The purpose of this study was to examine whether β-alanine ingestion for 8 weeks can regulate isokinetic knee strength, and 3km record in middle-long distance woman cyclists. Fourteen middle-long woman cyclists participated in this study and were divided into two groups; training group with beta-alanine ingestion and training group with placebo ingestion. All subjects took in beta-alanine or placebo supplement three times per a day for 8 weeks. Physical activity was evaluated by measuring the isokinetic muscular strength and 3km record before and after intervention for 8 weeks. As a results, in isokinetic test, there were significant interrelationships in peak torque of the right and left flexors at 60°/sec, peak torque of the right and left extensors at 180°/sec, peak torque of the right flexors at 180°/sec. In 3km record, result showed a significant interrelationship by groups and time. The results of present study provide evidence that beta-alanine supplement may be effective to increase physical activity and competition record in middle-long woman cyclists.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the current injury status and traits, including damage area, cause of damage based on the situation, and type of occurrence by age group for middle and high schools, university, and professional athletes, in record competition sports (swimming, track and field, and weightlifting). METHODS The study included 503 athletes enrolled in the Korean Sport & Olympic Committee in 2020, and an online survey was conducted using the R statistical program. RESULTS Approximately 38.4% athletes suffered injuries with weightlifting (0.81 times at university) and weightlifting (7.02 times at university) during training. The lower extremities were the most affected areas in all age groups (53.8% in middle school, 48.6% in high school, 44.4% in university, and 47.4% in professional). The causes of damage found to occur most frequently were ‘lack of physical strength, overuse or lack of rest, and recurrence’ and external factors, including ‘facility programs and weather problems.’ The results showed that internal factors during training were mostly associated with ‘overuse or lack of rest and excessive attempts at skills’, while external factors were found to occur in ‘weather problems’. According to the classification of each event, the top priority of frequent damage according to the damaged area was skin bleeding of the head in swimming and muscle inflammation in the torso and upper and lower extremities. Track and field resulted in muscle inflammation in the head, torso, and upper and lower extremities. Weightlifting caused damage to the head and torso, resulted in spinal diseases (disc, spinal stenosis, etc.), and muscle inflammation in the upper and lower extremities. CONCLUSIONS This study highlighted changes in the training environment and training environment, including level-specific physical training, reinforcement programs, scientific access to specific skills, sufficient rest and recovery, and continuous improvement of facilities and equipment.
PURPOSE This study explored psychological experiences in long jump competitions and examined the continuity of psychological experiences over time. METHODS A total of 28 adult long jumpers, 18 men and 10 women, were provided data through in-depth interviews. Data on psychological experiences were extraced through inductive content analysis, while continuity by period was analyzed by calculating the response frequency ratio using Excel. RESULTS First, the psychological experience in the long jump competition was categorized as fundamental, competition intelligence, emotional control, and communication capacity experience. Second, in long jump competitions, results showed that jumpers experienced mixed feelings of anxiety and pressure, self-confidence, and concentration in the first period; peer communication and analysis thinking were necessary in the second period; practical intelligence and pressure control were important in the third period; learning ability and creativity were crucial in the fourth period; learning ability and coach communication were applied in the fifth period; and fighting spirit and creativity were present in the sixth period. Third, the psychological experience of long jumpers by period, basicphysical strength was maintained; competition intelligence increased in the second and fourth periods; communication skills increased until the fifth period, and decreased after; while emotional control decreased. This reflects the contextual changes over time andthe change in competition records owing to that. CONCLUSIONS In the long jump competition, psychological experience changes by period and affects competition records. This study will contribute to further understanding of psychological continuity.
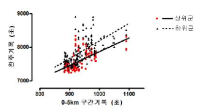
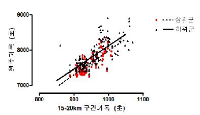
The purpose of this study was to examine that the reciprocal relationship between every 5km and full course running time record. In this study we extended our research scope to investigate whether any notable running time differences were existed among top level of marathoners. Comparisons were made using data which were drawn from 34 championship competitions had been held between year 2000 and year 2009 in Korea. Total 340 full time data was obtained from 340 marathoners who successfully completed their 42.195km running race, and divided into one of two categories, either upper ranked group (URG, ranked 1st~5th position in competitions they participated) or lower ranked group (LRG, ranked 6th~10th position in competitions they participated). Mean and standard deviation were calculated from SPSS (VER. 20.0), and repeated measures of ANOVA and Pearson's correlation was adopted to perform statistical analyses. There was no statistical difference of the running record during first 5km, however running time form all other 5km running sections was significantly faster in URG than LRG (p<.001). The gap of running time record between URG and LRG was getting more and more significant after 20km running. The quickest running record was found during 2nd 5km section (i.e., 5~10 km) and the each section's race time was getting drastically slower during 6th~7th 5km section running regardless of the study groups. Drawn conclusions from this study were that athletes use the strategy of deciding victory in both the beginning and the latter phase of marathon running. This implies that athletes who have the capacity, which make them run faster than others during the very beginning of marathon competition, and/or during 25~35km running sections would be the most preferable for the victory at the finish line.







PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to section the stages of performance development based on the track and field athletes' performance records, derive the performance development span, which was a continuum of the development stages, and extract the psychological experience of the performance development span. METHODS In this study, 56 retired track and field athletes were provided with competition records, and 10 athletes participated in in-depth interviews. With the stage of performance development partitioned using long and short-term moving averages and regression slope in PRR, a continuous of performance development span was derived. To extract psychological experiences in the performance development span, a subject analysis was conducted after an in-depth interview. RESULTS First, the track and field athletes' performance development stage calculated short and long-term moving averages in the PRR. Based on the average difference in the regression slope of the initial 20% CPR in which the long-term moving average was not calculated, it was divided into beginning, rising, peak, and decline periods. Second, the performance development span was a continuum of the stage was of performance development, and the beginning period was 0 < PRR ≤ 7, it was a time when the competition record rises sharply. The rising period was 7 < PRR ≤ 60, which was a virtuous cycle time of growth athlete. The peak period was 60 < PRR ≤ 74, which was a time when the peak record was maintained. The decline period was 74 < PRR ≤ 100, which was a time when the competition record was downward. Third, throughout the performance development span physical intelligence of track and field athletes was based on their natural physical superiority, the technical skills rises and remains at its peak and then enters a downward trend. Competitional Intelligence aims to become personalization as it matures gradually while its competition management capability and game knowledge are immature. Psychological intelligence overcomes the initial psychological atrophy to form confidence, and after experiencing psychological burden at the peak, confidence decreases. In the environmental context, the competition record rises in the early stages, continues to rise, peaks, and enters a downward trend. CONCLUSIONS Track and field athletes' performance development span was implemented as a continuum of beginning, rising, peak, and decline periods, and the psychological experience of the performance development span formed a span of physical intelligence, competitional intelligence, psychological intelligence, and environmental context.

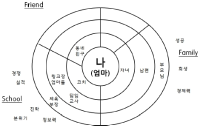
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate how the educational zeal of mothers with winter sports students in secondary schools appears on the network charts. Methods It lasted 28 days from February 6 to March 5, 2017. Starting with a description of the QNA, all interviews were recorded on a tape recorder to carry out the project. Data analysis were divided into four areas(Family, Friend, School, etc.) and 13 associative words(enthusiasm, intelligence, performance, entry, success, sacrifice, atmosphere, polarity, competition, vicarious, satisfaction, economic power, anxiety, stress) to attach associative word stickers according to color. Results As a result of inducing arbitrary interpretation of the network subject's educational network, it was possible to analyze the factors affecting mothers' sports education in three dimensions. In addition, although there is not much difference in areas around "I" on sports education charts, the distance between associative words and network charts has gradually moved away from the same person as their children go on to school. Conclusions The methodological significance of this study has been found to be very useful in visualizing an individual's educational network by utilizing qualitative network analysis and in understanding the characteristics associated with education.




PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the occurrence of sports injuries among badminton national team candidates during training camps and to identify appropriate measures for players to effectively manage and respond to such injuries in the future. METHODS The participants consisted of 123 individuals who took part in national team candidate training camps for badminton in 2022 and 2023. Record sheets were utilized to document the athletes' thoughts and opinions related to exercise injuries during the training period. RESULTS Badminton national team candidates experienced exercise-related injuries in various areas, including the ankles, thighs, knees, hips, shoulders, and back. Female players had a higher incidence of lower body injuries compared to their male counterparts. Through interviews with players about these injuries, individualized approaches involving appropriate rest and training adjustments were found to be necessary; additionally, educating the players about rehabilitation strategies for exercise injuries is essential. CONCLUSIONS When conducting recreational training activities, it is important to avoid fostering excessive competitive attitudes. Additionally, if potential risks are present within the exercise environment, it is crucial to assess and address these with the utmost caution.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the technique and power of the Korean national athletes and international athletes in the start phase of the 500 m speed skating to improve the performance and to understand the relationship between the biomechanical variables affecting the record. Method The subjects were 8 Korean national athletes (Korean athletes) and 6 international athletes (international athletes). For the three dimensional motion analysis, 5 high-speed cameras were used to capture the 40 m start phase of the athletes participating in the international competition. The variables selected for analysis were the kinematic chain, 100 m net time, time to 9 strokes, horizontal position of center of mass after 2.5 sec, range of motion of trunk, knee, push-off angle, net power output, total power loss. Results The correct kinematic chain ratio of Korean athletes was 61.2%, which was lower than 76.0% of international athletes. The time to 9 strokes was 2.82±0.25 sec for Korean athletes, which was significantly lower than 2.53±0.11 sec for international athletes (p=.001). The range of motion of the push-off angle was 60.15±2.75° for Korean athletes, which was significantly lower than 64.76±2.55° for international athletes (p=.001). The net power output was 887.2±269.9 W for Korean players and 1103±264.1 W for international players (p=.021). The variables related to the 100 m net time were the horizontal position of center of mass after 2.5 sec (r=-.956, p=.001), the net power output (r=-.931, p=.001), and the total power loss (r=-.904, p=.001). Conclusion In order to improve the start performance of Korean athletes, it is necessary to maximize the efficiency of skating through skill training to use the correct kinematic chain. Also power enhancement training is needed to improve leg power because the net power output related with 100 m net time.

