PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to examine the goalkeeper’s area of defense and how the range varies depending on the relative position of the goal, goalkeeper, and ball in a 9-meter jump shot during handball matches. METHODS Data was collected from seven qualifying divisions in mens handball from the 99th National Sports Festival in Korea. A total of 231, 9-meter jump shots were analyzed with the goalkeeper‘s area of defense measured from the point the ball left the shooter’s hand and calculated based on the relative position of the goal, goalkeeper, and ball. Video analysis was conducted using the Kwon3D 3.01 program and three-dimensional coordinates calculated using the DLT method. RESULTS First, dimension of handball goals measure 3m wide and 2m high, however, results show that goalkeeper’s actual area of defense was narrower than the width of the goal posts, while vertically, area exceeded the height of the cross bar. Second, if the goalkeeper defended the striker’s shot from the side rather than from the front, the goalkeeper’s defense range was higher for the opposite side of the goal post than the near side of the goal post. CONCLUSIONS Key factors influencing goalkeeper’s area of defense include height of shot and position of goalkeeper. Results also indicate that vertical movements are more important than horizontal movements for goalkeepers in handball thus such implementation in training may lead to performance enhancement.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop an effective college life adaptation program for freshman student-athletes. Methods A total of 160 student-athletes and 5 experts agreed to participate in this study. Four procedures were followed in this study: the needs assessment, the preliminary program development, and the application of the program. For the needs assessment, in-depth interviews were conducted, and the data were analyzed using an inductive reasoning process. Results The results of the needs investigation showed seven need factors and four interruption factors for college life adaptation. In addition, three need factors based on experience and seven interruption factors based on experience were found. The preliminary program was developed based on the needs assessment through the expert meeting, and the program consisted of four stages. Each stage consisted of three sessions, and each session contained a specific topic. The program was provided to nine freshman student-athletes in two months. As a result, the final program which consisted of four stages and thirteen sessions was developed after the reinforcement process based on evaluation of the preliminary program was conducted. Conclusions It is concluded that, the program is able to be expected to help them to understand their roles, have a better sense of responsibility and improve their self-esteem. Therefore, coaches and mental performance consultants should provide the college life adaptation program for freshman student-athletes to reduce their stress and have a better college life.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to examine the differences in physique and physical fitness factors affecting exercise performance according to the vitamin D receptor (VDR) FokI gene polymorphism in athletic gifted children. Methods FokI VDR polymorphisms were genotyped in 82 boys (9.1±0.9 years) and 55 girls (9.3±0.9 years). Basic physical fitness (basketball throw, half-squat jump, standing long jump, 15m pacer, 50m run, handgrip strength, side-step, trunk forward flexion, sit-up) and physique were measured and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with bonferroni’s correction. Results No association was found between the VDR FokI genotypes and all the physical fitness variables as well as physique variables in boys and girl. However, Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium results for VDR polymorphism distribution showed significant differences (χ2= 6.516, df=2, p=.038). Conclusion Although there was no significant difference in the fitness variables according to the VDR Fok1 genotype, it was difficult to exclude the potential for predicting fitness in that the H-W equilibrium test showed a significant difference. Therefore, in order to confirm the true potential of the VDR Fok1 gene to predict physical fitness, it is considered that additional studies on general children should be conducted.

Purpose This study was to investigate the effect of various motor leaning techniques which were applied on the youth soccer training program. Methods 12 elementary soccer players and the director of R youth soccer team have participated in the study. The expertise level of youth soccer team were ranged from beginner to advance. To investigate the effect of new soccer training program we adopted a methodology of action research. We first analyzed the problems of original youth soccer program and reconstructed the training program considering of individualized characteristics. The 3 main problems of original soccer program (1. feedback provisions 2. difficulty of task level 3. time distribution of training) have been reconstructed by four motor learning experts. For the data analysis, several qualitative analyze techniques were conducted to observe player’s improvements. Results First, participants had a better understanding on proper motion of shooting and lifting skills from the guidance techniques. Second, utilizing the personal skills and team cohesion have been improved by the modified rules and space competition. Third, the ability of active problem solving have been improved from the self-learning environment. Forth, the player’s confidence level have been improved by eliminating performance outcome. Conclusions From the aspects of variety circumstances in sport education field, the comprehensive motor learning program should be developed and applied.


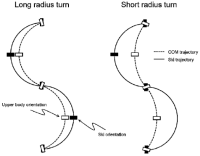
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the three dimensional joint angles of the ankle, knee and hip during basic long turn, carving long turn, basic short turn and carving short turn. Methods Fourteen alpine ski instructors from Korea Ski Instructor Association participated in this study. Each skier asked to perform 4-types of turning technique, classified by radius and level. 8 inertial measurement units were used to measure three-dimensional joint angles of the ankle, knee and hip joint. Results Significant differences were found the lower extremity joint angles on the mediolateral and vertical axis during long-turn and carving-turn (p<.05). significant differences were found the lower extremity joint angles on the anteroposterior axis in the steering phases 1, 2 and complete phase (p<.05). Conclusions In the Alpine skiing, the short turn requires a complex movement of the lower limb joint compared to the long turn. When performing a long turn, the movement of the ankle joint on the vertical axis are required compared to the short turn. And the carving and short turn need to the movements of the lower limb joint on the mediolateral axis.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of regular vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) level, aging- and lifestyle disease-related blood components in middle-aged women. Methods The participants were recruited from a total of 19 physically healthy people aged 50-59 years, and were randomly divided into vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise (VIAE, n = 10) and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (MIAE, n = 9) group. The participants were performed vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise three times a week for eight weeks, and body composition measurement, graded exercise test, blood collection were performed before and after. Results Mean exercise time was significantly longer in the MIAE group than in the VIAE group. The V̇O2max was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. Body weight, BMI, and body fat percentage were significantly lower than pre both groups. The BDNF concentration was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. The dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-s) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentration were significantly higher than pre both groups. The free fatty acid and triglyceride concentrations were significantly lower than pre both groups, and HDL-C concentrations were significantly higher than pre both groups. Conclusions Vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise not only increases maximal oxygen uptake and blood BDNF level in middle-aged women, but also induces positive changes in aging-related hormones and lifestyle-related blood variables.

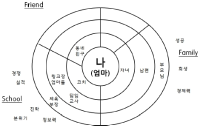
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate how the educational zeal of mothers with winter sports students in secondary schools appears on the network charts. Methods It lasted 28 days from February 6 to March 5, 2017. Starting with a description of the QNA, all interviews were recorded on a tape recorder to carry out the project. Data analysis were divided into four areas(Family, Friend, School, etc.) and 13 associative words(enthusiasm, intelligence, performance, entry, success, sacrifice, atmosphere, polarity, competition, vicarious, satisfaction, economic power, anxiety, stress) to attach associative word stickers according to color. Results As a result of inducing arbitrary interpretation of the network subject's educational network, it was possible to analyze the factors affecting mothers' sports education in three dimensions. In addition, although there is not much difference in areas around "I" on sports education charts, the distance between associative words and network charts has gradually moved away from the same person as their children go on to school. Conclusions The methodological significance of this study has been found to be very useful in visualizing an individual's educational network by utilizing qualitative network analysis and in understanding the characteristics associated with education.




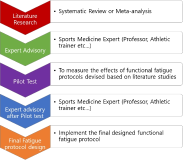
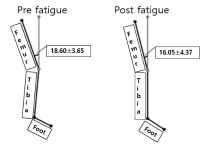
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of a functional fatigue protocol on lower extremity dynamic and static postural control. Methods A total of 20 physically active collegiate students participated in this study (ten males, ten females; age 22.5±2.7 years; mass 67.0±13.0 kg; height 168.0±8.9 cm). A unilateral stance with eyes closed for 10 seconds was performed to test static postural control using a balance force plate and single-leg drop landing on 30cm box was performed as a dynamic postural control test and captured using VICON motion analysis system. Results The results of this study showed an average heart rate of 176.3 beats/minute, an 18 rating on the perceived exertion scale, significant differences in blood lactate, and a static postural control deficit after fatigue as compared with before fatigue(p<.05). Dynamic postural control after fatigue changed landing strategy in the form of stiff landing. Knee flexion was decreased at initial contact and at peak vertical ground reaction force, also, both decreased valgus and internal rotation of knee joint. Conclusions This protocol may use for enhancing fatigue-endurance training as well as for inducing fatigue. Further, to ascertain a landing strategy, it is recommended to increase landing height to clearly observe changes in landing strategy.







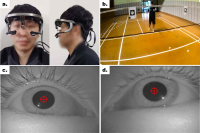
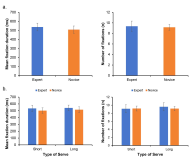
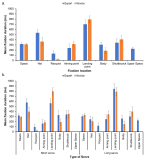
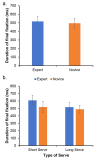
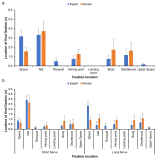
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to examine the differences in visual search strategies between expert and novice badminton players while performing badminton serve. [Method] To this end, expert (more than 10 years experience) and novice (less than 6 months experience) badminton players performed 15 trials of two types of serve (i.e., short-serve and long-serve), in total 30 trials. All the participants’ eye movement was recorded during each trial, and mean fixation duration, fixation distribution, final fixation duration and location, and gaze entropy were analyzed. [Results] The results showed that there was no difference in mean fixation duration between expert and novice players. The analysis of mean fixation duration on each location showed that participants fixated more on the net while doing short serve whereas fixated more on the space when they did long serve. In particular, expert players fixated more on the space while doing long serve than novice players, and fixated more on the net and racquet for the short serve. However, novice players fixated more on the location of shuttle would be landed. The final fixation duration was not different between expert and novice players. Further, expert players showed higher gaze entropy than novice players. [Conclusion] The findings indicate that expert players fixated more on the net for the short serve, and the space for the long serve, and visual search strategies of experts were more varied than novice players.


[Purpose] The present study attempted to verify the effectiveness of an early childhood physical health improvement program (subsequently in the present study, KICCE Early Childhood Health Improvement Program) developed in Korea by modifying and improving the Mission-X: Train Like an Astronaut program developed by NASA to be suitable for children of ages 4 and 5. [Methods] The subjects in the study were 679 children at 7 facilities in Seongnam city, Osan city, and Yongin city, of which 4 were daycares and 3 were kindergartens. The participant group consisted of 339 children, and the control group consisted of 340 children. The program consisted of total 24 activities 3 times a week over 8 weeks, of which 8 activities were related to nutrition and 16 activities were related to physical activity, and in the 9th and 10th weeks, the 16 physical activities were reconfigured and performed 3 times a week. Physical parameters and related fitness parameters were measured before and after the program, and an ANCOVA analysis was performed in which descriptive statistics and scores before the program were the covariate variables. [Results] The results show that first, growth statuses of participant children were in the upper middle section of the distribution, and second, of the 6 fitness developments, flexibility, balance, and quickness were improved, and in most areas, boys and below-normal-BMI group showed beneficial effects. [Conclusion] Thus, KICCE Early Childhood Health Improvement Program is conclusively proven to be effective for early-childhood physical development.