The frailty, characterized by reduced physiological function is closely related to a fall, disability, institutionalization, hospitalization, and mortality in the elderly. A reduced physical fitness is a major phenotype of the frailty. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship among pre-frailty, physical activity (PA) and functional fitness in the community dwelling elderly women. The study participants were elderly women (n=338, 70.6±4.2years) aged over 65 who took part in the Korean Healthy Fitness Criteria study for the National Fitness Award Project in 2015. The pre-frailty was defined using the Cardiovascular Health Study frailty criteria. PA was assessed using the International PA Questionnaire (IPAQ). The participants were classified as regular PA participants if they meet the World Health Organization (WHO) PA recommendation for the elderly. Functional fitness was assessed using the composite of the National Fitness Award fitness testing for the elderly. Quality of life was evaluated using EuroQoL visual analogue scale and WHO quality of life assessment. As the results, the pre-frail elderly women were significantly older and obese (body mass index, percent body fat, waist circumference) than the healthy elderly. The pre-frail elderly presented significant decreases in walking, moderate intensity, and total PA compared to the healthy elderly even after adjusted for age and percent body fat. However, no significant difference was found in vigorous-intensity activity between the pre-frail and healthy elderly. Also, the pre-frail elderly women showed the decrease in functional fitness and quality of life compared to the healthy elderly. Regular PA was associated with high levels of muscular endurance and coordination in healthy and pre-frail elderly. In pre-frail elderly, high levels of cardiorespiratory endurance was associated with PA. In conclusion, regular PA is inversely associated with fitness decline in healthy and pre-frail community-dwelling elderly women. Regular PA might attenuate fitness decline in pre-frail elderly women.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of National Fitness Award program group exercise classes on daily fitness and balance-confidence among the elderly participants(n=496, 80.2% women). This study investigated body composition, daily fitness, and balance-confidence, and quality of life among the subjects who participated in the combined exercise program of improving physical fitness class for 8-week in the 10 national physical fitness certification centers by the demonstration project for the elderly of 2013 Korean National Fitness 100 project. Body composition and physical fitness for daily living were defined by Korean National Fitness 100 project for elderly, also the balance-confidence and health-related questionnaires were added. The following results were obtained by comparing the pre-test and post-test. In body composition body weight (p<.05), body mass index (p<.05), fat mass (p<.01), and percent body fat (p<.05) were significantly decreased, but muscle mass was not. Except for walking-around-two-cones-in-a-figure 8, all other daily fitness items such as relative grip strength (p<.001), chair sit to stand, two minutes place to walk, and sit-and-reach significantly increased (p<.01), and timed up and go were significantly decreased (p<.01). In balance confidence rating ABC tests (p<.001) were shown significantly increased. Although, quality of life measured by EQ-5D was not significantly improved, self-health status measured by EQ-VAS (p<.001) showed significant increase. Therefore, the group exercises of National Fitness Award program improved body composition, daily fitness and balance confidence in Korean elderly participants.
Purpose The study was designed to compare physical fitness, indices of lifestyle disease, and biochemical property of muscle according to sarcopenia and obesity in elderly women. Methods One hundred elderly women were alloted to one of four groups, i.e., sarcopenia+obesity (SO: n=20) group, sarcopenia (S: n=20) group, obesity (O: n=29) group, and normal (N: n=31) group. Criterion for sarcopenia was 'appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM)/height2<5.4 kg/㎡', and criterion for obesity was 'percent body fat>35%'. Dependent variables regarding physical fitness, lifestyle disease, and biochemical property of muscle were measured and compared among four groups. Results 1) Regarding daily living fitness, grip strength, upper arm flexion, sit-and-reach, up and go, and VO2max in SO group and S group were significantly lower than N group. Regarding isokinetic function, peak torque and average power in SO group and S group were significantly lower, and relative values to body weight in SO group and O group were significantly lower than N group. 2) Regarding hypertension, resting HR and RPP in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Regarding diabetes mellitus, fasting plasma glucose and HOMA-IR in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Regarding hyperlipidemia, HDL-C in SO group and O group were significantly lower than S group and N group. Regarding atherosclerosis, TC/HDL-C ratio and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. 3) Regarding biochemical property of muscle, IL-6 in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Conclusion It was concluded that physical fitness was declined in sarcopenia elderly, and that relative value of isokinetic function, indices of lifestyle disease, and inflammation markers were deteriorated in obesity elderly. Especially, the decline and deterioration of physical fitness and indices of lifestyle disease were even more severe in the elderly who had the both status. Therefore, the efforts should be made to prevent and improve sarcopenia and/or obesity.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of 16 weeks’ combined exercise training on insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, oxidative stress, leukocyte telomere length, body composition, and daily living fitness in elderly women with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). Methods Twenty-eight participants were randomly assigned into one of two groups, i.e., exercise training group (EX: n=14) and control group (CON: n=14). Subjects in EX participated in 3 sessions of 60 min-combined exercise for 16 weeks, whereas subjects in CON were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same period. The variables regarding insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, oxidative stress, leukocyte telomere length, body composition, and daily living fitness were measured and compared between two groups as well as between pre-post test utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. Results Main results were as follows: 1) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR tended to decrease in EX, whereas increased significantly in CON. 2) IL-6, TNF-α, hs-CRP decreased in EX, but the changes were not statistically significant. 3) MDA increased significantly and GPx decreased significantly in both EX and CON. 4) Leukocyte telomere length increased significantly in EX. 5) Fat-free mass increased in EX, whereas fat mass and percent body fat decreased significantly in EX. 6) Arm curl, chair stand, sit & reach, tandem test, 10m walking speed, and up & go improved significantly in EX. Conclusion It was concluded that the combined exercise for 16 weeks had a positive effect on improving insulin resistance, increasing leukocyte telomere length, as well as enhancing body composition and daily living fitness in elderly women with type 2 diabetes.
This study was designed to investigate the effects of increment of physical activity for 12 weeks through aerobic exercise training or change from own vehicle to public transportation for commuting on physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function in middle-aged men. Forty-four subjects, aged 30-50 yrs, were randomly assigned to either one of three groups, i.e., aerobic exercise training group (TR: n=14), change to public transportation group (PT: n=15), or control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR performed aerobic exercise for 30 min per sessions, three sessions per week, subjects in PT changed from their own vehicle to public transportation for commuting, and subjects in CON maintained their life patterns during the same intervention period. Physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function were measured at pre- and post-test, and the data were analyzed by repeated two-way ANOVA. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables related to physical fitness improved significantly in TR. Right grip strength, standing long jump, side step test, and sit-and-reach improved significantly in PT. 2) Although there were no significant changes in all variables related to insulin resistance, the variables tended to be improved in TR and PT. 3) TNF-α decreased significantly in TR and PT. IL-6 and CRP tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. 4) ALT decreased significantly in PT. AST and γ-GT tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. It was concluded that the 12 weeks of change to public transportation as well as aerobic exercise training would be beneficial for physical fitness and inflammatory markers. These interventions also would be possible to improve insulin resistance and liver function. The increment of physical activity through change from own vehicle to public transportation was found to be equally beneficial for health promotion compared to aerobic exercise.
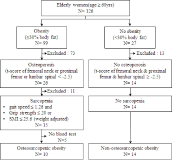
Purpose The purpose of this study were to assess physiological and biochemical characteristics in elderly women with osteosarcopenic obesity (OSO), and to analyze relationships among irisin, adipokines and bone metabolism markers. Methods 126 elderly women were selected and among them 10 women were classified into OSO group (76.9±5.2 yrs) and 14 women were classified as a NOSO group (72.9±5.6 yrs). Physique, body composition and bone mineral density were measured. Senior fitness tests were 30-s chair stand, 30-s arm curl, chair sit-and-reach, back scratch, 8-foot up-and-go, grip strength, and 2-min step test. Isokinetic muscle strength was measured by isokinetic dynamometer (Cybex 770, USA). Nutrition intake and physical activity were administered. Biochemical parameters including irisin, FNDC-5, leptin, adiponectin, CTx, 25(OH)D, osteocalcin, and PTH were measured. All data were analyzed by SAS 9.4. Independent t-test was applied to compare between OSO and NOSO groups. Multiple regression analysis was used. The level of significance was set at .05. Results The results of the study showed that there were significantly high for waist circumference, hip circumference, WHR, and BMI in OSO group compared to those of NOSO group. Higher results were also obtained for fat tissue and percent body fat but significantly low for lumbar bone mineral density. OSO group showed significant lower results for grip strength and 2-min step test compared to NOSO group. Peak torque, and relative peak torque at 60° were significantly lower for left and right knee flexion in OSO group. Protein intake was significantly low in OSO group, but no difference was obtained in level of physical activity between two groups. Irisin was significantly related to adiponectin, FNDC-5 and osteocalcin in explaining 35.2%, 81.5% and 92.1% of the variance, respectively. Conclusions This study shows that elderly women with OSO have higher results for physique and body composition parameters except body height. However, lower values were obtained for functional fitness, and isokinetic muscle strength. OSO may have more risks for metabolic syndrome, bone fractures, fall, lack of daily physical activity and limit of locomotion due to the imbalance of quadriceps and biceps femoris in non dominant leg. This study suggests that criteria and mechanism of OSO should be clarified by follow-up study.

PURPOSE This study was designed to propose a quantitative base training evaluation method through alpine ski training monitoring using a triaxial accelerometer. METHODS Twelve Korean alpine ski athletes, six each in France and New Zealand, participated in this study. Activity data during training and daily living were collected for 7 days via the Actigraph GT9X. The collected data were downloaded through ActiLife Ver 6.13.1. Energy expenditure was calculated with Freedson (2011), and the resting metabolic rate was corrected using the Harris & Benedict (1918) formula. Further, the physical activity intensity classification criteria and METs formula of Freedson (1998) were used to classify hourly activity intensity. The collected data were organized by date, time, intensity, and energy expenditure using Microsoft Excel 2016. Differences between weekdays vs. weekends and skiing vs. physical training were analyzed through a paired sample t-test using Windows SPSS 23 with a significance level of a=.05. RESULTS First, both groups showed repetitive on and off high-intensity activities during scheduled ski training and competition. Second, moderate-intensity activities accounted for an average of 6-10%, and the weekly total time and intensity of MVPA was very high. Finally, the group from France showed differences in total energy expenditure during weekdays vs. weekends (p<.05) and the energy expenditure of both ski training and physical training during weekdays vs. weekends (p<.05). The New Zealand group showed a difference in total energy consumption during weekdays vs. weekends (p<.05). CONCLUSIONS A systematic training program based on quantitative training evaluation should be developed for alpine ski athletes to maintain proper rest and exercise intensity levels.