Purpose: This study was to verify the relationship between coaching behavior(autonomy/controlling behavior), self-regulation motivation and performance. Method: 356 athletes (from middle to work and professional team) in individual and team sport completed coaching behavior scale developed by this researchers assessing autonomy and controlling coaching behavior perceived by players, Korea Basic Pyshoclogical Needs Scale (KBPNS) assessing basic psychological needs, Behavioral Regulation in Sport Questionnaire (BRSQ) assessing sports motivation level based on self-determination theory, and sport performance score. To estimate the relationship between coaching behavior, self-regulation motivation and performance, this study employed the structure equation modeling analysis. Results: The relationship between psychological needs, regulation motivation and performance showed that autonomy coaching behavior tend to reinforce competence and autonomy of player. These variables have a positive effect on more inner regulation motivation. Moreover, the intrinsic motivation through stimulation experience was a key factor leading to a positive performance by improving the performance strategy and skill of athletes. Conclusion: These results are meaningful as an empirical evidence that relationship between motivation and performance can be changed according to the type of coaching behavior, and that autonomous coaching behavior play an important role in maximizing the performance of player that provided theoretically form.

PURPOSE This study developed and applied a group counseling program for university athletes’ career development. METHODS Following Kim’s (2002) procedure for developing group counseling, this program was based on social cognitive career theory and finalized by using two preliminary studies and expert validation evaluation. Afterward, Taekwondo players from University A in Chungcheongnam-do and University B in Seoul were assigned to experimental and control groups, respectively, and then a nonequivalent control group design was conducted. The experimental group was provided with a six-step career group counseling program, including introduction, understanding personal and distal context, enhancing self-efficacy and outcome expectations, developing career interest, deciding on a career, and closing, for ten 45-minute sessions, twice a week. RESULTS First, results of two-way repeated measures ANOVA showed statistically significant changes in career decision self-efficacy (self-appraisal, occupational information, goal selection, planning, and problem-solving) and career attitude maturity (determination, certainty, and independence). Second, analysis of the outcome assessment by session showed the following positive results: consideration about the future after sports retirement, self-understanding, identification of jobs that fit aptitude, improvement of self-efficacy, having a positive mindset when switching careers, confidence in one’s preferred career, exploration into solutions to career barriers, understanding of preferred career, setting specific career goals, and deeper understanding of careers. CONCLUSIONS In sum, these findings indicate that the career counseling program had a positive effect on university athletes’ career development. We hope this study will serve as a catalyst to expand the discussion on retirement from sports and career development.
PURPOSE This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the effectiveness of exercise programs in improving physical fitness among middle-aged adults in Korea. METHODS A literature search was conducted using KCI-registered databases on DBpia, RISS, and KISS up to September 21, 2023. The review followed the PICOSD framework (population: middle-aged adults; intervention: exercise program; comparison: did not participate in exercise program; outcome: physical fitness; study design: randomized controlled trials). Two researchers independently evaluated bias using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2). The data was synthesized using the CMA 3.0 program, applying a random effects model to estimate the overall effect size using Hedges’g. RESULTS Out of 914 screened documents, 15 studies were selected, comprising 405 participants. The overall effect size for improving physical fitness was significant (g=0.994, 95% CI: 0.712–1.276). Sub-analysis indicated significant improvements in various components, including muscle strength (g=1.295, 95% CI: 0.909-1.682), muscular endurance (g=0.972, 95% CI: 0.637-1.308), cardiorespiratory endurance (g=1.092, 95% CI: 0.453–1.731), flexibility (g=0.883, 95% CI: 0.555–1.210), muscle power (g=1.421, 95% CI: 0.656– 2.186), and agility (g=1.854, 95% CI: 0.347–3.361) compared to the control group. An additional analysis focusing solely on women revealed a slight increase in effect size, although the order of effect sizes remained consistent across fitness components. CONCLUSIONS This meta-analysis confirms the effectiveness of exercise programs in enhancing physical fitness in middle-aged adults. The systematic review also highlights key considerations for designing exercise programs for this demographic. Future studies should aim to minimize bias and enhance the quality of reporting to ensure more robust results.
PURPOSE This study analyzed the difference in lower extremity joint angle and shock absorption patterns at the point of maximum ground reaction force during single-leg drop landing with or without anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR). METHODS Forty adult males were recruited for this study, with 19 in the ACLR group (age: 20.52±1.43years, height: 179.26±5.18cm, weight: 74.91±6.29kg) and 21 in the control group (age: 21.42±1.61years, height: 174.97±6.83cm, weight: 69.27±7.56kg). Participants performed single-leg landings on a 30cm tall box. An independent sample t-test was used to analyze the difference in kinetics variables at the point of maximum ground reaction force upon landing, with significance set at p=0.05. RESULTS The lower limb joint angle showed significant differences in hip flexion, hip abduction, knee flexion, and knee valgus (p<0.05) between groups. There was no significant difference between the groups in terms of the results of kinetics variables during single-leg landing (maximum ground reaction force, lower extremity stiffness, and shock absorption time). CONCLUSIONS The ACLR group showed a clear difference in kinematics compared to the control group, but no significant difference in kinetic results was found. The two groups compensated for the same impact with different movements, though movements in the ACLR group may increase the risk of ACL re-injury. Those with ACLR should strive to reduce the risk of re-injury by training to use correct movements.
PURPOSE This study investigates the effectiveness of biomechanics information on intermediate golfers driver swing learning. It analyzes changes in center of pressure (COP) patterns, GRF Direction Inclination, driver performance, and learners psychological responses to determine the learning effects. METHODS Subjects were 32 right-handed male golfers (handicap 15-23) who had no difficulty in performing the golf driver swing (Full swing). Four groups were selected, BF (Biomechanics Feedback group), BVC (Biomechanics Verbal Cue group), CB (Combination group), and CT (Control group), and assigned randomly. Driver swing learning showed results after 6 weeks,and a transfer test was conducted 1 week after the completion of the learning. RESULTS Analysis of COP patterns and GRF Direction Inclination indicated changes in the BF, BVC, and CB groups. Furthermore, analysis of driver distance (m), club head speed (km/h), and ball spin rate (rpm) revealed that during the 6-week acquisition phase, all three groups (excluding the control group) showed improvements in driver distance, club head speed, and ball spin rate. However, there were no statistically significant differences among the groups. In contrast, the transfer test showed statistically significant differences among the groups, with the CB group exhibiting the highest driver distance. Learners' psychological responses during the learning process were trust, understanding, and satisfaction. The understanding factor was relatively higher in the CB and BVC groups compared to the BF group. CONCLUSIONS In summary, biomechanics information (BI) was effective in improving driver performance, and changesappeared in the COP pattern and GRF Direction Inclination, indicating a change in movement. Therefore, BI can be fully utilized for athletes or high-level advanced players and for motor learning for intermediate-level students.However, BI can only improve learning effects by strengthening learners' “understanding” when visual feedback forms and verbal cues are provided together.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the applicability of proprioceptive-dependent training as an effective physical training method by analyzing the effects of proprioceptive-dependent training on the accuracy of perceived and actual distance as well as the correlation between the changes in the two variables. METHODS Thirty-six male college students took part in the experiment. Participants were beginners with no previous experience in golf or less than five times of experience. They were randomly assigned to one of three groups; proprioceptive-dependent training, visual-dependent training, and control, maintaining the same sample size per group. The experiment was carried out in the order of pre-test, practice section, and post-test. In the pre-test, putting was tested to assess the accuracy of perceptual and actual distance in the 1-15m distance in a random order using a digital putting analyzer. In the practice section, proprioceptive-dependent and visual-dependent training groups practiced a total of 90 putting, six times per distance with the eyes closed or open. The post-test was the same as the pre-test. The accuracy of perceived and actual distance and the correlation between the changes in the two variables were analyzed using the calculated absolute errors. RESULTS The results of this study showed that there was no difference between groups in pre-test. In contrast, in post-test, the absolute error was significantly decreased in the order of proprioceptive-dependent training, visual-dependent training, and control group in the three distance conditions. Besides, for the proprioceptive-dependent training group and visual-dependent training group, there was a significant positive correlation between the changes in the accuracy of perceived and actual distance. CONCLUSIONS These results provide insight into the applicability of proprioceptive-dependent training for enhancing motor performance by showing the effects of proprioceptive-dependent training on perceived distance, actual distance, and the correlation between the two variables.
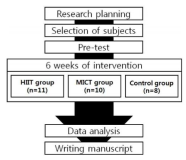
The primary purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 6 weeks of high-intensity intermittent training (HIIT) and moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) under relatively equal energy expenditure on body composition, aerobic capacity, cardiovascular function, insulin resistance, and blood lipid profiles in 20s overweight males. Twenty-nine males were randomized into one of the following groups: HIIT group (n=11), MICT group (n=10), and control group(n=8). Subjects in HIIT group completed 6 weeks of training for 25 min/sessions, three times/wk, and subjects in MICT group exercised for 33 min/session to equalize the energy expenditure with HIIT group. Subjects in control group were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same intervention period. Data were analyzed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post hoc test. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Body weight, BMI, fat mass, and WHR decreased significantly in HIIT group. 2) VO2max, VEmax, and time to exhaustion increased significantly in HIT group. 3) SBP decreased significantly in HIIT group and HRrest was tended to decrease in HIIT. 4) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR were tended to decrease in HIIT, but the changes failed to reach the statistically significant level. 5) HDL-C and TG were tended to improve in HIIT, but the changes failed to reach the statistically significant level. Results indicate that high intensity intermittent exercise training is more beneficial in aerobic capacity and cardiovascular function. It was also suggested that 6 weeks of aerobic exercise training in either high intensity intermittent or moderate intensity continuous was not sufficient enough to induce changes in body composition, insulin resistance and blood lipid profiles.


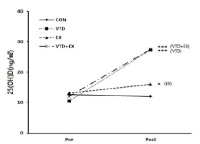
The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of 12-weeks of vitamin D supplementation and circuit training on skeletal muscle mass in elderly women with type 2 diabetes mellitus and vitamin D deficiency. Forty eight elderly women with type-2 diabetes mellitus and vitamin D deficiency were randomly assigned to control(n=10), vitamin D supplement(n=11), exercise(n=12), and vitamin D supplement+exercise(n=15) groups. Dependent variables were measured before and after the 12-week interventions. Major outcomes included body composition, fasting glucose, insulin, and 25(OH)D concentration. ASM(apeendicular skeletal muscle mass), SMI(skeletal muscle mass), and HOMA-IR (homeostasis model for insulin resistance) were calculated. Women assigned to the vitamin D supplement consumed 1,200 IU of vitamin D orally per week for 12 weeks. Women assigned to the exercise intervention performed a circuit training at an intensity of 60%~80% of HRmax with a frequency of 3 days per week for 12 weeks. Compared to control group, all groups had significant loss of body weight and increases in serum 25(OH)D after the 12-week intervention. ASM and SMI increased significantly in only vitamin D+exercise group. Regardless of treatments, no significant group differences were found in changed scores of fasting glucose, insulin, and HOMA-IR. In conclusion, vitamin D + exercise would improve the loss of ASM and SMI compared with vitamin D or exercise alone.

PURPOSE This study assessed Taekwondo’s impact on functional fitness and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in older women from South Korean multicultural families. METHODS Through purposive sampling, 16 participants were divided into an experimental group that underwent a 12-week Taekwondo training program and a control group without this intervention. RESULTS Pre- and post-intervention assessments showed that the Taekwondo group experienced significant improvements in both functional fitness and HRQoL. These findings suggest that Taekwondo could be an effective physical activity for enhancing the well-being of older women in multicultural families, advocating for inclusion of culturally sensitive physical activities in health promotion programs targeting this demographic. CONCLUSIONS This study contributes to the growing body of evidence supporting physical activity’s benefits for elderly populations, particularly in multicultural family dynamics.
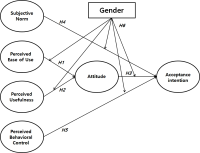
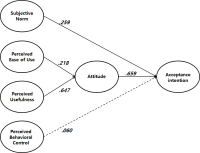
Purpose The current study was aimed to examine acceptance intention of sports wearable smart device using the Technology Acceptance Model and Theory of Planned Behavior. Methods Data were drawn from 357 consumers who had experience purchasing sports products. Data were analyzed through frequency analysis, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling using SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 program. Results First, perceived ease of use had a positive effect on attitude. Second, perceived usefulness had a positive effect on attitude. Third, attitude had a positive effect on acceptance intention. Fourth, subjective norm had a positive effect on acceptance intention. Fifth, perceived behavioral control did not affect acceptance intention. Sixth, differences of path coefficients between attitude and acceptance intention, subjective norm and acceptance intention were significant according to gender. Conclusion The significance of this research is to provide the basis of positioning strategy for domestic companies of sports wearable smart device.