Purpose The current study investigated the effects of exercise information using social network service(SNS) to identify changes of physical activity and psychological variables among inactive college students. Methods Inactive college students(30 experimental group, 30 control group) were voluntarily participated in the 12-weeks intervention. During this period, the experimental group received exercise information through SNS. And all study participants’ physical activity, stages of physical activity, self-efficacy, motivation, and perceived benefits and barriers were measured at the pre, mid and post intervention. Frequency analysis, chi-square test, 2-way ANOVA RM were conducted to analyze data obtained in the study. All procedures were performed by using SPSS 23.0. Results The exercise information intervention using SNS during 12 weeks had a positive effect on the stages of physical activity of inactive college students, and there were statistically significant differences. In addition, physical activity, perceived benefits and barriers, self-efficacy, motivation positively improved after the intervention, but there were no statistically significant differences between experimental and control group. Conclusions The present study suggests that psychological strategies using various SNS programs have positive effects for inactive college students to increase physical activity and its related psychological variables.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of regular vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) level, aging- and lifestyle disease-related blood components in middle-aged women. Methods The participants were recruited from a total of 19 physically healthy people aged 50-59 years, and were randomly divided into vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise (VIAE, n = 10) and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (MIAE, n = 9) group. The participants were performed vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise three times a week for eight weeks, and body composition measurement, graded exercise test, blood collection were performed before and after. Results Mean exercise time was significantly longer in the MIAE group than in the VIAE group. The V̇O2max was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. Body weight, BMI, and body fat percentage were significantly lower than pre both groups. The BDNF concentration was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. The dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-s) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentration were significantly higher than pre both groups. The free fatty acid and triglyceride concentrations were significantly lower than pre both groups, and HDL-C concentrations were significantly higher than pre both groups. Conclusions Vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise not only increases maximal oxygen uptake and blood BDNF level in middle-aged women, but also induces positive changes in aging-related hormones and lifestyle-related blood variables.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of 16 weeks’ combined exercise training on insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, oxidative stress, leukocyte telomere length, body composition, and daily living fitness in elderly women with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). Methods Twenty-eight participants were randomly assigned into one of two groups, i.e., exercise training group (EX: n=14) and control group (CON: n=14). Subjects in EX participated in 3 sessions of 60 min-combined exercise for 16 weeks, whereas subjects in CON were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same period. The variables regarding insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, oxidative stress, leukocyte telomere length, body composition, and daily living fitness were measured and compared between two groups as well as between pre-post test utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. Results Main results were as follows: 1) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR tended to decrease in EX, whereas increased significantly in CON. 2) IL-6, TNF-α, hs-CRP decreased in EX, but the changes were not statistically significant. 3) MDA increased significantly and GPx decreased significantly in both EX and CON. 4) Leukocyte telomere length increased significantly in EX. 5) Fat-free mass increased in EX, whereas fat mass and percent body fat decreased significantly in EX. 6) Arm curl, chair stand, sit & reach, tandem test, 10m walking speed, and up & go improved significantly in EX. Conclusion It was concluded that the combined exercise for 16 weeks had a positive effect on improving insulin resistance, increasing leukocyte telomere length, as well as enhancing body composition and daily living fitness in elderly women with type 2 diabetes.
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to determine the influence of complex exercise and chromium supplement on healthe-related physical fitness, appetite regulating hormones, and diabetes risk factors in obese elementary school students. [Methods] The subjects were 32 obese elementary students over 25 kg/m2 to BMI, 8 complex exercise with high chromium supplement group (CE+HC), 8 complex exercise with low chromium supplement group (CE+LC), 8 complex exercise with placebo group (CE+PL), and 8 placebo group (PL). The subjects have performed the exercise program for 70 minutes a day and 3 times a week with aerobic and anaerobic exercise during 12 weeks. Also, low and high chromium supplement group took a peel 50 ug and 400 ug respectively at the same time and place. [Results] There were significant decreases in body fat to CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) and significant increase in muscle mass compared with CE+PL (p<.05). However, there were no significant differences in body weight, BMI, muscular strength, muscular endurance, and flexibility between groups. For appetite regulating hormones, there is a significant difference to ghrelin in CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) and there were significant differences to glucose and insulin significantly decreased in CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) in diabetes risk factors. [Conclusion] In conclusion, there were positive responses for body composition and diabetes risk factors for the twofold cases through complex exercise and high chromium supplement, but not for physical fitness and appetite regulating hormones.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of a 10-week aerobic exercise training on cardiovascular function, atherosclerosis, and vascular endothelial function in elderly women. Methods Twenty impaired fasting glucose (IFG) and normoglycemic elderly women volunteered to participate in the study. The participants in aerobic exercise training group (TR: n=9) completed 20-40 minutes of aerobic exercise program at 30-50% HRR for 3 times per week during 10 weeks. The participants in control group (CON: n=11) were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same intervention period. Results Main results of the study were as follows: 1) There were no significant main effect or interaction in body weight, fat-free mass, fat mass, percent body fat, and body mass index. 2) There were no significant main effect or interaction in heart rate, stroke volume, cardiac output, total peripheral resistance (TPR), systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial blood pressure, pulse pressure, and rate pressure product. However, interaction between group and test in TPR was close to statistically significant level (P =.054), and it tended to be decreased in TR group. 3) There was a significant main effect of test in high sensitivity C-reactive protein(hs-CRP), it tended to be decreased in TR group. There were no significant changes in total cholesterol(TC)/high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) ratio, triglyceride/HDL-C ratio, and low density lipoprotein-cholesterol/HDL-C ratio. 4) There were significant main effect of group, main effect of test, as well as interaction between group and test in % flow mediated dilation(FMD), and it increased significantly (P<.01) in TR group. Nitric oxide tended to be increased in TR group, even though it did not change significantly in both groups. Conclusions It was concluded that the 10-week aerobic exercise training would be beneficial for improvement of vascular endothelial function, resulting from the decrement of total peripheral resistance.
Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of 8 weeks of circuit exercise training on blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and metabolic syndrome risk factors in 40~50s male bus drivers. Methods Twenty-nine bus drivers were randomly assigned to one of two groups, i.e., circuit exercise training group (TR: n=14) and control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR participated in circuit exercise training 30-40 min per session, three sessions per week for 8 weeks, whereas subjects in CON were asked to maintain their normal life pattern for same intervention period. The variables regarding body composition, blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and number of metabolic syndrome risk factors were measured and compared between two groups as well as between pre- and post-test. Data were analyzed using repeated two-way ANOVA with post hoc test. Results Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, body mass index, and percent body fat decreased significantly in TR. 2) LDL-C decreased and HDL-C increased significantly in TR. 3) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in TR. 4) Regarding cardiovascular function, diastolic blood pressure and mean arterial pressure decreased significantly in both TR and CON. hs-CRP were not changed significantly; however, it tended to be decreased TR. 5) Number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased significantly in TR(2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76). Conclusions It was concluded that 8 weeks of circuit exercise training would be beneficial for improvement of blood lipid profiles and insulin resistance, resulting in preventing metabolic syndrome. In particular, it would be very clinically meaningful that number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased from 2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76 by the circuit exercise training.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 8 weeks of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation on a body composition, physical fitness, insulin resistance, liver function, blood pressure, and heart rate. Fifty-one elderly women were randomly assigned to aerobic training group (EX: n=12), resveratrol supplementation group (R: n=13), combined aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation group (EX+R: n=12), and control group (CON: n=14). The subjects in EX group exercised three sessions per week, 40 minutes per session for 8 weeks, the subjects in R group took 500 mg of resveratrol per day for 8 weeks, and the subjects in EX+R group received both treatments. The subjects in CON group were asked to maintain normal daily life pattern without any treatment for the same period of intervention. Body composition, physical fitness, insulin resistance, liver function, blood pressure, and heart rate were measured at pre- and post-test and the data were compared among groups and between tests by utilizing two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Physique and body composition did not change significantly in all groups. 2) Muscular endurance increased significantly in EX+R group, whereas the other physical fitness-related variables showed no significant changes in all groups. 3) Fasting glucose, fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, and HbA1c tended to be improved in EX+R group. 4) AST, ALT, and γ·GT showed no significant changes in all groups. 5) Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure increased significantly in CON group. Heart rate tended to be decreased in EX+R group and EX group. It was concluded that the 8 weeks of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation had positive effects on muscular endurance, insulin resistance, and blood pressure in T2DM elderly women. Research investigating the effects of a longer period of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation on the same variables would be warranted in the future.
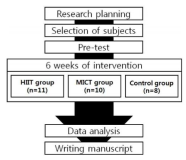
The primary purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 6 weeks of high-intensity intermittent training (HIIT) and moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) under relatively equal energy expenditure on body composition, aerobic capacity, cardiovascular function, insulin resistance, and blood lipid profiles in 20s overweight males. Twenty-nine males were randomized into one of the following groups: HIIT group (n=11), MICT group (n=10), and control group(n=8). Subjects in HIIT group completed 6 weeks of training for 25 min/sessions, three times/wk, and subjects in MICT group exercised for 33 min/session to equalize the energy expenditure with HIIT group. Subjects in control group were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same intervention period. Data were analyzed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post hoc test. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Body weight, BMI, fat mass, and WHR decreased significantly in HIIT group. 2) VO2max, VEmax, and time to exhaustion increased significantly in HIT group. 3) SBP decreased significantly in HIIT group and HRrest was tended to decrease in HIIT. 4) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR were tended to decrease in HIIT, but the changes failed to reach the statistically significant level. 5) HDL-C and TG were tended to improve in HIIT, but the changes failed to reach the statistically significant level. Results indicate that high intensity intermittent exercise training is more beneficial in aerobic capacity and cardiovascular function. It was also suggested that 6 weeks of aerobic exercise training in either high intensity intermittent or moderate intensity continuous was not sufficient enough to induce changes in body composition, insulin resistance and blood lipid profiles.


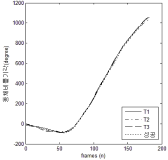
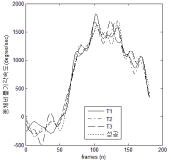
The research was a case study conducted in order to develop a new technique “YANG Hak Seon 2” for YHS athlete. A comparative kinematical three dimensional video analysis was performed with the use of high speed cameras. One successful trial and three of failure trials (T1: Falling backward while landing, T2: sitting reluctantly while landing, T3: Falling of sideways while landing). The result obtained from the study are as follows. Firstly when comparing the successful operation of the technique with failure trials, relatively higher landing angle was secured through increasing the thigh rotation and the body’s rotational velocity. Furthermore, despite increase in rotational velocity at twisting, stable landing was achieved through increasing the moment of inertia by spreading the left shoulder. Secondly, in case of failure trials while taking off the board, the thigh rotational angular velocity was comparatively less which ultimately affected the body position in the next phase of approach to the vault. Thus, due to the affected body position the athlete was not able to utilize the proper momentum of twist in positive direction Hence, it is considered that the velocity of center of mass might have also effected the operation not only the velocity while approaching the board.






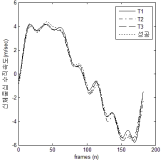


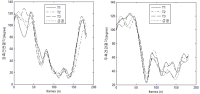
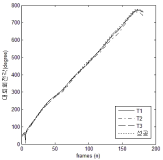



This study was designed to investigate the effects of increment of physical activity for 12 weeks through aerobic exercise training or change from own vehicle to public transportation for commuting on physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function in middle-aged men. Forty-four subjects, aged 30-50 yrs, were randomly assigned to either one of three groups, i.e., aerobic exercise training group (TR: n=14), change to public transportation group (PT: n=15), or control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR performed aerobic exercise for 30 min per sessions, three sessions per week, subjects in PT changed from their own vehicle to public transportation for commuting, and subjects in CON maintained their life patterns during the same intervention period. Physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function were measured at pre- and post-test, and the data were analyzed by repeated two-way ANOVA. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables related to physical fitness improved significantly in TR. Right grip strength, standing long jump, side step test, and sit-and-reach improved significantly in PT. 2) Although there were no significant changes in all variables related to insulin resistance, the variables tended to be improved in TR and PT. 3) TNF-α decreased significantly in TR and PT. IL-6 and CRP tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. 4) ALT decreased significantly in PT. AST and γ-GT tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. It was concluded that the 12 weeks of change to public transportation as well as aerobic exercise training would be beneficial for physical fitness and inflammatory markers. These interventions also would be possible to improve insulin resistance and liver function. The increment of physical activity through change from own vehicle to public transportation was found to be equally beneficial for health promotion compared to aerobic exercise.