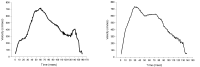
The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of the functional movement improvement training program on the score of high-school baseball players’ functional movement screen (FMSTM) test. After 16-weeks treatment period, a significant increase of Deep Squat, Hurdle Step, In-Line Lunge, Shoulder Mobility, Active Straight Leg Raise, Rotary Stability, and total score was found only in treatment group. There was decrease on the number of players in treatment group whose total score is less than 14; the criteria vulnerable being injured. The results of this study suggested that applying functional movement improvement training program on high-school baseball players can be effective to prevent injuries.






















The primary purpose of the study was to identify the characteristics of Korean national youth soccer players’ functional movements. The secondary purpose was to examine whether certain tests of Functional Movement Screen (FMS) meaningfully achieve goodness-of-fit for the soccer-specific movements. Korean national youth soccer players (30 male players, 18.37 ± 0.67 yrs, 178.7±7.09 cm, 70.2±6.46 kg), performed FMS tests [deep squat (DS), hurdle step (HS), in-line lunge (IL), shoulder mobility (SM), active straight leg raise (ASLR), trunk stability push-up (TSP), and rotary stability (RS)]. The mean (±SD) FMS composite score and each test score were calculated. Rasch analysis, which was used to determine the goodness-of-fit for the tests, was applied to examine the item difficulty of the FMS tests. The mean FMS composite score was 10.2± 1.79; the mean DS, HS, IL, SM, ASLR, TSP, and RS score were 1.13±0.35, 1.27±0.45, 1.4±0.56, 1.6±0.77, 2.07±0.69, 1.43±0.82, and 1.3±0.47 respectively. According to the results of Rasch analysis, 4 tests (DS, IL, ASLR, and RS) were shown to be within the acceptable range (infit & outfit > 0.5 ~ < 1.5). The other 3 tests (HS, SM, and TSP) were shown to be out of acceptable range. The additional analysis revealed the DS (logit = 2.08) as the most difficult test and ASLR (logit = -3.16) the least. The results of the study showed that the players’ FMS composite score was lower (< 14) than the cut-off points used by previous studies for different athletes. The further study is warranted to examine the relationships between the scores of the tests appeared to be soccer-specific in the present study and the level of performance variables.

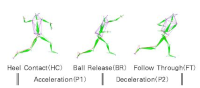
The purpose of this study was to classify high school baseball players as superior or inferior group by Functional Movement Screen(FMS) and to provide basic information for finding great pitcher and improving exercise performance by comparing and analyzing the pitching motion. The results of this study are as follows. The inferior group’s center of mass(COM) moved significant on the left side than superior group at heel contact(HC), ball release(BR), and follow throw(FT)(p<.05). There were no significant difference in linear velocity of shoulder, elbow and wrist between two groups, but inferior groups showed large difference in each joint. The superior group controled rotation of pelvis at HC and showed significant higher knee extension at BR and FT than inferior group(p<.05). The angular velocity of superior group’s throwing arm were higher in acceleration period(p<.05). Taken together based on the results, the players who have higher muscle function showed great pitching motion, so we can conclude that FMS could be useful for evaluating the potential of pitcher.

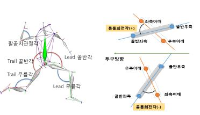
PURPOSE This study aimed to explore the functional movement in rope climbing. METHODS The rope climbing experiment included 16 healthy young male participants, and the methods of hand, cross-leg, and foot-hooking climbing were employed. The muscle activity and joint range of motion were measured and analyzed using EMG (Electromyography) and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) sensors. One-way analysis of variance was conducted (α<.05). RESULTS The activity of the forearm and biceps muscle was lower in cross-leg and foot-hooking climbing compared to hand climbing (p<.01), and the rectus femoris muscle activity in cross-leg climbing was smaller than that in hand climbing (p<.05). Furthermore, the adductor muscle activity in cross-leg climbing was higher than that of other types (p<.01). The range of motion for the elbow and shoulder flexion was smaller in hand climbing than in other types (p<.05); furthermore, the range of motion in the pelvis, thigh, and knee joint was the smallest in cross-leg climbing (p<.05). CONCLUSIONS Because the pulling muscles such as the forearm, biceps, pectoralis major, and latissimus dorsi play an important role in the entire climbing motion, it is necessary to train the upper-body pulling-muscle group along with strengthening the core and lower body muscles.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of trunk stabilization exercise (TSE) with abdominal expansion maneuver (AEM) that lasted for 8 weeks on postural stability and functional movement in college athletes. METHODS Twenty college athletes participated in the program (AEM=9, Control=11) and were subjected to 8-week TSE. The AEM group performed exercise by applying AEM techniques during TSE, and control group performed TSE without breathing-related instructions. Both groups measured postural stability with lower-quarter Y-balance test (LQYBT) and functional movement with functional movement screen (FMS) before and after applying TSE to verify the interaction before and after this study with the two groups. Two-way repeated analysis of variance was performed to evaluate the differences between groups and time for an absolute value of LQYBT and FMS, followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests for post-hoc analysis. RESULTS As a result of the left and right LQYBT, there was a significant difference between the time x group (p=.041, p=.033), and post-hoc analysis indicated that there was a significant difference between the AEM and control groups (p=.000, p=,000). Furthermore, the FMS total score indicated that there was a significant difference between the time × group (p=.039), and the post-hoc analysis showed the AEM group had significant results (p=.001), while there were no significant results in the control group (p=.255). CONCLUSIONS Application of AEM during TSE seems to be effective with regard to postural stability and functional movement in college athletes.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of an eye movement exercise intervention on cognitive function and prefrontal cortex connectivity in the elderly with mild cognitive impairment. METHODS Ten older adults with mild cognitive impairment participated in eye movement exercise consisting of saccadic eye movement, pursuit eye movement, vestibular-ocular eye movement, and vergence eye movement for 4 weeks. Cognitive function (MoCA-K), reaction time during stroop task, and prefrontal cortex connectivity were measured using the functional near-infrared spectrometric analyzer (fNIRS) before and after the intervention. RESULTS First, cognitive function of the elderly with mild cognitive impairment showed significant improvement after the eye movement exercise (p < .05). Second, reaction time decreased significantly from 1.16 to 0.91 ms after eye movement exercise. Third, the strength of prefrontal cortex connectivity (left OFC - right FPC, right OFC - right FPC) increased after the intervention in the older adults with mild cognitive impairment. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study suggest that eye movement exercise is an effective intervention for improving cognitive function through improvement of brain functional connection in the elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment.
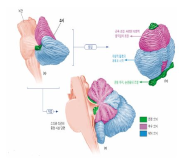
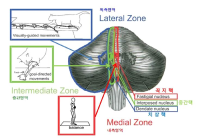
The cerebellum is one of the major parts of the brain involved in the motor control including motor coordination, muscle tone, balance, and the learning of motor skills. The purpose of this review paper was to explore of pathophysiology, anatomical function and neurophysiological mechanism for cerebellum. For this, we sought to examine of previous study related cerebellar disease. Specifically, this paper suggested that motor deficiency of limb movements, coordination, gait/posture balance, adaptation of during movement execution through information proprioception or kinaesthesia, and motor planning and programming of cerebellar patients. We expect that this review will be able to offer the useful information to research. For example, movement scientists will provide an academic information about cerebellar ataxia. Patients and their families will provide relevant information to the daily life (e.g., management and rehabilitation exercise).




PURPOSE Increased body mass index (BMI) increases ankle instability and adversely affects human movement. This study aims to compare and analyze the muscle function and proprioception of the ankle joint based on Body Mass Index (BMI) to determine potential differences. METHODS Twenty-eight healthy male and female college students were categorized into overweight (≥ BMI 23) and normal (< BMI 23) groups. Measurements included BMI, isokinetic strength of dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, eversion, inversion, ankle joint range of motion, and ankle joint proprioception. RESULTS In dorsiflexion, right 30°/sec (p=.035), left 30°/sec (p=.009) and right 120°/sec (p=.011); in plantarflexion, left 30°/sec (p<.001), right 120°/sec (p=.007) and left 120°/sec (p=.006) in ankle inversion, left 30°/sec (p=.001), right 120°/sec (p=.021) and left 120°/sec (p=.007), left 30°/sec (p=.014), 120°/sec (p=.001) in ankle inversion-eversion ratio, right (p=.003) and left (p=.003) in ankle joint range of motion, right (p<.001) and left (p=.022) in total proprioception, and left (p<.001) in left-right proprioception were significantly different between the normal and overweight groups. CONCLUSIONS It was found that the overweight group had lower muscle strength, joint range of motion, and proprioceptive control function of the ankle joint than the normal group according to BMI. Therefore, exercise programs should be provided to strengthen the periarticular muscles involved in ankle movement, such as the tibialis anterior, soleus, and peroneus longus, and to control dynamic proprioception to prevent ankle injuries and function of the ankle joint according to BMI.

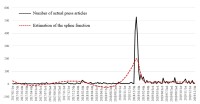
Purpose The purpose of this study is to analyze issues of sexual violence case in sports field reported in the press by using spline function model and text mining. In specific, spline function model is used to measure social interest level based on issue attention cycle theory and figure out the flow of issues by applying text mining. Methods Study material is 2,660 news articles reported from January 1, 2017 to December 31, 2019 and press DB(Big Kinds) of Korea Press Foundation is used to collect study material. Results Social interest level on sexual violence case in sports field is dramatically increased due to disclosure of Sim player starting from Me Too movement started from the culture and art world. Because of this, as structural problem in sports field arises, social interest level comes to a climax, and then it was founded that the government’s countermeasures establishment and special audits by the Ministry of Education were in progress. From the perspective of the issue attention cycle, it has the stages of latent-occurrence-rising-decision-decay-disappearance, but the period from rising to declining is short, so it corresponds to a breaking issue attention cycle. Conclusion This study examines the progress of sexual violence case in sports field from rising to disappearance in the perspective of the issue attention cycle. With this incident, the world of sports is establishing sports ethics center and proceeding policies such as Basic Sports Act, and the future studies need to review the effectiveness of this policy.

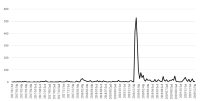

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of coupled high frequency rTMS and prism illusion in elderly stroke patients, based on the result of previous studies which discovered the effect of bilateral training, mirror rehabilitation treatment, and rTMS. Methods This is a case study of 4 stroke patients who were homogeneous on the basis of selection criteria such as brain injury area, duration of onset, degree of upper limb movement function. A total of 24 rehabilitation sessions were conducted three times a week during the training period, and TMS(transcranial magnetic stimulator), EMG, motion analysis system, and prism optical glasses were used for apparatus. Results The results of the study were as follows: Combined rehabilitation exercises were found to be beneficial to restore upper limb function in stroke patients. Particularly, the maximum speed of stretching and JTT(Jebsen-taylor Test) performance showed improvement after training. The amount of total map volume and MEP(megnetic evoked potential) increased in evaluation of neurophysiology. Conclusion The upper limb dysfunction of stroke patients could be restored by combine rehabilitation exercises.