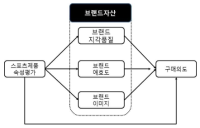
The purpose of this study was to examine competitiveness of sport product companies by brand origin in the Korean market by analyzing attribute evaluation of sport products, brand equity, and purchase intention and their causal relationship. Competitive sport brands were selected in global, Japanese, and Korean brands by a pilot survey. Then, this study selected a population participating in sports for all, elite sports, professional sports, and leisure sports and 498 effective questionnaires were secured. As a result, Korean consumers for sport products evaluated global sport brands in the highest level, Japanese sport brands in the moderate level, and Korean sport brands in the lowest level in the evaluation of attribute evaluation of sport products, brand equity, and purchase intention. Moreover, the evaluation of participating types in sports for all, elite sports, professional sports, and leisure sports showed the same result in the order of global, Japanese, and Korean sport brands. Global sport brands had a sequential causal relationship from attribute evaluation of sport products to brand equity and purchase intention and formed a consumption behavior model that attribute evaluation of sport products led to purchase intention. On the other hand, while Korean sport brands had a sequential causal relationship from attribute evaluation of sport products to brand equity and purchase intention, attribute evaluation of sport products did not lead to purchase intention. Finally, it was confirmed that global brands such as Nike and Adidas had a high market position and Korean sport consumers’ purchase behavior was determined based on information of product attributes and brand equity.

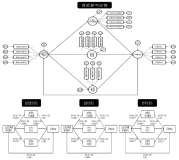
PURPOSE Sporting events constitute attractive platforms for providing participants with unique experiences. This study was aimed at investigating the structural relationships among perceived sporting event quality, image, trust, satisfaction, and loyalty of small-scale golf tournament participants. METHODS The questionnaire was structured in five dimensions: sporting event quality (4 sub-dimensions and 13 items), image (3 items), trust (3 items), satisfaction (3 items), and loyalty (4 items). A total of 217 amateur golfers from four Ecolian public golf clubs (Gwangsan, Jechon, Jeoungsun, and Younggwang) during the golf tournament participated in this study. Factor, reliability, validity, and structural equation model analyses were performed utilizing SPSS 24.0 and AMOS 24.0. RESULTS This study indicated that sporting event quality in a small-scale sporting event was the crucial factor of image, trust, and satisfaction, which, in turn, significantly impacted loyalty. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study contribute to theoretical understandings of sporting event quality factors that predict sport consumers’ image, trust, and satisfaction in the context of sports and leisure. Additionally, this study offers practical suggestions for administrators who develop marketing strategies for small-scale sporting events.
This study aims to find the alternative to increase the participation rates of physical activities and to analyze socio-demographic factors that determine sporting participation in Korea. We estimates the sporting participation model with ʼ2012 national sport participation survey in Korea' and binary logit analysis. The results are as follows: sporting participation is positively related to gender(male), age, education level, household income, health status, leisure time in weekday, proximity to public and private sports facilities. The most significant factors influencing the raising the participation rates of physical activities factors are age and proximity to sports facilities. Therefore, to make many people to participate in sports activities, we need to supply the public sports facilities that in proximity to house and the facilities needs to be taken into participant's age such as elderly group. Also, we make effort to improve the accessibility to sports facilities of poor and unhealthy people.
PURPOSE The United Nations (UN) has proposed 17 Sustainable Development Goals and has been extending its efforts to achieve them. Sport can be linked closely to the third goal, which is related to health and well-being. Therefore, this study aimed to explore and to analyze individual's changed sport activities during the COVID-19 pandemic, focusing on ways to achieve health and well-being related goals through sport. METHODS A qualitative research method was employed, and in-depth interview methods were used for data collection. For data analysis, categorization and itemization were used along with content analysis. RESULTS Looking at the derived results, in the context of an infectious disease such COVID-19, sport activity patterns have changed due to reasons such as stadiums or facilities, interpersonal reasons, fear, inconvenience, staying healthy, increase in leisure time, and individual preferences. CONCLUSIONS Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the indicators of health and well-being related SDGs are exhibiting a downward trend. At this point, it is necessary to find a way to achieve the goal through sport that can participate voluntarily for the purpose of pursuing pleasure.
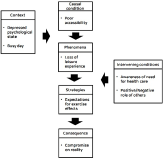
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the alienation and the overcoming process of the physical activity participation of people with Adventitious Visual Impairment(AVI) Methods 21 Adults with AVI were recruited and one on one semi-structured interview was conducted. Ground theory was used to analyze the data. Member check, peer debriefing was conducted to enhance the trustworthiness of this study. Results As a result, a total of 203 concepts were derived. This consisted of 21 subcategories and the common themes of the subcategories were categorized into nine categories. Specific results are as follows. First, the physical activity of people with AVI was directly affected by the sports facilities, physical activity programs, and professional instructor. This causal condition resulted in the loss of leisure experience in the context of the busy daily life and the depressed psychological state. Second, due to the perceived need of health care and the positive involvement of others, people with AVI came to expect the effect of exercise. Third, people with AVI participated in physical activity again as a tool to achieve the purpose of health improvement. This type of physical activity has a limitation that it can not guarantee the continuity of physical activity due to the limitation that it does not contain autonomy and interest of people with AVI. Conclusions Based on these results, the following suggestions were made. First, it is necessary to improve the environment for ensuring participation in physical activity of people with AVI. Moreover education and promotion of the effects and values of the exercise should be carried out for people with AVI and their guardians. Second, it is necessary to diversify physical activity types and reconstruct existing exercise programs.
