
Purpose In general, motor imagery and action observation have been distinguished from each other. Recently, several studies demonstrated that combined approach to motor imagery and action observation can be more effective in motor learning. The present study examined the effects of observation learning combined motor imagery and action observation during acquisition basketball shooting skills. Methods We divided with control group, action observation group and observation learning group combined mental image and action observation in the three middle school. Action observation group provided the action observation program, and observation learning group was performed observation learning combined mental image and action observation training. All groups were perform basic basketball skills. Experimental intervention was performed for 10 weeks, and data analysis was performed 3 groups × 2 time repeated ANOVA. Results The results indicated that all group were improve after intervention, and subjects who participated in combined mental image and action observation was significant in the interaction effect on the front shoot. Moreover, the interaction effect on the motor imagery ability was significant. Conclusions These findings suggest that the use of observation learning combined mental image and action observation strategy potentially optimizes motor skills performance and motor image ability by incorporating motor imagery, especially when observing movements with intent to imitate.



Sport Imagery Questionnaire of Hall et al.(1998) was developed to investigate the imagery type of athletes objectively. The purpose of this research is to verify validity and reliability of Korean SIQ by using Rasch Model, in order to make up for complement drawback of SIQ which was developed only using factorial analysis. This research conducted first and second questionnaire survey. Second survey was conducted targeting different study participants from those of first survey. The participants of first survey was 265 athletes of Chungcheong Province, and the participants of second survey was 169 athletes of Chungcheong Province. SPSS 21, Winstep 3.62, and AMOS 18 was used for date analysis. The result of Rasch Model verification for the data of first survey revealed that 8 items of SIQ were unfit. Thus, 5 factors and 22 items were determined. 7 point Likert scale was revealed to be a good fit. The result of Confirmatory Factor Analysis for the data of second survey revealed that Construct Validity of 5 factors and 22 items was valid and reliability was high by recording Cronbach’α value .954. External Validity was revealed to be high by showing that correlation between sport confidence and MG-M imagery was high.

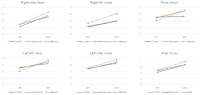
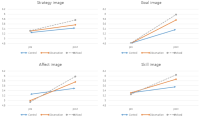
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the effects of motion analysis and image training using self-modeling with visual cues on the skill performance, imagery, and sports confidence of adolescent female soccer players. METHODS The participants were elite soccer players from two girls’ high school soccer teams divided into an experimental group (D girls’ high school, n=16) and a control group (I girls’ high school, n=13). The experimental group underwent motion analysis and image training when performing penalty kicks, short kicks, and long kicks using self-modeling with visual cues, while the control group underwent training using self-modeling videos without visual cues. Before and after the training, the evaluation score was calculated according to kick performance, and the imagery and sports confidence factors were measured. For the statistical analysis of all collected data, descriptive statistics, the Friedman test, the Mann-Whitney U test, and two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance were used. RESULTS First, on the motion analysis using self-modeling with visual cues, the experimental group’s penalty kick and short kick scores were improved and differed significantly, but no significant change was noted in long kick score. Second, as a result of image training using self-modeling with visual cues, all visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability factors of the experimental group improved except for the auditory factor, and the interaction effect was confirmed. In addition, the stated sports confidence of the experimental group was improved and the interaction effect confirmed. CONCLUSIONS The analysis of kick motion using self-modeling with visual cues was effective for the penalty kicks and short kicks of adolescent female soccer players. Moreover, this study confirmed that the analysis of kick motion improved the visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability sub-factors of imagery and significantly affected the players’ stated sports confidence.

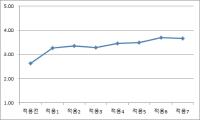
Purpose This study was to investigate the systematic application of the life skills program and its effects in a sport setting. Methods Participants were 14 college students(8 males and 6 females) majoring in Taekwondo. Survey tools were utilized to measure items of life skills and journals. Data analyses were conducted by using Excel program and inductive content analysis. Results First, life skills in this study consisted of goal setting, self-talk, imagery, cognitive restructuring. Life skills program has undergone a procedure, such as the introduction, training, development, application, and evaluation. Second, the average scores of life skill variables have been changed according to measured points. Specifically, the average scores of goal setting and self-talk were highly increased over time and the average score of imagery indicated gradual rising line. The average score of negative thought was slightly reduced over time. Third, regarding effects of this program, participants’ responses were categorized into six components; performance enhancement, positive thoughts, chances of change, goal setting, struggling efforts, and motivation formation. Further, participants stated this program was a great opportunity to develop these components. Conclusion The application of life skills program in sport settings will contribute to participants’ life span developmental change in cognitions, emotions, and behavior.



This study aimed to explore elite taekwondo competitors’ imagery strategies . The study participants were 10 elite taekwondo athletes, who worked for S business team. Data were collected through open-ended questionnaires and in-depth interviews. The data were collected based on Gould et al. (1992)’s proposed qualitative research method. The inductive content analysis of the imagery was conducted following the imagery type of Paivio (1985) and Suinn (1996). The law data and case of imagery were separated by three specialists. The results were as follows. First, elite taekwondo competitors generally used the types of imagery proposed by Paivio (1985) and Suinn (1996). In particular, imagery of anxiety regulation appeared with the highest frequency among factors and ordered imagery of motivation, imagery of skills, imagery of mental skills, and imagery of competition. Second, elite taekwondo competitors mainly used imagery of skills before two weeks for competition. They mainly used imagery of anxiety regulation the day before a competition. They used imagery of anxiety regulation and imagery of motivation on the day of a competition. They used imagery of motivation after the competition. In sum, elite taekwondo competitors used individual strategies in terms of imagery in order to ensure effective training and peak performance in competition. The strategy of imagery was applied differently based on the juncture of the competition.
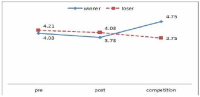
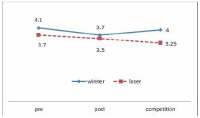
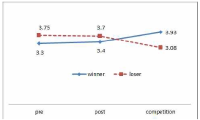
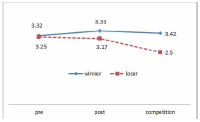
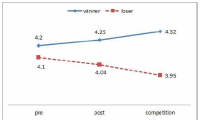
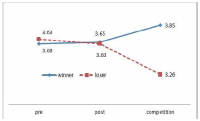
The purpose of this study was to confirm the differences between winner and loser groups of national team participated in the World Taekwondo Championships statistically and trends of psychological status according to applying mental coaching. In order to achieve the purpose it was the selection of 16 national members participated in the 2013 World Taekwondo Championships in Puebla. Data was selected by TOPS(test of performance strategy). The survey was conducted before and after applying the mental coaching and the game soon after. Data processing results were calculated utilizing Excel and SPSS 21.0 version. Based on the findings issue the conclusions were as follows. First, the psychological state of the winner and loser groups showed a different trend in the self-talk, emotion control, performed automatically, imagery, struggle, negative thinking, relaxation, condition factor. Winner group was shown maintenance or better trends of psychological state in the three times measurements on the other hand, loser group was shown decrease in the game soon after. Secondly, winner and loser groups are statistically significant differences in the psychological state of competition in self-talk, struggle, negative thinking, solving tension factors. In other words, The winner group had higher score in the four factors than loser group in the competition.

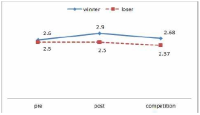
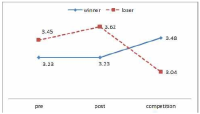
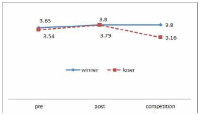
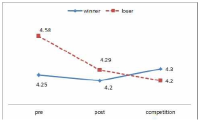
The purpose of this study was to examine psychological capital acquisition through Asian Games Participation. 17 of national women football players were completed Psychological Capitals Questionnair. The psychological capital consists of optimism, psychological skills, self-management, collective efficacy, and performance perception was investigated after the team call-ups and before the team-release. The data was analyzed by paired t-test. As results, Korean women football players’ collective efficient and performance perception showed a statistical significance at the beginning of the team call-ups but optimism, psychological skills, and self-direction did not show statistic significances. The team-harmony, interpersonal-management, team-power, sufficient training, trust in coach, efficient communication, and psychological football factors, which were subfactor of football players’ psychological capital, showed statistical significances. However, confidence, concentration, goal-setting, imagery, willpower, anxiety-control, mental-management, life-management, training-management, innate-behavior management, physical-management, football skills, mediative skills, and football intelligence factors did not have statistic significances. These results demonstrate that effects of mega sporting events-like experiences and psychological factors’ variability and inflexibility according to weather changes should be considered when it comes to discussion of psychological factors regarding players’ performance. It is expected that this study would be a fundamental resource for understanding of psychological influences through participations in mega sporting events and discussions about further psychological interventions for teams with environmental consideration as well as methodological developments which could measure effects of the psychological interventions.

This study was to verify the structure of efficacy related to performance perceived by short-track athletes when playing a match. Therefore, 50 players answered open questionnaires and 200 players participated in construct validity verification, a total of 250 players of short-track members of national, business and university team were sampled during the research phase. The data was analyzed through the study procedures. The results were as follows: First, efficacy structure of players during the match were categorized into three groups as game managing strategy(including course management, race control, match management and selective attention ability), psychological control ability(including positive imagery, match competition, competitive spirit, ability to handle hardship, anxiety control, and patience), and physical usage of ability(including physique, endurance, and quickness). Second, the result of the first construct validity verification through exploratory factor analysis showed 7 factors in 29 items as game management, course management, psychological control, physical use, coping with hardship, speed control and psychological stability. Finally, as a result of confirmatory factor analysis, short-track self-efficacy showed the 5 factor in 15 items except for coping with hardship and psychological stability.
