
This study aimed to explore the types of traumatic event experienced by Volleyball players and then prepare to take-off the serial process of posttraumatic growth to schematize a causal network by organizing the factors for overcoming adversity. Participants experiences were collected by distributing open-ended questionnaires to 77 professional Women's volleyball players in 2013-2014 and collected data was categorized by inductive content analysis. These results were schematized by the causal network. As a result of the study, according to the trauma were categorized into four general areas: member conflict, competence loss, physical injury, and coach conflict and the emotions relative to the trauma were categorized into four general areas: powerlessness, pressure, dejection, and hostility also coping factors were categorized into three general areas: social support, intervention strategies, and psychological control. Finally, positive growth emerged as psychological leap, performance improvement, psychological maturity, and emotional stability. And as a result of the categorized study, bring about a better understanding to the posttraumatic growth by causal network. Based on the study results, that volleyball players experienced a positive development on themself after overcoming the problem that they had suffered psychological scars from a traumatic event. In doing so, they contributed to the formation of resources that helped them in their positive lives. In this regard, this study expects to provide the players who have been scratched in mind because of the traumatic experience.





PURPOSE This study investigates the impact of injury experience on ankle dorsiflexion, quadriceps extensibility, and dynamic stability in elite adolescent and adult volleyball players. METHODS A total of 485 players (adolescents=337, adults=115) reported lower extremities injuries, with measurements taken for ankle dorsiflexion and quadriceps extensibility using the weight- bearing lunge test and Ely’s test, respectively. The Y-balance test was used for dynamic stability. Measurements were conducted on the injured leg of players with knee and/or ankle injuries and the dominant leg of healthy players. Four groups were classified based on injury experience, and comparisons were made between both legs. Additionally, the variables of adolescent players were compared to those of adults. RESULTS Adolescent players with knee injuries exhibited a larger difference in ankle dorsiflexion between both legs, while adult players with ankle injuries demonstrated an asymmetry of ankle dorsiflexion. Regardless of age, players with knee or ankle injuries displayed lower dynamic stability compared to healthy players. Notably, adults with knee injuries showed a larger difference in dynamic stability between both legs. CONCLUSIONS To prevent and rehabilitate volleyball-related injuries, comprehensive injury risk factors, including age, should be managed in the injury prevention strategies.

The purpose of this study was to verify the effect on elementary school students in the exercise start stage by performing a sport psychological skill training to improvement of psychological skill and life skill. Participants were eight elementary school boys volleyball player. The program consisted of psychological skills and life skills in educational counseling model of Visek et al(2009). It was conducted 40-50 minutes a session in total for 22 sessions. Data was collected through a psychological test, worksheet and participant observation, in-depth interviews. The collected data was analyzed to verify difference by paird t-test after pre-middle-post test and to extract meaningful data category. Quantity analysis showed that a result of sport psychological skill test proved a significant difference in willingness to overcome, confidence, concentration, anxiety regulation. Life skill test were no significant differences in all factors. However, the rise of scores was observed on result of the pre-middle paired t-test of life skill during season. Quality analysis showed possibility of goal setting, concentration on the routine, decrease of competitive anxiety, increase of positive thinking, self-understanding and understanding of others, promotion of communication among team members. This sport psychology skill training had a significant effect on the psychological skills of elementary players change. But it seems to be necessary life skills in a more through review of the information.




Purpose This study aimed to investigate the psychological capitals created by the experience of winning an Olympic medal by using the photovoice method. Methods Data were collected on the way the participants-five Bronze medalists in the Women's volleyball in 1976 Montreal Olympics-take and send photographs. The interviews were conducted by phone based on the collected data. The photographs were placed into the parent category after conducting inductive content analysis, and their validity was confirmed from the expert meetings. Results The results of the study, indicate that the participants have earned psychological capitals such as my matter volleyball for diligence, the gift of a Bronze medal to gratitude, the source of achievement, challenges, and key of relationship tenderness from the experience of winning an Olympic medal. Conclusion In this regard, this study provides an opportunity to extend the study on the lives of retired athletes who won an Olympic medal to various perspectives, as well as the impact of sports experience on everyday life.









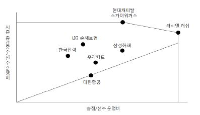
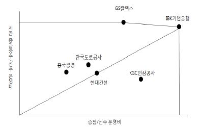
Professional volleyball league, which was launched and its popularity was steadily increased since 2005, has suffered from difficulties in its operation due to deficits after 2013. In addition, each professional volleyball team has worked out for parent company so far as a means of advertisement but does not look like effective management. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to evaluate each professional female and male volleyball team management efficiency through Data Envelopment Analysis. Player salary for the input variable and points and the number of spectators for output variable were used respectively then data were analyzed using Frontier Analyst 4.0. The results were as follows. First, Hyndai capital and Rush & Cash recorded the most efficient management among all professional male volleyball team. On the other hand, Samsung showed inefficient management, followed by LIG, KEPCO, Woori Card, and Korean Air. Second, GS Caltex and IBK were discovered as the highest management efficiency among all professional female volleyball team. On the contrary, KGC recorded inefficient management, followed by Korea Expressway Corporation, Hyundai Construction and Heungkuk life.

PURPOSE This study aimed to prove the mediator effect of skill level on participation frequency and injury level of leisure sports players with the highest injury rate. METHODS Raw data of the “2019 Sports Safety accident data” conducted by the Korea Sports Safety Foundation were used for this study. We analyzed 857 leisure sports players participating in events with the top four highest injury rates (Basketball, Soccer, Baseball/Softball, Foot Volleyball). Frequency, descriptive statistics, and correlation analyses using SPSS version 27.0 and Process macro model 4 were employed for analysis. RESULTS The results regarding participation frequency, injury severity, and skill level among recreational athletes are as follows. First, a positive correlation was established between the participation frequency of recreational athletes and their skill levels. Second, the correlation between participation frequency and injury severity was observed only in soccer and basketball. Third, skill level plays a mediating role in the relationship between participation frequency and injury level. The results indicate that as the participation frequency among leisure sports players who participate in ball sports with a high injury rate increases, this affects the degree of injury. CONCLUSIONS Skill level appears to play a mediating role in the relationship between participation frequency and injury level. Based on the results, we recommend safety education not only on the relationship between participation frequency and injury level, but also the intermediary role of skill level.