, p=,000). Furthermore, the FMS total score indicated that there was a significant difference between the time × group (p=.039), and the post-hoc analysis showed the AEM group had significant results (p=.001), while there were no significant results in the control group (p=.255). CONCLUSIONS Application of AEM during TSE seems to be effective with regard to postural stability and functional movement in college athletes.
PURPOSE Blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive individuals is reduced by the accumulation of post-exercise hypotension (PEH) induced by a long period of training. This study aimed to investigate the effects of intensity of two different aerobic exercises with identical energy expenditure on post-exercise blood pressure and cardiovascular function in prehypertensive men. METHODS Eleven prehypertensive men in their 30s participated in two trials repeatedly. In the first trial, the exercise was moderate in intensity and continuous (MICE) with 70% of VO2max, and the exercise in the second trial was high-intensity interval exercise (HIIE) with 50% and 90% of VO2max. Each exercise was performed for 30 min, and the variables related to BP and cardiovascular function were measured at certain times for 1 hr during the recovery phase. RESULTS Our main findings are as follows: (1) Systolic blood pressure was significantly lower at 30 and 45 min of recovery time than the baseline in the HIIE trial, and systolic blood pressure was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 10, 15, and 30 min of recovery time. (2) The rate pressure product was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15, 30, 45, and 60 min of recovery time. (3) The heart rate was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15, 30, 45, and 60 min of recovery time. (4) Stroke volume was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 30 min of recovery time. (5) Cardiac output was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 min of recovery phase. (6) Total vascular conductance was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 and 30 min of recovery phase. (7) Total peripheral resistance was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 and 30 min of recovery phase. CONCLUSIONS The HIIE shows a higher cardiovascular stress than MICE; however, HIIE contributes to the augmentation of PEH and improvement of cardiovascular function. Therefore, HIIE rather than MICE should be suggested in BP control and enhancement of cardiovascular function in prehypertensive males.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of training methods on body composition, isokinetic strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function, and anaerobic power in female judo players. Methods Subjects performed weight training (n=10) and circuit weight training (n=10) consisting of 10 sports items for 12 weeks. In order to analyze the effects of training, body composition, isokinetic strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function, and anaerobic power were measured and the effect of training was verified. Results First, the comparison of body composition between WT and CWT groups showed that significant interaction effect between group and period was found in all variables (weight: F=1082.694, p=.001, body fat mass F=199.999, p=.001; skeletal muscle mass F=2481.698, p=.001, and percentage body fat: F=496.246, p=.001). Second, there was a significant interaction effect between group and duration in shoulder muscle strength and knee endurance (EPTL: F=6.598, p=.019; EAPL: F=12.860, p=.002). Conclusions The result of this study showed that the interaction effect between period and group was not significant according to the training method but the overall effect of the circuit weight training group was more positive than the weight training group. Therefore, it can be concluded that the 12 weeks circuit weight training can contribute to improve the performance of female Judo players by improving body composition, strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function and anaerobic power.