Purpose The study was designed to investigate the effects of 12 weeks of circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation on physical fitness and metabolic syndrome. Methods Forty-one menopausal women were randomly assigned to one of three groups. i.e., combined circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation group (CT+T: n=14), L-tryptophan supplementation group (T: n=14), and control group (CON: n=13). The subjects in CT+T exercised three sessions per week and took 3g of L-tryptophan per day for 12 weeks. The subjects in T took 3g of L-tryptophan per day for 12 weeks. The subjects in CON were asked to maintain their life pattern for the same period of intervention. Physical fitness and metabolic syndrome-related variables were measured at pre- and post-test. The data were compared by utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. Results Main results of the study were as follows: 1) Standing long jump, one leg standing with eyes closed, sit-and-reach, sit-up, and maximal oxygen uptake increased significantly in CT+T. 2) Body weight, body mass index, waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, fat mass, and percent body fat decreased significantly in CT+T. 3) Total cholesterol decreased significantly in CT+T. 4) Fasting plasma glucose (FPG), fasting plasma insulin, and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in CT+T. FPG and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in T. 5) Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and rate pressure product decreased significantly in CT+T. DBP and MAP decreased significantly in T. 6) Number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased significantly in CT+T and T. Conclusion It was concluded that the circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation would have positive effects on physical fitness and metabolic syndrome, and that L-Tryptophan supplementation would have positive effects on metabolic syndrome by improving insulin resistance and hypertension in menopausal women.

Purpose This study was to investigate the effect of various motor leaning techniques which were applied on the youth soccer training program. Methods 12 elementary soccer players and the director of R youth soccer team have participated in the study. The expertise level of youth soccer team were ranged from beginner to advance. To investigate the effect of new soccer training program we adopted a methodology of action research. We first analyzed the problems of original youth soccer program and reconstructed the training program considering of individualized characteristics. The 3 main problems of original soccer program (1. feedback provisions 2. difficulty of task level 3. time distribution of training) have been reconstructed by four motor learning experts. For the data analysis, several qualitative analyze techniques were conducted to observe player’s improvements. Results First, participants had a better understanding on proper motion of shooting and lifting skills from the guidance techniques. Second, utilizing the personal skills and team cohesion have been improved by the modified rules and space competition. Third, the ability of active problem solving have been improved from the self-learning environment. Forth, the player’s confidence level have been improved by eliminating performance outcome. Conclusions From the aspects of variety circumstances in sport education field, the comprehensive motor learning program should be developed and applied.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to understand student athletes coaches’ occupational challenges from the dual perspectives(social relationship-political system), to analyze the nature of the coping strategies for the challenges, and to provide implications for building a human rights-friendly student athletes club culture. Methods Five coaches(n=5, average career length= 19.2 years) were selected through purposeful sampling. Data were collected by semi-structured interviews with participants. The collected data were inductively analyzed(Patton, 2015). Results First, participants struggled with informal roles demanded by the interested parties(principals, athletic directors, parents, and university coaches). Second, the system for protecting student athletes’ learning rights, the 52-hour work system and the human rights system added difficulties to the coaches’ work environment. Third, the disharmony between interested parties’ demands and government agencies’ institutional ideals pushed participants to choose anti-institutional, un-ethical, un-educational coping strategies. Conclusion The findings suggest that the government, academia and the community should empower coaches as ‘the subject of reform’ who can solve the problem together rather than regarding them as ‘the object of reform.’ Furthermore, this conclusion is expected to provide implications to alleviate disharmony between interest parties’ demands and government agencies’ systems.’

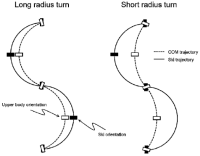
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the three dimensional joint angles of the ankle, knee and hip during basic long turn, carving long turn, basic short turn and carving short turn. Methods Fourteen alpine ski instructors from Korea Ski Instructor Association participated in this study. Each skier asked to perform 4-types of turning technique, classified by radius and level. 8 inertial measurement units were used to measure three-dimensional joint angles of the ankle, knee and hip joint. Results Significant differences were found the lower extremity joint angles on the mediolateral and vertical axis during long-turn and carving-turn (p<.05). significant differences were found the lower extremity joint angles on the anteroposterior axis in the steering phases 1, 2 and complete phase (p<.05). Conclusions In the Alpine skiing, the short turn requires a complex movement of the lower limb joint compared to the long turn. When performing a long turn, the movement of the ankle joint on the vertical axis are required compared to the short turn. And the carving and short turn need to the movements of the lower limb joint on the mediolateral axis.


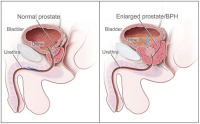
Purpose Prostate problems, such as prostate cancer, and benign prostate hyperplasia have been recognized as problems largely related to androgens and genetic factors. They affect a large fraction of the elderly population, contributing significantly to morbidity and mortality. Therefore, the purpose of this review paper was to investigate a therapeutic strategies for prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia. Methods In order to determine the therapeutic exercise strategies for prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia, previous literature was reviewed with MEDLINE, PubMed, and Scopus databases. Results Prostate cancer and its associated treatments can cause significant and lasting morbidities, such as cardiovascular and sexual dysfunctions. Various interventions have attempted to prevent or mitigate these dysfunctions. This review summarizes the available evidence concerning the effects of exercise training on male sexual health in the cancer prevalent population. Smoking cessation, regular exercise, and maintaining healthy weight are important public health targets for intervention. Importantly, several lifestyle modifications may lower the risk of developing more aggressive cancer or offer survival benefits to prostate cancer patients. Conclusions In this review article, physical exercise training can increase apoptosis markers in the prostate, suggesting exercise training as a potential novel therapeutic strategies for treating prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia. Future studies in more advanced and varied prostate cancer populations are required to ascertain the duration, intensity and frequency of exercise that optimizes the effects of exercise training on prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia.


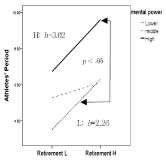
Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the differences between the three simple control models of Hayes (2012) and to determine whether there were Moderating Effects depending on the level of self-esteem, willpower and belief that are psychological factors in the relationship between athlete's retirement and Athlete's period. Methods To achieve this objective, a total of 259 retirees were collected from data on retirement and psychological factors. The data processing method presented the reliability and feasibility of the measuring instrument through technical statistics, frequency analysis, confirmation factor analysis, and reliability analysis. In addition, we conducted a hierarchical regression analysis using the PROCESS command statement in IBM 20 to examine the regulatory effects. Results The results of the study are as follows: The first was the significant model of Hayes (2012)'s three simple control models. It is up to the researcher to choose which model to choose, but when selecting the model, the justification of the variables must be established on the basis of theoretical basis, and the reliability of the variables must be put in to produce reliable and reasonable results. The second was to verify that the relationship between the retirement factor(10) and the Athlete's period has an adjustment effect based on self-esteem, willpower and belief. Among the psychological factors, the Moderating Effects was greatest in the influence of belief on the Athletes' period, and the more reasons for retirement, the longer the Athletes' period than the weaker. The combined mental strength of all three psychological factors combined shows that the combined effect of control also significantly increases the player's ability to survive by combining with the retirement factor. In particular, sportsmanship has resulted in a better mix of retirement factors than the sense of Self-esteem and will, resulting in a longer increase in the capacity. Conclusions Therefore, players who long for a player always keep their dreams of becoming a big star in mind, and ask me to always keep the belief in hope that I will enjoy my career for a long time.






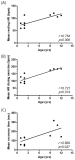
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate changes of the cardiovascular system by comparing heart rate (HR) and blood responses to exercise in younger and older adult dogs and to verify the value of dogs as aging model in exercise science research. Methods A total of 11 healthy beagles were divided into 2 groups according to age: younger adult dogs (1~2 years old, 7 animals) and older adult dogs (9~11 years old, 4 animals). Each animal exercised on the treadmill for 25 minutes, twice a week, and for 4 weeks. The exercise intensity was gradually increased by applying four different protocols. Resting HR, HR during exercise, and HR recovery time were determined as HR parameters. Biochemical analysis was performed on blood samples. The independent Student’s t-test and one-way ANOVA were used to analyze the mean difference of each variable. The associations between age and HR parameters were determined using Spearman‘s analysis. Results Older adult dogs showed higher HRs during rest and exercise than younger adult dogs. HR recovery time was significantly longer in older adult dogs than in younger adult dogs. A strong positive relationship was observed between beagles’ age and resting HR, HR during exercise, and HR recovery time, respectively. The heart rate response to the treadmill exercise was similar between the 1st week and 4th week in younger and older adult dogs. Exercise significantly reduced the white blood cell level in older adult dogs and increased the alkali phosphatase level in younger adult dogs. Conclusions The results of this study demonstrated that short-term treadmill exercise may have a positive effect on the aerobic capacity, inflammation, and bone formation, suggesting that dogs are valuable as aging model in exercise science research.

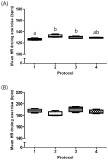
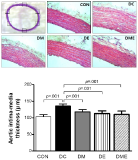
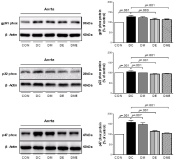
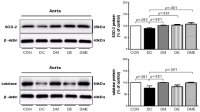
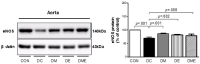
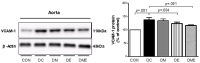
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment on NADPH oxidase, antioxidation and vascular function-related factors in aortic of D-galactose-induced aging rats. Methods To induce the animal model of aging, D-galactose was diluted in saline, and a dose of 100mg /kg was intraperitoneally injected into Sprague-Dawley rats once a day for a total of 10 weeks. Rats were divided into five groups: Control group (CON, n=9), D-galactose control group (DC, n=9), D-galactose+MitoQ group (DM, n=9), D-galactose+Exercise group (DE, n=9), D-galactose+MitoQ + Exercise group(DME, n=9), and treadmill exercise was conducted for 5 days/week during 8 weeks with gradual increase of intensity. MitoQ treatment was intraperitoneally injected at a concentration of 100μM/kg twice a week for 8 weeks during the research period. Results The result showed that treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment decreased the expression of NADPH oxidase level and increased antioxidant enzyme such as SOD-2, catalase. It lead to positive effects such as increasing the level of eNOS, a protein involved in vascular function while decreasing the level of VCAM-1. In addition, as a result, it showed the structurally reduced intima-media thickness. Conclusions It can be concluded that treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment are effective in ameliorating and treating vascular dysfunction resulting from aging.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a psychic energy management scale that construct a concept and based on extracted contents of structural validity and reliability of university athlete psychic energy management inventory. Methods To develop the scale, the researches were completed <research ⅰ; constructing sub-factors of Psychological Energy Management, ⅱ; developing scales of psychic energy management, ⅲ; verifying validity of psychic energy management>. The results shown are a follows. Results The psychic energy management inventory contents of the university athlete were categorized into five categories ; team energy, game energy, environment energy, leisure energy and body energy. Through statistical procedures and factor analysis, the psychic energy management inventory was developed with 4 factors 18 items (coach energy 4 question items, game/environment energy 6 question items, colleague energy 4 question items, body energy 4 question items). Conclusion Convergent validity and discriminant validity was demonstrated through the external validity, the multi-group analysis confirmed the structural equivalence of the scale between the school grades.
Purpose The aim of this study is to find how the pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise effect on the body composition, exercise performance ability, blood factor and obesity related hormone, and to verify the effect of pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise as an effective substance for obesity improvement. Methods This study selected 20 obese men in their twenties who has more BMI than 25kg/m2, and are applicable in 25% of the body fat, and randomly sampled group of 10 people for pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise (PYA), and 10 people for placebo intake and aerobic exercise (PLA). Intake of pyruvate and placebo was implemented for 10 weeks, 6 g a day, and aerobic exercise, treadmill exercise in the intensity of 50 ~ 60%’s target heart rate, was conducted for 10 weeks, 3 times a week, 60 minutes a day. To demonstrate the effect of pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise, all of the body composition, exercise performance ability, Lactate, and blood factor and hormone related to obesity were measured before and after the test in the same manner. Results The main results from this study are as follow; 1) In the case of body composition, in PYA, weight(p < .01), BMI(p < .05), body fat percentage(p < .01), and body weight without fat(p < .001) are reduced meaningfully. 2) In the exercise performance ability increased significantly in both PYA(p < .01) and PLA(p < .001) for V˙O2max, Also, in the case of distance during the exercise, PYA(p < .01) and PLA(p < .05) increased significantly in 15 minutes and PYA(p < .01) and PLA(p < .05) 30 minutes, but only in PYA from 45 minutes(p < .01) to 60 minutes(p < .05) 3) In case of Lactate, the significant decrease in PYA during stabilization and the significant increase in PYA after 30 minutes of exercise was not seen after 45 minutes 4) In the case of blood factor, HDL-C showed a meaningful decrease in PLA(p < .05) and Leptin showed a meaningful decrease in PYA(p < .001). Conclusions To sum up these results, it was more effective for the group of PYA which ingested pyruvate in improving obesity, even when the same aerobic exercise is conducted.