The purpose of present study is to develop the'Golf Mental Scale'that measures and assesses golf players' cognitive, emotional, behavioral response per golf mental factor experienced while competing in depth. In order to achieve this research purpose, Researcher collected raw data of golf mental question through literature review and interview with 8 members of Korean male national golf team and gathered questions per factor through Deductive-Inductive Content Analysis for the raw data. Then, Researcher conducted first and second questionnaire survey targeting 253 of elite & pro golf players and conducted Rasch Model and Confirmatory Factor Analysis for the data collected using SPSS 21.0, Winsteps Ver. 3.65 Program, AMOS 18. The conclusion reasoned out through these research process was as follows: First, golf players' psychological factor structure identified was revealed as Concentration, Self-confidence, Anxiety and Arousal control, Emotion control, Thought control. Total 37 questions were determined. Second, 5 point scale was revealed to be a good fit for Golf Mental Scale. Third, the result of Construct Validity Verification of CFA showed that Golf Mental Scale model was a good fit. Fourth, Reliability of Golf Mental Scale showed high level by recording Cronbach' α value .936. Fifth, Internal Consistency of Convergent Validity and Discriminant Validity was revealed to be satisfied. Eventually, Golf Mental Scale is expected to be used practically as a functional test tool that provides participant's response toward each situation-specific questions concretely and an objective evaluation of participant's golf mental ability per factor considering questions'level of difficulty and participants'characteristic.

PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the underlying dimensions of brand (professional sport team) authenticity and to develop a valid, reliable scale to measure these dimensions. METHODS A pool of 67 potential items was drawn through a literature review, content analysis, qualitative research (n=43), and an expert evaluation. The identified items were subjected to exploratory factor analysis (n=248) and confirmatory factor analysis (n=285). In addition, multiple regressions were conducted to examine the criterion validity of the scale. RESULTS The results showed that the brand authenticity scale for professional sport teams consists of 42 items representing 8 dimensions: continuity, originality, quality commitment, heritage, symbolism, credibility, stakeholder-related integrity, and consumer-related integrity. The study has proven evidences of internal consistency and convergent, discriminant, and criterion validity of the scale. CONCLUSIONS The findings suggest that the scale developed in this study offers a vital foundation to understand the structure of brand authenticity in the context of sport fans and its impact on sport consumer behavior.
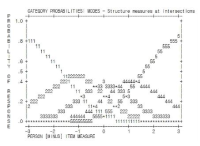
Purpose Recently, studies associated with the negative physical and mental effects of athletes’ pain have received extensive attention. This study confirmed the validity of the pain catastrophizing scale (PCS) developed in clinical settings and is widely used in the sports field, and examined their relationship between the perceived stress levels and fear of pain. Methods The pain catastrophizing consisted of 13 items of three factors which are Helplessness (6 items), Rumination(4 items), Magnification(3 items). To verify the validity, PSC was revised by following the recommended revision guideline procedures. To test the validation of pain catastrophizing, 206 adult athletes were recruited including the collegiate, professional, and national levels. The participants were instructed to complete questionnaires to assess the level of pain catastrophizing, perceived stress, and fear of pain. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to test the fit of measurement model was adopted to examine three higher-order three-factor measurement models. Results In results, confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the Korean version of the pain catastrophizing scale demonstrated a good model fit of measurement when removing one item with a significantly lower factor load as well as the reliability of the scale was reasonable. The pain catastrophizing had a meaningful positive direct relation with perceived stress level and fear of severe pain. In addition, construct validity and predictive validity of PCS showed valid. Conclusions Based on the results of this study, the Korean sports pain catastrophizing scale can be used to measure the subjective pain intensity of Korean athletes. In addition, it is expected to provide fundamental information for evaluating athletes’ post-injury rehabilitation processes.

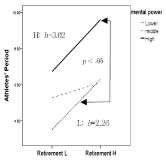
Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the differences between the three simple control models of Hayes (2012) and to determine whether there were Moderating Effects depending on the level of self-esteem, willpower and belief that are psychological factors in the relationship between athlete's retirement and Athlete's period. Methods To achieve this objective, a total of 259 retirees were collected from data on retirement and psychological factors. The data processing method presented the reliability and feasibility of the measuring instrument through technical statistics, frequency analysis, confirmation factor analysis, and reliability analysis. In addition, we conducted a hierarchical regression analysis using the PROCESS command statement in IBM 20 to examine the regulatory effects. Results The results of the study are as follows: The first was the significant model of Hayes (2012)'s three simple control models. It is up to the researcher to choose which model to choose, but when selecting the model, the justification of the variables must be established on the basis of theoretical basis, and the reliability of the variables must be put in to produce reliable and reasonable results. The second was to verify that the relationship between the retirement factor(10) and the Athlete's period has an adjustment effect based on self-esteem, willpower and belief. Among the psychological factors, the Moderating Effects was greatest in the influence of belief on the Athletes' period, and the more reasons for retirement, the longer the Athletes' period than the weaker. The combined mental strength of all three psychological factors combined shows that the combined effect of control also significantly increases the player's ability to survive by combining with the retirement factor. In particular, sportsmanship has resulted in a better mix of retirement factors than the sense of Self-esteem and will, resulting in a longer increase in the capacity. Conclusions Therefore, players who long for a player always keep their dreams of becoming a big star in mind, and ask me to always keep the belief in hope that I will enjoy my career for a long time.






PURPOSE This study aims to provide empirical foundational data for the development of a new profit model in Korean professional baseball. It does so by examining the influence of professional baseball NFT product attributes on customer perceptions of value, satisfaction, and purchase intention. METHODS Data were collected from consumers who have experience purchasing KBOLLECT. A total of 363 samples were collected for analysis. Surveys were utilized for data collection, encompassing 39 items that measured product characteristics, perceived value, satisfaction, purchase intention, and demographic information. Using the collected data, various statistical analyses were conducted including descriptive statistics, exploratory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis and multiple regression using SPSS version 21. The ensuing results from the correlation analysis and multiple regression analysis are as follows. RESULTS Product features, including aesthetics, symbolism, and scarcity, had a positive impact on consumer’s perceived emotional value. Moreover, product features, encompassing aesthetics, symbolism, scarcity, and creativity played a significant role in enhancing consumer’s perceived economic value. Furthermore, product attributes such as aesthetics, symbolism, and creativity positively contributed to consumer’s perceived social value. Similarly, product features comprising aesthetics, scarcity, creativity, and symbolism positively affected consumer’s perceived intellectual value. Additionally, the research revealed that product features related to aesthetics, symbolism, creativity, and scarcity were instrumental in bolstering consumer. Importantly, these very attributes, including aesthetics, symbolism, scarcity, and creativity, exhibited a positive influence on consumers’ purchase intentions. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, this study underscores the substantial impact of professional baseball NFT product characteristics on consumers’ perceptions, satisfaction, and purchase intentions. To maintain enduring relationships with consumers who engage with professional baseball NFT products, it is essential to fortify these product attributes and offer diverse services utilizing them.
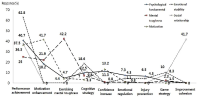
This study aimed to explore the psychological factors affecting sports performance and their purposes as perceived by adolescent athletes. Study data were collected by conducting an open-ended survey with 232 student athletes from adolescent athletes in S city. The collected data were categorized using content analysis, which was conducted twice to explore the psychological factors affecting sports performance and their purposes. From 537 answers, 30 performance-affecting psychological factors—including confidence, endurance, effort/dedication, optimal tension, and social support—were identified, and they were classified into five categories: psychological fundamental, mental toughness, motivation, emotional stability, and social relationships. From 588 answers, the purposes of the psychological factors were identified, including performance achievement, motivation enhancement, demonstrating mental toughness, cognitive strategy, confidence increase, emotional regulation, injury prevention, game strategy, and reinforcement cohesion. These performance-affecting psychological factors and their purposes may serve as a reference to understand how secondary school students perceive the relationships among various psychological factors and the relationship between the psychological factors and performance. This study is expected to inform goal setting and content organization in psychological skills training.

PURPOSE This study aimed to subdivide the market based on the general characteristics and consumer psychology of sports brand collaboration consumers and provide basic data for efficient collaboration marketing activities of sports companies. METHODS The subjects of this study were high school, college, and graduate students from high schools and universities in the Seoul and Gyeonggi area. Of the 600 copies of the questionnaire distributed, 475 were selected and analyzed in the final sample. Regarding the statistical method for this study, the PASW 18.0 statistical program was used for the frequency, exploratory factor, reliability, hierarchical cluster, K-means clustering, and cross analyses, as well as the one-way ANOVA. RESULTS The results of the analysis suggested five subdivided clusters with according marketing strategies: “external male,” “practical male,” “twenties design preferred female,” “low-interest women,” and “high consumption optional attributes” groups.
PURPOSE This study aimed to verify the influence of imposter syndrome tendencies in athletes on their achievement goal orientation, and regulatory focus. METHODS Data collected from 413 athletes through surveys were analyzed using SPSS version 27.0 and AMOS version 21.0 to assess reliability and validity, conduct independent sample t-tests, perform correlation analysis, and conduct multiple regression analyses. RESULTS The findings revealed significant sex-based differences in imposter syndrome tendencies, achievement goal orientation, and regulatory focus. Moreover, significant correlations were observed between sub-factors of imposter syndrome, achievement goal orientation, and regulatory focus. Imposter syndrome tendencies had varying effects on achievement goal orientation, with the discount factor significantly influencing approach orientation, the fake factor significantly affecting avoidance orientation, and fear factors significantly impacting self-avoidance. Additionally, imposter syndrome tendencies influenced regulatory focus, as the discount factor significantly affected both promotion focus and prevention focus, while fake and fear factors significantly influenced prevention focus. CONCLUSIONS This study underscores the importance of athletes' imposter syndrome tendencies as significant contributors to psychological variables related to motivation, including achievement goal orientation and regulatory focus.

This study was to verify the structure of efficacy related to performance perceived by short-track athletes when playing a match. Therefore, 50 players answered open questionnaires and 200 players participated in construct validity verification, a total of 250 players of short-track members of national, business and university team were sampled during the research phase. The data was analyzed through the study procedures. The results were as follows: First, efficacy structure of players during the match were categorized into three groups as game managing strategy(including course management, race control, match management and selective attention ability), psychological control ability(including positive imagery, match competition, competitive spirit, ability to handle hardship, anxiety control, and patience), and physical usage of ability(including physique, endurance, and quickness). Second, the result of the first construct validity verification through exploratory factor analysis showed 7 factors in 29 items as game management, course management, psychological control, physical use, coping with hardship, speed control and psychological stability. Finally, as a result of confirmatory factor analysis, short-track self-efficacy showed the 5 factor in 15 items except for coping with hardship and psychological stability.


Purpose This study has been conducted to explore the factors that ignite the mental toughness of Taekwondo players and to compare report ratios concerning the explored factors between training and competition. Methods An open-ended questionnaire conducted 123 Taekwondo players offered raw data that stemmed the from 379 training and 369 competition situation. The raw data was categorized by an inductive approach, and the report ratios of both general and specific domain mental toughness in training and competition were compared. Results The results of this categorization were as follows. First, the mental toughness ignition factors of Taekwondo players are commonly categorized as willing to goal, external pressure, reward expectation, challenge, and social support. Second, factors were prioritized into reward expectation, challenge, willing to goal, social support, and external pressure. Third, willing to goal and external pressure were often reported in training, while reward expectation and challenge were more often reported in a competition. Social support showed similar ratios in both settings. Conclusion This study is expected to offer interesting results in the context of the ignition of mental toughness, while being utilized as a fundamental database for the development of mental social support strategies the help Taekwondo players ignite their mental toughness in competition.


