PURPOSE This study aimed to test the impact of sport consumers‘ self-construal levels on their responses toward an athlete scandal by conducting a cross-cultural experimental study. In particular, it focused on sport consumers’ subsequent responses toward an athlete scandal, such as the perceived target of responsibility and perceived the main agent for the public apology. METHODS Participants (total=151; KOREA=75, USA=76) were selected for a cross-national comparative study. MANCOVA and Descriptive Statistical Analysis were conducted using the SPSS Windows program version 26.0 to validate the research hypothesis. RESULTS The results indicate that sport consumers’ responses to an athlete scandal vary across the countries. Participants from Korea reported perceived responsibility to the athlete, team, and league. Conversely, those from the United States reported perceived responsibility only to the athlete. CONCLUSIONS There are cultural differences in sport consumers’ subsequent perceptions of an athlete scandal. The present study's findings are expected to provide stakeholders such as teams and leagues with practical implications to understand better sport consumers’ responses to athlete scandals in the globalized sports industry.
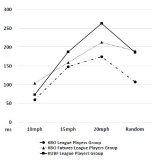
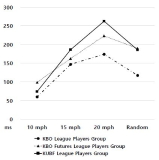
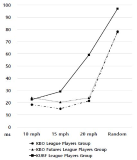
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to investigate effects of baseball expertise and stimulus speeds on coincidence-anticipation timing accuracy of batting. [Methods] Participants were 21 baseball batters, 7 of Korea Baseball Organization(KBO) League, 7 of Korea Baseball Organization Futures League, and 7 of Korea University Baseball Federation(KUBF) League. All of the participants were asked to swing the bat exactly at the time when the light arrived the target point of the runway. The Bassin Anticipation Timer was used to present stimulus with stimulus speed of 10, 15, and 20mph. Participants performed 10, 15, 20mph trials (3 kinds of speed per 5 times) and random trials (3 kinds of speed per 3 times randomly). The timing error of coincidence anticipation task was recorded and raw scores were transformed to constant error(CE), absolute error(AE) and variable error(VE). For data analysis, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures were used. And post-hoc test (Tukey HDS) were conducted. [Results] Results indicated a significant interaction on expertise and stimulus speeds for CE, AE and VE. The KBO League players group showed more accurate and consistent performance than the KBO Futures League players group and the KUBF League players group in baseball batting timing. [Conclusion] This findings revealed that coincidence-anticipation timing accuracy batting in baseball can be used as a factor to distinguish the ability of the other.

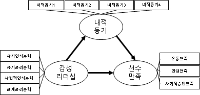
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the influence of coaches’ emotional leadership on athletic satisfaction and to investigate mediating effect of intrinsic motivation perceived by professional female basketball athletes in Korea and Japan. Methods 154 professional female basketball athletes in Korea and Japan participated in this study and responded to questionnaires which consisted of coaches’ emotional leadership, intrinsic motivation, and athletic satisfaction. The collected data were analyzed by frequency analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, descriptive statistical analysis, correlation analysis, and structure equation analysis with using SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0. Results The results of this study were as follows; Firstly, coaches’ emotional leadership had positive effect on athletic satisfaction. Secondly, coaches’ emotional leadership had positive influence on intrinsic motivation. Thirdly, intrinsic motivation had positively affect on athletic satisfaction. Lastly, intrinsic motivation completely mediated the relationship between coaches’ emotional leadership and athletic satisfaction. Conclusion In conclusion, these findings imply that coaches’ emotional leadership and intrinsic motivation are critical factors for improving athletic satisfaction.

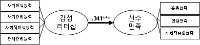
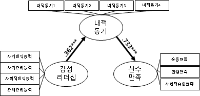
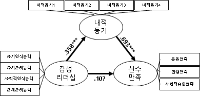
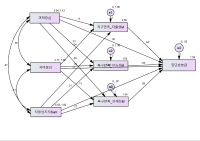
In sport context, the motivational climate created by significant others (e.g., coachs and peers) has been influences on the athletic-student's motivation, engagement, performance, and skill development. Collective efficacy is important for team performance because it influences a group's task choice, effort expenditure, persistence in the face of failure, and resistance to discouragement. This study was to examine the influence of peer motivational climate (i.e., task-involving and ego-involving motivational climate) and coach autonomous support for basic psychological need satisfaction and collective efficacy. In the study, participants were 289 athletic-students' of team sports. In the study then, questionnaire was assessed using by the correlation and path analysis. The results showed that task-involving motivational climate significantly predicted of collective efficacy, while ego-involving motivational climate were negatively predict to the collective efficacy. The results suggest the importance of considering peer influence in addition to coach influence when examining motivational climate in team sport.

PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze the difference between scores and loss of world-class fencing sabre players. METHODS A total of 78 match videos and 1969 points of international competition over 3 years were analyzed for the nine major competitors of the national fencing team (Males = 5, Females = 4). The characteristics of each skill, body section and location according to the score were analyzed by dividing them into male and female groups. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS ver. 25.0. RESULTS First, in the situation analysis according to the men's sabre score, attack skills were the most common in the winning situation (447 points, 73%) and in the situation of losing points (389 points, 72%); however, the difference was not significant. In the analysis of the piste location according to the score, B4 was the most common appearing 254 times (41.5%) in the scoring situation and A4, 243 (45%) times in the losing situation, with a significant difference (p < 0.001). Second, in the situation analysis according to the women’s sabre score, 315 attacks (70.6%) were found in the winning situation and 277 (74.7%) in the losing situation; however, the difference was not significant. In the analysis of the scoring body part, the Sixte area scored the highest with 121 points (27.1%), and the arm area lost the most points with 105 points (28.3%); however, the difference was not significant. In the analysis of the piste location according to the score, A4 was the most common in, appearing 179 times (40.1%) in the scoring situation, and 182 times (48.8%) in the losing situation, with no significant difference at the p < 0.001 level. CONCLUSIONS In the men's game, there were many scored points in B4 and many lost points in A4. In the women's game, there were many scored points and lost points in A4; therefore, the difference in goals and losses according to the piste position was confirmed. These results suggest that it is possible to infer the game management patterns of world sabre players and the flow of world fencing.

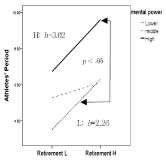
Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the differences between the three simple control models of Hayes (2012) and to determine whether there were Moderating Effects depending on the level of self-esteem, willpower and belief that are psychological factors in the relationship between athlete's retirement and Athlete's period. Methods To achieve this objective, a total of 259 retirees were collected from data on retirement and psychological factors. The data processing method presented the reliability and feasibility of the measuring instrument through technical statistics, frequency analysis, confirmation factor analysis, and reliability analysis. In addition, we conducted a hierarchical regression analysis using the PROCESS command statement in IBM 20 to examine the regulatory effects. Results The results of the study are as follows: The first was the significant model of Hayes (2012)'s three simple control models. It is up to the researcher to choose which model to choose, but when selecting the model, the justification of the variables must be established on the basis of theoretical basis, and the reliability of the variables must be put in to produce reliable and reasonable results. The second was to verify that the relationship between the retirement factor(10) and the Athlete's period has an adjustment effect based on self-esteem, willpower and belief. Among the psychological factors, the Moderating Effects was greatest in the influence of belief on the Athletes' period, and the more reasons for retirement, the longer the Athletes' period than the weaker. The combined mental strength of all three psychological factors combined shows that the combined effect of control also significantly increases the player's ability to survive by combining with the retirement factor. In particular, sportsmanship has resulted in a better mix of retirement factors than the sense of Self-esteem and will, resulting in a longer increase in the capacity. Conclusions Therefore, players who long for a player always keep their dreams of becoming a big star in mind, and ask me to always keep the belief in hope that I will enjoy my career for a long time.






PURPOSE This study assessed elite Taekwondo athletes’ physical fitness and developed reference standards for both their basic and specialized physical fitness. METHODS Data for analysis were collected from 870 athletes: from national teams, 123 elite Taekwondo athletes from the Performance Analysis and Assessment System (PAAS) administrator website (1999–2020); from regional sports centers, 731 collegiate and general division elite Taekwondo athletes (2015–2019); and from Y University, 16 elite Taekwondo athletes. Through measurement items’ selection and categorization, 20 physical fitness items were selected for the reference standards’ development, including 9 for basic fitness and 11 for specialized fitness. Taekwondo weight classes were divided into two: light + middle (fin, fly, bantam, feather) and middle + heavy (light, welter, middle, heavy). RESULTS Descriptive statistics for basic and specialized physical fitness items were categorized by gender and athletes’ fitness level. The reference standards’ development was aligned with existing standards, integrating the Cajori physical fitness 5-levels. It also introduced minimum physical fitness reference standards and target achievement reference standards for evaluating elite Taekwondo athletes’ physical fitness. CONCLUSIONS The reference standards proposed here can serve as objective indicators in selection of national representative athletes and also provide foundational data to establish fitness goals and evaluate future elite athletes’ physical fitness.