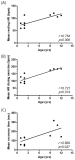
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate changes of the cardiovascular system by comparing heart rate (HR) and blood responses to exercise in younger and older adult dogs and to verify the value of dogs as aging model in exercise science research. Methods A total of 11 healthy beagles were divided into 2 groups according to age: younger adult dogs (1~2 years old, 7 animals) and older adult dogs (9~11 years old, 4 animals). Each animal exercised on the treadmill for 25 minutes, twice a week, and for 4 weeks. The exercise intensity was gradually increased by applying four different protocols. Resting HR, HR during exercise, and HR recovery time were determined as HR parameters. Biochemical analysis was performed on blood samples. The independent Student’s t-test and one-way ANOVA were used to analyze the mean difference of each variable. The associations between age and HR parameters were determined using Spearman‘s analysis. Results Older adult dogs showed higher HRs during rest and exercise than younger adult dogs. HR recovery time was significantly longer in older adult dogs than in younger adult dogs. A strong positive relationship was observed between beagles’ age and resting HR, HR during exercise, and HR recovery time, respectively. The heart rate response to the treadmill exercise was similar between the 1st week and 4th week in younger and older adult dogs. Exercise significantly reduced the white blood cell level in older adult dogs and increased the alkali phosphatase level in younger adult dogs. Conclusions The results of this study demonstrated that short-term treadmill exercise may have a positive effect on the aerobic capacity, inflammation, and bone formation, suggesting that dogs are valuable as aging model in exercise science research.

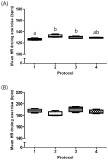
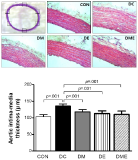
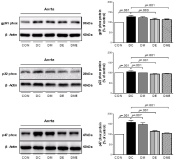
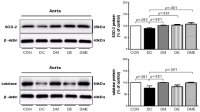
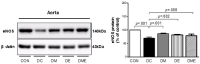
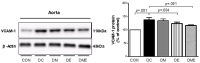
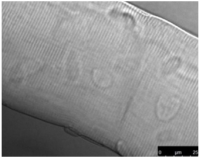
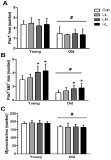
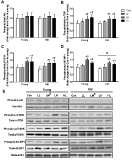
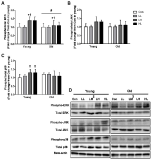
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment on NADPH oxidase, antioxidation and vascular function-related factors in aortic of D-galactose-induced aging rats. Methods To induce the animal model of aging, D-galactose was diluted in saline, and a dose of 100mg /kg was intraperitoneally injected into Sprague-Dawley rats once a day for a total of 10 weeks. Rats were divided into five groups: Control group (CON, n=9), D-galactose control group (DC, n=9), D-galactose+MitoQ group (DM, n=9), D-galactose+Exercise group (DE, n=9), D-galactose+MitoQ + Exercise group(DME, n=9), and treadmill exercise was conducted for 5 days/week during 8 weeks with gradual increase of intensity. MitoQ treatment was intraperitoneally injected at a concentration of 100μM/kg twice a week for 8 weeks during the research period. Results The result showed that treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment decreased the expression of NADPH oxidase level and increased antioxidant enzyme such as SOD-2, catalase. It lead to positive effects such as increasing the level of eNOS, a protein involved in vascular function while decreasing the level of VCAM-1. In addition, as a result, it showed the structurally reduced intima-media thickness. Conclusions It can be concluded that treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment are effective in ameliorating and treating vascular dysfunction resulting from aging.

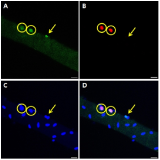
Purpose This is the first study to examine whether age impacts the response of single muscle fibers to high/low frequency and high/low volume electrical pulse stimulation. We performed in vitro experiments to evaluate the effect of low-frequency high-volume electrical pulse stimulation (EPS) on mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, and satellite cell activation in singles fibers of young and aged muscles. Methods Isolated single fibers from gastocnemius in 12-wk (n=21) and 72-wk (n=21) old male C57BL/6 mice were divided into four groups: 1) control (Con) received no EPS, 2) low-frequency low-volume EPS (LL), 3) low-frequency high-volume EPS (LH), and 4) high-frequency low-volume EPS (HL) were made to contract using independent EPS protocols. Satellite cell activation and anabolic pathway (mTOR and MAPK signaling) were measured before and after EPS. Results The number of quiescent (Pax7+/Ki67-) and active (Pax7+/Ki67+) satellite cells, myonuclear content and the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and ERK were higher in young when compared with old. However, regardless of age, LH and HL EPS significantly increased the number of activate satellite cells (142%, both) and phosphorylation of mTOR (129% and 133%, respectively), p70S6K (133% and 136%, respectively) and 4E-BP1 (140% and 129%, respectively) compared with Con. The protein expression of ERK phosphorylation only increased by LH EPS in both the young and old groups (123% and 125%, respectively). Conclusion Low-frequency high-volume EPS stimulated satellite cell activation and the mTOR signaling pathway in older similar to young muscle.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of regular vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) level, aging- and lifestyle disease-related blood components in middle-aged women. Methods The participants were recruited from a total of 19 physically healthy people aged 50-59 years, and were randomly divided into vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise (VIAE, n = 10) and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (MIAE, n = 9) group. The participants were performed vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise three times a week for eight weeks, and body composition measurement, graded exercise test, blood collection were performed before and after. Results Mean exercise time was significantly longer in the MIAE group than in the VIAE group. The V̇O2max was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. Body weight, BMI, and body fat percentage were significantly lower than pre both groups. The BDNF concentration was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. The dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-s) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentration were significantly higher than pre both groups. The free fatty acid and triglyceride concentrations were significantly lower than pre both groups, and HDL-C concentrations were significantly higher than pre both groups. Conclusions Vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise not only increases maximal oxygen uptake and blood BDNF level in middle-aged women, but also induces positive changes in aging-related hormones and lifestyle-related blood variables.

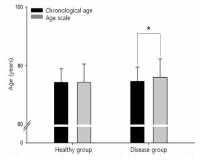
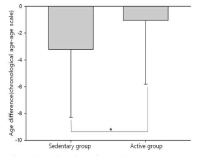
Purpose Evaluating the aging of senior and providing optimal sevices are important things for successful aging. This study identified functional fitness related with heath of aged 65 years or older and developed an age scale (longevity fitness age) for assessing their aging. Methods Participants were 458 older people (166 male, 292 female). They were divided into healthy group and disease group. Healthy group was used for the development of the longevity age equation and disease group was for investigating the validity of the equation. Participants completed 13 function fitness variables. The first principal component obtained from a principal component analysis was used to compute the equation. All variables except for grip strength and carrying beans were correlated with chronological aged. Grip strength and variables related lower functional fitness had differences between healthy group and disease group. Finally, 4 variables were selected for the equation. Results It was the following: longevity fitness age=0.942*X1+2, 185*X2+0.673*X3+0.051*X4+0.588*chronological age+58.401, where X1=standing up from a supine position, sec (s), X2=maximum walking (s), X3=standing up and sitting down a chair (s), X4=one leg balance with eyes open (s). The longevity fitness age of healthy group do not have a difference compared to their chronological age but disease group had a difference significantly. Age difference (chronological age-longevity fitness age) of sedentary group in disease group was significantly bigger than its active group. Longevity fitness age could assess an aging of senior. Conclusion We suggest that it can use as the tool for early detecting senior who need the health care service.


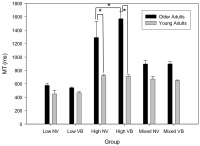
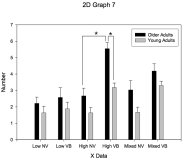
Purpose The present study was to investigate to extent that effects of sensory information distortion by muscle vibration on continuous limb movement in aging and accuracy constraint. Methods Young adult group (n=11) and older adult group (n=11) were divided. All participant were instructed to perform repetitive aiming movement to specified targets under three-accuracy constraints (i.e., low, high, and mixed accuracy constraints) in the vibration and no-vibration conditions. Kinematic data was collected by movement time and movement error frequence. Results The results showed that compared with young adult, older adult increased movement time when accuracy constraint was high under vibration condition. Older adult also was a high degree of movement errors than young adults when accuracy constraint was high under vibration condition. Conclusion The muscle vibration stimulation may influence considerably on the continuous limb movement probably due to degeneration in sensory information processing by aging.

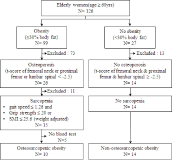
Purpose The purpose of this study were to assess physiological and biochemical characteristics in elderly women with osteosarcopenic obesity (OSO), and to analyze relationships among irisin, adipokines and bone metabolism markers. Methods 126 elderly women were selected and among them 10 women were classified into OSO group (76.9±5.2 yrs) and 14 women were classified as a NOSO group (72.9±5.6 yrs). Physique, body composition and bone mineral density were measured. Senior fitness tests were 30-s chair stand, 30-s arm curl, chair sit-and-reach, back scratch, 8-foot up-and-go, grip strength, and 2-min step test. Isokinetic muscle strength was measured by isokinetic dynamometer (Cybex 770, USA). Nutrition intake and physical activity were administered. Biochemical parameters including irisin, FNDC-5, leptin, adiponectin, CTx, 25(OH)D, osteocalcin, and PTH were measured. All data were analyzed by SAS 9.4. Independent t-test was applied to compare between OSO and NOSO groups. Multiple regression analysis was used. The level of significance was set at .05. Results The results of the study showed that there were significantly high for waist circumference, hip circumference, WHR, and BMI in OSO group compared to those of NOSO group. Higher results were also obtained for fat tissue and percent body fat but significantly low for lumbar bone mineral density. OSO group showed significant lower results for grip strength and 2-min step test compared to NOSO group. Peak torque, and relative peak torque at 60° were significantly lower for left and right knee flexion in OSO group. Protein intake was significantly low in OSO group, but no difference was obtained in level of physical activity between two groups. Irisin was significantly related to adiponectin, FNDC-5 and osteocalcin in explaining 35.2%, 81.5% and 92.1% of the variance, respectively. Conclusions This study shows that elderly women with OSO have higher results for physique and body composition parameters except body height. However, lower values were obtained for functional fitness, and isokinetic muscle strength. OSO may have more risks for metabolic syndrome, bone fractures, fall, lack of daily physical activity and limit of locomotion due to the imbalance of quadriceps and biceps femoris in non dominant leg. This study suggests that criteria and mechanism of OSO should be clarified by follow-up study.
