The purpose of this study was to conduct an in-depth exploration of Korean national badminton players’ psychological momentum strategies. Data were collected using an open-ended questionnaire and group interviews of 66 badminton players, including 40 members of the 2018 Korean national badminton team and 22 college and semi-pro badminton players who each had badminton careers of 10 or more years and were registered in the Badminton Korea Association. The data were analyzed using inductive content analysis and the deductive process based on the inductively categorized results. The results are as follows. First, regarding strategies for maintaining positive momentum, 188 raw data were collected and classified into three category (keeping pace, dominating the play, and psychological facilitation) and 10 sub-category (including speedy resumption of the game, attacking weak points, and fighting shout). The results suggest that badminton players maintain positive momentum by using strategies to control the speed and tempo of the game at their preferred pace, implement special techniques, exploit their opponent’s weaknesses, and cheer or talk amongst themselves to motivate each other and communicate with their partners and coaches. Second, regarding strategies for overcoming negative momentum, 293 raw data points were collected and classified into three category (time outs, psychological reminders, and changes in plays) and 11 sub-category (including delaying the game, seeking social support, and play change). The data demonstrate that badminton players overcome negative momentum using strategies to intentionally delay the game and exchange equipment, focus on performance cues, and interact with their coaches and partners to change plays and prevent errors. It is hoped that these study findings will inform efforts to provide psychological support that is effective in increasing the odds of winning for the national badminton players in the Asian Games and the Olympic.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of 16 weeks’ combined exercise training on insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, oxidative stress, leukocyte telomere length, body composition, and daily living fitness in elderly women with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). Methods Twenty-eight participants were randomly assigned into one of two groups, i.e., exercise training group (EX: n=14) and control group (CON: n=14). Subjects in EX participated in 3 sessions of 60 min-combined exercise for 16 weeks, whereas subjects in CON were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same period. The variables regarding insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, oxidative stress, leukocyte telomere length, body composition, and daily living fitness were measured and compared between two groups as well as between pre-post test utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. Results Main results were as follows: 1) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR tended to decrease in EX, whereas increased significantly in CON. 2) IL-6, TNF-α, hs-CRP decreased in EX, but the changes were not statistically significant. 3) MDA increased significantly and GPx decreased significantly in both EX and CON. 4) Leukocyte telomere length increased significantly in EX. 5) Fat-free mass increased in EX, whereas fat mass and percent body fat decreased significantly in EX. 6) Arm curl, chair stand, sit & reach, tandem test, 10m walking speed, and up & go improved significantly in EX. Conclusion It was concluded that the combined exercise for 16 weeks had a positive effect on improving insulin resistance, increasing leukocyte telomere length, as well as enhancing body composition and daily living fitness in elderly women with type 2 diabetes.

Purpose The study examined the effects of a 12-week high intensity circuit training (HICT) on abdominal fat, physical fitness, blood lipids, and insulin resistance in middle-aged obese women. Methods Thirty obese women, aged 32-48 yrs, were recruited and randomly assigned to either HICT group (TR; n = 15) or control group (CON; n = 15). Subjects in the TR group participated in HICT of which resistance exercise and aerobic exercise were performed with a duration of 40 min/session and 3 sessions/wk for 12 weeks, whereas subjects in the CON group were asked to maintain their normal life patterns. Dependent variables included abdominal fat area, body composition, physical fitness, blood lipids profiles, and insulin resistance index. Analysis of variance with repeated measures with Bonferroni corrections was used to compare the outcomes between two groups. Results Main findings of the present study were as follows: 1) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant reductions in overall (i.e., body mass index and percent body fat) and abdominal obesity (i.e., waist circumference, total abdominal fat area, visceral fat area, subcutaneous fat area, and visceral fat area-subcutaneous fat area ratio), 2) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant improvements in health-related physical fitness (i.e., muscular strength, muscular endurance, muscle power, flexibility, balance, and cardiorespiratory endurance), and 3) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant improvements in fasting lipids, glucose, insulin, and insulin resistance. Conclusions The current findings of the study suggested that HICT would be an effective exercise intervention to improve metabolic complications associated with obesity and poor physical fitness in obese middle-aged women.




[Purpose] The study was designed to examine the effects of a 10-week sports climbing training on body composition and surrogate indices of major lifestyle disease in obese elderly women. [Methods] Twenty elderly women, whose percent body fat was over 35%, were randomly assigned into one of two groups, i.e., sports climbing training group (TR: n=10) and control group (CON: n=10). The subjects in TR completed sports climbing training program with 5.8 and 5.9 of difficulty, at 11-13 of ratings of perceived exertion (RPE), 60 min/session, three sessions/wk for 10 weeks. Independent variables regarding body composition and major lifestyle disease, i.e., hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis, were measured and compared between two groups as well as between two tests simultaneously using a repeated two-way ANOVA. [Results] Regarding physique and body composition, there were significant interactions between group and test in body weight, body mass index, fat mass, and percent body fat. These variables decreased significantly in TR. 2) Regarding indices of hypertension, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure, and pulse pressure decreased significantly in TR. Regarding indices of dyslipidemia, triglyceride decreased significantly in TR. Regarding indices of atherosclerosis, TG/HDL-C ratio decreased significantly in TR. [Conclusions] It was concluded that the 10-week sports climbing training would be beneficial for reduction of body fat despite its’ influence on fat-free mass was limited, and would also contribute on improving surrogate indices of hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis in obese elderly women. Future research investigating the effects of various period, intensity, duration, and frequency of sports climbing training would be warranted.


Purpose This study was conducted to investigate the appropriateness of the concept of condition for athletes and to conceptualize condition in a way suitable for field and then to produce a tool to test condition that reflects usability. Methods 30 college athletes and national athletes with more than 5 years of experience were selected. In the conceptual review stage, the appropriateness of the concept of condition was verified. In the conditional element collection stage, the condition concept reflecting usability was extracted. In the development stage of the conditional questionnaire, a condition questionnaire was developed in consultation with the data provider to reflect usability. Results Previous studies on the condition of athletes were complicated and the necessity for consideration of usability was raised. As a result of conceptualization with consideration of the application to the sport scene, condition in a scene is summarized into both physical and psychological states. As a result of the appropriateness evaluation of the tool that produced the condition inspection tool reflecting the condition element based on universality and peculiarity of conditionality, the athletes evaluated that the condition inspection tool properly reflects condition, is easy to apply and can be used for condition control. Conclusion The development and application of psychological testing instruments reflecting usability will accelerate the application of sports psychology in the appropriate direction. The reflection of usability will contribute not only to the reliability and validity of the psychological testing tools used in the field of sports psychology, but also to the improvement of the possibility of intervention by leaders and athletes, the convenience of development procedures, and the utility of response results.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of detachable forefoot outsole on muscle activity of the lower extremity during downhill walking. Methods Thirteen male university students (age: 23.5±2.1 yrs, height: 175.7±4.6 cm, weight: 651.9±55.5 N) who have no musculoskeletal disorder were recruited as the subjects. Each subject walked down 20° ramp with forefoot’s design for the detachable outsole’s angle(5°, 10° and 20°) and type(A and B). To assess the myoelectric activities of selected muscles, six of surface EMG(QEMG8, Laxtha Inc. korea, sampling frequency = 1,024 Hz, gain = 1,000, input impedance > 1012 Ω, CMRR > 100 dB) electrodes with on-site pre-amplification circuitry were attached to ES, RF, BF, TA, LG, and MG. For each dependent variable, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures was used to determine whether there were significant differences among forefoot’s design for the detachable outsole’s angle and type (p<.05). When correlation effect was not statistically significant, post hoc analyses were performed using the multiple comparison through bonferroni, and if correlation effect was statistically significant, one-way ANOVA was performed as for the form of outsole which is an inter-group variable in order to find out simple main effect, and the paired t-test was performed to find out the angle of outsole, which is an intra-group variable. Results In IDLS phase, In terms of Rectus Femoris, 10°-B outsole showed statistically higher muscle movement than 5°-B, 5°-A outsole showed statistically higher muscle movement than 5°-B, 20°-A outsole showed statistically higher muscle movement than 20°-B. Among these outsoles, Conclusion 5°-B outsole was found to the most useful outsole for improving stability and controlling the bodily movement due to the body weight load when walking down the ramp.








Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of 8 weeks of circuit exercise training on blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and metabolic syndrome risk factors in 40~50s male bus drivers. Methods Twenty-nine bus drivers were randomly assigned to one of two groups, i.e., circuit exercise training group (TR: n=14) and control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR participated in circuit exercise training 30-40 min per session, three sessions per week for 8 weeks, whereas subjects in CON were asked to maintain their normal life pattern for same intervention period. The variables regarding body composition, blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and number of metabolic syndrome risk factors were measured and compared between two groups as well as between pre- and post-test. Data were analyzed using repeated two-way ANOVA with post hoc test. Results Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, body mass index, and percent body fat decreased significantly in TR. 2) LDL-C decreased and HDL-C increased significantly in TR. 3) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in TR. 4) Regarding cardiovascular function, diastolic blood pressure and mean arterial pressure decreased significantly in both TR and CON. hs-CRP were not changed significantly; however, it tended to be decreased TR. 5) Number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased significantly in TR(2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76). Conclusions It was concluded that 8 weeks of circuit exercise training would be beneficial for improvement of blood lipid profiles and insulin resistance, resulting in preventing metabolic syndrome. In particular, it would be very clinically meaningful that number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased from 2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76 by the circuit exercise training.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 8 weeks of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation on a body composition, physical fitness, insulin resistance, liver function, blood pressure, and heart rate. Fifty-one elderly women were randomly assigned to aerobic training group (EX: n=12), resveratrol supplementation group (R: n=13), combined aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation group (EX+R: n=12), and control group (CON: n=14). The subjects in EX group exercised three sessions per week, 40 minutes per session for 8 weeks, the subjects in R group took 500 mg of resveratrol per day for 8 weeks, and the subjects in EX+R group received both treatments. The subjects in CON group were asked to maintain normal daily life pattern without any treatment for the same period of intervention. Body composition, physical fitness, insulin resistance, liver function, blood pressure, and heart rate were measured at pre- and post-test and the data were compared among groups and between tests by utilizing two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Physique and body composition did not change significantly in all groups. 2) Muscular endurance increased significantly in EX+R group, whereas the other physical fitness-related variables showed no significant changes in all groups. 3) Fasting glucose, fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, and HbA1c tended to be improved in EX+R group. 4) AST, ALT, and γ·GT showed no significant changes in all groups. 5) Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure increased significantly in CON group. Heart rate tended to be decreased in EX+R group and EX group. It was concluded that the 8 weeks of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation had positive effects on muscular endurance, insulin resistance, and blood pressure in T2DM elderly women. Research investigating the effects of a longer period of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation on the same variables would be warranted in the future.
Purpose : The purpose of this study was to investigate coaching information with which coaches provided players during badminton competition. Methods : To this end, we generated an open-ended questions and presented it to 88 high school athletes registered in the Badminton Korea Association. The survey was conducted during a tournament and immediately after the tournament to collect the data. The collected data were categorized through inductive content analysis. Results : As a result of this study, a total of 480 raw data points collected through the open-ended survey were categorized into four general areas: psychological information, technical information, tactical information, and game operation information. Specifically, psychological information was divided into six subdivisions: concentration, confidence, relaxation/stabilization, mental toughness, play thought, and passion; technical information was broken into four subdivisions: strokes, footwork, swing and posture, and position preparation; tactical information had four subdivisions: coping to opponents, play changes, rotation, and manipulation of opponents; and, game operation information was divided into two subdivisions: taking the lead in a game and changing atmosphere. Conclusions : In other words, in badminton competition, the coaches strengthened psychological skills that promote psychological stability to attain the athletes’ peak performance and modified the athletes’ motion into the action necessary for achieving accurate techniques. Furthermore, they provided a variety of coaching information so that the athletes will respond appropriately to their opponents’ play, take the lead in games and induce a positive mood. The psychological, technical, tactical and game operation information offered by badminton coaches are the main factors influencing the performance of badminton players and suggest a need for the proper management and control of the coaches as well as athletes for the peak performance.

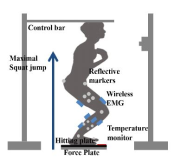
The human foot is only part that directly contact between the body and the external environment, and is ideally positioned to provide sensory information to the Central Nervous System (CNS) during static and dynamic tasks. Through cutaneous mechanoreceptors located in the dermis, the foot is able to recognize touch pressure and vibration stimuli, which provide important feedback information used for the fine coordination of movements. The purpose of this study is to quantitatively examine the effect of changing the foot cutaneous sensory by temperature stimulus on maximal performance and muscle activation using wavelet technique. Sixteen healthy subjects volunteered to participate in this study (Male: Age 21.4±2.4years; Height 174.7±5.3츠; Weight 70.6±5.2kg; Female: Age 20.5±0.6years; Height 163.2±3.1cm; Weight 55.6±4.8kg). Sensory pressure thresholds were determined for the plantar surface of the foot using monofilament. Kinematic, kinetic and EMG data which relative to maximal performance were collected while squat jumping in each temperature condition(cool 12-15℃ normal 28-30℃ hot 45-48℃). Maximal jump height was significant higher in normal condition. Vertical GRF in normal condition showed higher peak value the other conditions. And then EMG signal were significant different between temperature conditions during maximal performance. By changed sensory feedback on temperature, one can alter maximal performance and muscle activation pattern. Cutaneous feedback is important in performance and neuromuscular control, and temperature changes significantly influence on lower extremity during maximal squat jump performance of healthy subjects.