PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the effects of motion analysis and image training using self-modeling with visual cues on the skill performance, imagery, and sports confidence of adolescent female soccer players. METHODS The participants were elite soccer players from two girls’ high school soccer teams divided into an experimental group (D girls’ high school, n=16) and a control group (I girls’ high school, n=13). The experimental group underwent motion analysis and image training when performing penalty kicks, short kicks, and long kicks using self-modeling with visual cues, while the control group underwent training using self-modeling videos without visual cues. Before and after the training, the evaluation score was calculated according to kick performance, and the imagery and sports confidence factors were measured. For the statistical analysis of all collected data, descriptive statistics, the Friedman test, the Mann-Whitney U test, and two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance were used. RESULTS First, on the motion analysis using self-modeling with visual cues, the experimental group’s penalty kick and short kick scores were improved and differed significantly, but no significant change was noted in long kick score. Second, as a result of image training using self-modeling with visual cues, all visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability factors of the experimental group improved except for the auditory factor, and the interaction effect was confirmed. In addition, the stated sports confidence of the experimental group was improved and the interaction effect confirmed. CONCLUSIONS The analysis of kick motion using self-modeling with visual cues was effective for the penalty kicks and short kicks of adolescent female soccer players. Moreover, this study confirmed that the analysis of kick motion improved the visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability sub-factors of imagery and significantly affected the players’ stated sports confidence.

Purpose In general, motor imagery and action observation have been distinguished from each other. Recently, several studies demonstrated that combined approach to motor imagery and action observation can be more effective in motor learning. The present study examined the effects of observation learning combined motor imagery and action observation during acquisition basketball shooting skills. Methods We divided with control group, action observation group and observation learning group combined mental image and action observation in the three middle school. Action observation group provided the action observation program, and observation learning group was performed observation learning combined mental image and action observation training. All groups were perform basic basketball skills. Experimental intervention was performed for 10 weeks, and data analysis was performed 3 groups × 2 time repeated ANOVA. Results The results indicated that all group were improve after intervention, and subjects who participated in combined mental image and action observation was significant in the interaction effect on the front shoot. Moreover, the interaction effect on the motor imagery ability was significant. Conclusions These findings suggest that the use of observation learning combined mental image and action observation strategy potentially optimizes motor skills performance and motor image ability by incorporating motor imagery, especially when observing movements with intent to imitate.


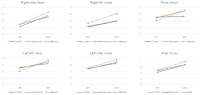

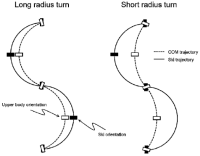
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the three dimensional joint angles of the ankle, knee and hip during basic long turn, carving long turn, basic short turn and carving short turn. Methods Fourteen alpine ski instructors from Korea Ski Instructor Association participated in this study. Each skier asked to perform 4-types of turning technique, classified by radius and level. 8 inertial measurement units were used to measure three-dimensional joint angles of the ankle, knee and hip joint. Results Significant differences were found the lower extremity joint angles on the mediolateral and vertical axis during long-turn and carving-turn (p<.05). significant differences were found the lower extremity joint angles on the anteroposterior axis in the steering phases 1, 2 and complete phase (p<.05). Conclusions In the Alpine skiing, the short turn requires a complex movement of the lower limb joint compared to the long turn. When performing a long turn, the movement of the ankle joint on the vertical axis are required compared to the short turn. And the carving and short turn need to the movements of the lower limb joint on the mediolateral axis.


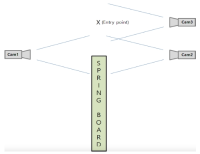
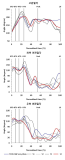
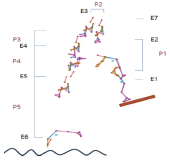
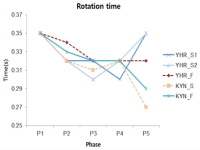
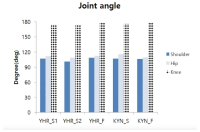
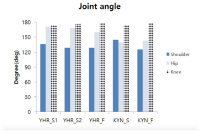
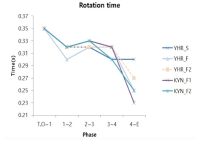
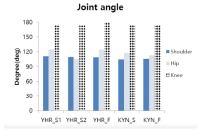
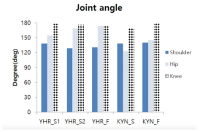
Purpose The purpose of this study is to overcome the shortcomings of 109C(Forward 4 ½ somersault) skill(Level 3.7) for two members of the men’s national diving team(YHR, KYN). Methods For qualitative analysis of the performed skill, three high-speed cameras and water-attached EMGs consisting of a total of ten placements were used. We instructed the two players to perform single-leg jump and double-leg jumps a total of three times each. Results The results of this study indicate that YHR and KYN appeared to increase their time or maintain the same time compared to the previous phase and displacement appeared higher when skill success occurred after the double-leg jump. The Shoulder & hip joints of YHR, KYN appeared larger in E2 and the hip joint of KYN appeared to increase in E1. Single-leg jump appeared similar or decreased the performed time of the previous phase in the last P5. YHR appeared larger only at a hip joint angle and KYN appeared smaller at the hip joint. The muscle activity(iEMG) of the two players appeared greater during skill failure than most of the muscles. Conclusions When perfectly performing 109C skills, the acquisition of medals in international competitions is possible. Therefore, in the future, it is necessary to study all of the variables that pertain to 109C.



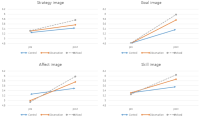
PURPOSE This study examined the effects of focus of attention on beginning golfers’ competitive anxiety and motor performance. METHODS Forty-eight college students with no prior golf putting experience were selected as participants and randomly assigned to internal-focus, external-focus, holistic-focus, and control groups (12 participants each). All subjects performed 5-m golf putting in acquisition, noncompetitive, and competitive situations. RESULTS In competitive situations, the internal-focus, holistic-focus, and control groups showed golf putting accuracy and consistency similar to those in noncompetitive situations, whereas the external-focus group’s golf putting accuracy and consistency were significantly lower in competitive situations than in noncompetitive situations. In addition, the holistic-focus group showed significantly higher golf putting accuracy than the control group in both competitive and noncompetitive situations. CONCLUSIONS Holistic-focus can be used effectively as a strategy for beginners to learn motor skills and reproduce learned motor skills when state anxiety increases. However, external attention focus cannot be considered a strategy to induce effective beginners’ exercise performance when competitive state anxiety increases.
The purpose of the study was to investigate the relationship between the different kinematical variables with respect to the records and techniques performed by the participants during the 2011 Daegu IAAF World Championships Men's Pole Vault Event. Subjects chosen for the study were 8 male athletes who were selected for men's pole vault finals (highly skilled group) and 7 athletes who scored lowest record (skilled group) from the men's pole vault qualifying round. Personal best record of the each subjects were chosen to perform two dimensional (2D) and three dimensional (3D) video analyses. The data were obtained at 60 Hz with the use of five video cameras and digitizing was performed. Kinematical variables were calculated after smoothing the data using 2nd order Low-Pass Butterworth filter at cut-off frequency of 10 Hz and Independent samples t-test was performed to test any differences between two subject groups. The results: during the run-up stage, the horizontal velocity rate of the number of steps and run-up phase was obtained higher in highly skilled group than skilled group. During the take-off phase, deceleration in the horizontal velocity rate was observed in highly skilled group than skilled group. Distinct technical characteristics of distant and lower take-off of the take-off angle (angle of pole support) were also observed in highly skilled group than skilled group. During the pole bending and releasing phase, horizontal velocity was generally higher in highly skilled group than skilled group. It is considered that highly skilled group was able to jump higher as the vertical velocity during the pole bending as well as release phase was much higher in comparison to the skilled group.

Purpose This study is a phenomenological research which tries to describe the subjective experience and to analyze multi-layered meanings, and it finds out the men's training experience and meaning. The purpose of this study is to investigate why the men do Yoga and what the subjective meaning of Yoga experience, and the study examines critically whether Yoga experience especially focused on women is against gender performance and dominant body discourse. Methods For the study, 6 middle & young-old aged men who do Yoga more than 6 months every week are selected as participants. Results The meaning of Yoga for middle & young-old aged men in their lives is as follows. First, it is hard for men to experience Yoga because of social and cultural background. Finding Yoga class which takes men's membership is difficult. Second, middle & young-old aged men's physical feature(interest in their health and disease) and personal background(women friendly daily life) become specific motivation to overcome the barrier to do Yoga. Third, Yoga is 'alterative training', not a training. Yoga is considered as a training which replaces the feature of training called men's sports previously. Fourth, Yoga has a meaning of 'healing' to have our own time. Fifth, Yoga is changed by itself in Yoga culture which is focused on women even though middle & young-old aged men do Yoga for a long time. Sixth, middle & young-old aged men realize that the feature of Yoga is not 'for only women', and they thought it is 'neutral training that men can do too.' Conclusion Consequently, the reason why middle & young-old aged men do Yoga is started from the motivation regarding physical characteristics and personal background, and the main purpose is to cure and to heal our bodies and mind. For them, Yoga means 'alternative training to fit their bodies' and 'their own time'. Moreover, old male adult's training experience and meaning are against gender performance in that it cause a crack in stereotyped gender sports area, but it is notable that there is no intention to resist the dominant gender body discourse.
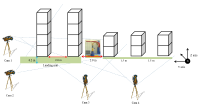
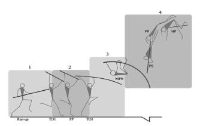
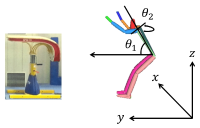
Purpose The purpose of the study was to perform a comparative analysis of the YANG Hak Seon technique carried out by "K" athlete with the kinematical data of "Y" athlete and propose a method to improve the YANG Hak Seon technique of "K" athlete. Method The subject recruited for the study was a male athlete from Korean national team (Age: 21, height: 1.65 m, body weight: 59.6 kg, and career: 11 years). Four high - speed cameras were used to analyze the 3D motion of the YANG Hak Seon technique performed by "K" athlete. The variables selected for analysis were the velocity of COM, displacement of COM, the rotational & torsional angle of the trunk and rotational & torsional angular velocity of the trunk. The results obtained were compared to the preexisting data of the "Y" athlete (data set from the published research). Results Firstly, the horizontal displacement of the YANG Hak Seon technique of the "K" athlete was observed to be shorter along with lower vertical displacement during landing compared to “Y” athlete. In addition, the overall horizontal velocity was low and vertical velocity was not generated which rises during the BC (board contact) phase. Although the rotational angular velocity of the trunk was lower during the BC, HC (horse contact) phase and LD (landing) phase, torsional angular velocity was higher during the LD. Conclusion In order to improve the completeness of the YANG Hak Seon technique of the K player, it is necessary to enter with a fast and low posture on the footplate during the initial phase. In the BC phase, it is essential to raise the COM simultaneously while landing on the footplate and increase the rotational angular velocity of the trunk.


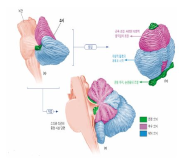
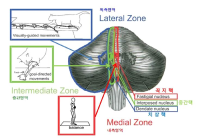
The cerebellum is one of the major parts of the brain involved in the motor control including motor coordination, muscle tone, balance, and the learning of motor skills. The purpose of this review paper was to explore of pathophysiology, anatomical function and neurophysiological mechanism for cerebellum. For this, we sought to examine of previous study related cerebellar disease. Specifically, this paper suggested that motor deficiency of limb movements, coordination, gait/posture balance, adaptation of during movement execution through information proprioception or kinaesthesia, and motor planning and programming of cerebellar patients. We expect that this review will be able to offer the useful information to research. For example, movement scientists will provide an academic information about cerebellar ataxia. Patients and their families will provide relevant information to the daily life (e.g., management and rehabilitation exercise).

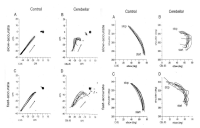
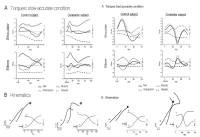



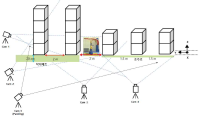
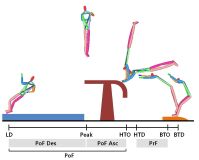
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to compare Yeo 2 vault and YANG Hak Seon vault to verify the possibility of YANG Hak Seon vault. [Methods] The YANG Hak Seon vault and Yeo 2 vault performed by five Korean national gymnastic athletes, and the photographic images were collected using a high-speed camera and their kinematic characteristics were analyzed by 3D image analysis. [Results] The main variable of the post-flight phase S1, S4, and S2 were similar to YANG Hak Seon vault. S1 showed the largest at shoulder angle and the highest body center of mass at horse take-off. S4 showed the smallest shoulder angle at horse take-off, slow twisting at the post-flight ascending period, but faster femoral rotation during horse contact. S2 showed the slowest twist velocity in the ascending period of the post-flight and the smallest rotational distance and twist distance at the peak. S3 showed the slowest horse take-off velocity, the least time in the post-flight phase, and the hip joint was flexed at the peak. [Conclusions] S1 is required to increase the twist velocity by narrowing the shoulder angle during post-flight. S4 is required to strong push-up and an increase in the twisting velocity in the post-flight ascending period. S2 is required to shorten the horse contact time and increase the horse take-off angle through powerful femoral rotation after board take-off. S3 will have to get enough power from the preparation phase.