The primary purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 6 weeks of high-intensity intermittent training (HIIT) and moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) under relatively equal energy expenditure on body composition, aerobic capacity, cardiovascular function, insulin resistance, and blood lipid profiles in 20s overweight males. Twenty-nine males were randomized into one of the following groups: HIIT group (n=11), MICT group (n=10), and control group(n=8). Subjects in HIIT group completed 6 weeks of training for 25 min/sessions, three times/wk, and subjects in MICT group exercised for 33 min/session to equalize the energy expenditure with HIIT group. Subjects in control group were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same intervention period. Data were analyzed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post hoc test. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Body weight, BMI, fat mass, and WHR decreased significantly in HIIT group. 2) VO2max, VEmax, and time to exhaustion increased significantly in HIT group. 3) SBP decreased significantly in HIIT group and HRrest was tended to decrease in HIIT. 4) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR were tended to decrease in HIIT, but the changes failed to reach the statistically significant level. 5) HDL-C and TG were tended to improve in HIIT, but the changes failed to reach the statistically significant level. Results indicate that high intensity intermittent exercise training is more beneficial in aerobic capacity and cardiovascular function. It was also suggested that 6 weeks of aerobic exercise training in either high intensity intermittent or moderate intensity continuous was not sufficient enough to induce changes in body composition, insulin resistance and blood lipid profiles.

PURPOSE This study aimed to explore and analyze research impact of Korean ’Kinesiology’ studies, especially in the aspects of international research impact gauged by the citation counts from Scopus bibliometric database. This study contributes to relevant literature in that it is the first endeavour to evaluate the pattern about how the entire Korean ’Kinesiology’ articles have been cited in international articles. METHODS TTwo types of sample articles were collected in this paper. Firstly, 19,867 target articles published in 23 KCI-accredited Korean ’Kinesiology’ related journals from 2001 to 2015. For the Korean target articles, secondly, international citing articles that took advantage of target articles as references were collected from Elsevier’s Scopus database separately. RESULTS As a result, just 5% of the target articles were cited at least once for five years after publication. The topics of top cited research topics include ‘exercise’, ‘physical activity,’ ‘Alzheimer’s disease, ‘ ’body composition’ and ‘insulin resistance’. Besides, the Korean 'Kinesiology’ articles were the most influential to articles about ‘Medicine,’ ‘Health Professions,’ ‘Multidisciplinary,’ ‘Social Sciences,’ and ‘Nursing’. CONCLUSIONS This study showed that one Korean ’Kinesiology’ article was cited 0.09 times on an average in international Scopus-indexed articles. Considering that the average number of citations in domestic articles is 5.6 times, the international citations of Korean ’Kinesiology’ research still have much room for growth. However, this study confirmed that the scope of the international impact is not limited to a few countries, but is spreading to various countries, and its impact has been growing in recent years.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to analyze the type of and interest in home training video contents using the YouTube platform. METHODS Web crawling was performed using Python and a total of 3,937 sets ofvideo information (title, content, number of views, upload date) were obtained, 3,155 of which were finally selected for the study material. Overlapping and unrelated content were excluded. The data of text underwent 3 stages of preprocessing, the TF and TF-IDF of the keywords were calculated to identify the main keywords, and the LDA algorithm was applied in the topic modeling to successfully identify the types. In order to understand the level of interest by type, the number of views was subdivided into the percentage of the assigned type. RESULTS First, the types of home training videos were classified into bare whole body exercise for aerobic and muscular power strengthening, Pilates exercise for core and upper body strengthening, upper body exercise using tools, lower body line exercise, posture correction and upper body stretching exercise for pain relief, hip-up exercise, dance and tabata exercise for diet, diet and lower body correction stretching exercise for diet, and bare body exercise for core and lower body strengthening. Second, it was found that the proportion and interest were high in the contents of bare whole body exercise for aerobic and muscular power strengthening, dance and tabata exercise for diet, diet and lower body correction stretching exercise for diet. CONCLUSIONS The findings of this study may provide baseline data about the development of the active online home training videos in the market.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate whether foam roller, preexhaustion, and static stretching had any effect on isometric muscular endurance of the finger flexors and climbing performance in sport climbers. METHODS Nine sport climbers who were able to perform at a climbing difficulty of 5.11d, were included in this study. Warm-up exercise consisted of myofascial release, pre-exhaustion exercises, and static stretching. Grip and back strengths were measured for muscular strength, and isometric muscular endurance of the finger flexors was measured as the time spent hanging on each hold according to the angle of the elbow joint. Repeated measures of ANOVA were performed to confirm the difference in treatment, and a significant difference between groups was confirmed by contrast test. RESULTS Myofascial release, pre-exhaustion, and static stretching before climbing did not affect muscle strength. However, the static stretching exercise significantly decreased isometric muscle endurance of the finger flexor at 90° open hold, and the pre-exhaustion exercise significantly decreased the hanging time at 180° crimp and slope grips. There was no effect on climbing performance according to the type of warm-up exercise. CONCLUSIONS Our findings suggested that various warm-up exercises did not directly affect muscle strength, muscular endurance, and climbing performance in sport climbers. Thus, we suggest that future research on complex warm-up exercises considering climbing postures should be conducted.
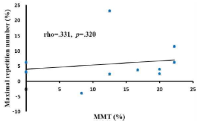
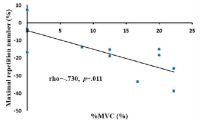
The purpose of this study was to determine whether maximum repetition number can be used as an indicator of strength imbalance. Eleven healthy, resistance-trained males were tested for one repetition maximum (1-RM) the chest-press exercise, and than manual muscle testing (MMT), two-arm at 80% of 1-RM and one-arm at 40% of 1-RM in the pectoralis major were measured for the maximum voluntary contraction (%MVC) and maximum number of repetitions during the chest press exercise. Exercise velocity was constantly 4 seconds (concentric: 2-s, eccentric: 2-s) per repetition. The changes in %MVC were significantly higher in non-dominant limb (NDL) compared with dominant limb (DL) pectoralis major during two-arm chest press (p < 0.01) and one-arm chest press exercise (p < 0.05). In contrast, the changes in MMT (p < 0.05) and maximum repetition number (p < 0.01) were significantly higher in DL compared with NDL during one-arm chest press exercise. There was no correlation between maximum repetition number and MMT (rho = 0.331, p = 0.320). However, maximum repetition number was significantly negative correlated with %MVC in two-arm chest press (rho = -0.730, p = 0.011). It is possible that maximum repetition number can be used as an indicator of strength imbalance.


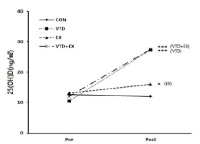
The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of 12-weeks of vitamin D supplementation and circuit training on skeletal muscle mass in elderly women with type 2 diabetes mellitus and vitamin D deficiency. Forty eight elderly women with type-2 diabetes mellitus and vitamin D deficiency were randomly assigned to control(n=10), vitamin D supplement(n=11), exercise(n=12), and vitamin D supplement+exercise(n=15) groups. Dependent variables were measured before and after the 12-week interventions. Major outcomes included body composition, fasting glucose, insulin, and 25(OH)D concentration. ASM(apeendicular skeletal muscle mass), SMI(skeletal muscle mass), and HOMA-IR (homeostasis model for insulin resistance) were calculated. Women assigned to the vitamin D supplement consumed 1,200 IU of vitamin D orally per week for 12 weeks. Women assigned to the exercise intervention performed a circuit training at an intensity of 60%~80% of HRmax with a frequency of 3 days per week for 12 weeks. Compared to control group, all groups had significant loss of body weight and increases in serum 25(OH)D after the 12-week intervention. ASM and SMI increased significantly in only vitamin D+exercise group. Regardless of treatments, no significant group differences were found in changed scores of fasting glucose, insulin, and HOMA-IR. In conclusion, vitamin D + exercise would improve the loss of ASM and SMI compared with vitamin D or exercise alone.

Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of 8 weeks of circuit exercise training on blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and metabolic syndrome risk factors in 40~50s male bus drivers. Methods Twenty-nine bus drivers were randomly assigned to one of two groups, i.e., circuit exercise training group (TR: n=14) and control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR participated in circuit exercise training 30-40 min per session, three sessions per week for 8 weeks, whereas subjects in CON were asked to maintain their normal life pattern for same intervention period. The variables regarding body composition, blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and number of metabolic syndrome risk factors were measured and compared between two groups as well as between pre- and post-test. Data were analyzed using repeated two-way ANOVA with post hoc test. Results Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, body mass index, and percent body fat decreased significantly in TR. 2) LDL-C decreased and HDL-C increased significantly in TR. 3) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in TR. 4) Regarding cardiovascular function, diastolic blood pressure and mean arterial pressure decreased significantly in both TR and CON. hs-CRP were not changed significantly; however, it tended to be decreased TR. 5) Number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased significantly in TR(2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76). Conclusions It was concluded that 8 weeks of circuit exercise training would be beneficial for improvement of blood lipid profiles and insulin resistance, resulting in preventing metabolic syndrome. In particular, it would be very clinically meaningful that number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased from 2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76 by the circuit exercise training.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the factors for setting proper training duration of frequency that can guarantee the student athletes' right to study and performance, and to derive the ranks of setting proper training duration of frequency of student athletes by school level. Consequently, to provide basic data for the development of training guidelines for the growth period of Korean student athletes. Methods Delphi and Analytic Hierarchical Process(AHP) techniques were used. The Delphi survey was conducted in three phases, and collected data through Delphi survey were computed by SPSS win ver. 22.0 and Excel, using the mean, standard deviation, median, and coefficient of variation. Using the AHP technique, we classified the factors for setting proper training duration of frequency derived through Delphi survey, and calculated the importance by using Microsoft Excel 2010. Conclusion First, elementary students should be guaranteed regular class participation, have basic after school training, and be provided with adequate rest so that they do not lose interest in the exercise. Second, middle school students are required to decide whether to continue exercise based on their ability to exercise and abundant experience. Therefore, when abandoning the exercise, students should be able to faithfully carry out their academic performance. Third, high school students are directly related to college entrance and employment, so they have to concentrate on performance rather than on academic performance.
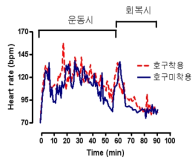
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of wearing of safeguard devices on various blood ions (i.e., Na+, K+, Ca2+) concentrations, gas parameters (PO2, PCO2, hematocrit [Hct], hemoglobin [Hb], Saturated [Sat] O2), and energy substrates (i.e., glucose, free fatty acid [FFA], lactate) concentrations during Kumdo training. Research scope extended to examine the heart rate changes during each exercise sessions. In order to achieve the research goal, 10 male elite Kumdo players, who play for G city in Gyeongsangbuk-do, were participated, and their mean maximum oxygen uptake level was 51.2(±6.1)mL· kg-1min-1. All subjects undertook Kumdo training sessions twice, which carefully pre-planned and consisted of routinely carrying out exercise program. Training period for each session was 80 min long including 10 min each for warm-up and warm-down period, but the conditions with wearing body protection devices were different following either with wearing complete set of safeguard devices or without wearing any safeguard devices except general training cloth. Heart rate was measured by every minute interval. K+ and Ca2+ showed interaction effect between the conditions with wearing safeguard devices and conditions with time of Kumdo training. Hct and Hb level significantly increased after 60 min Kumdo exercise regardless of wearing safeguard devices. Kumdo training induced dropping of blood pH independently with wearing safeguard device conditions, however the values and/or concentrations of PO2, Na+, glucose, lactate, Sat O2were significantly increased. Heart rate was maintained marginally higher values throughout exercise period when safeguard devices were worn. Based on these results, it was concluded that wearing the safeguard devices could possibly be causing a physiological metabolic changes, and this may be drawn by increased body fluid loss and energy expenditure. Further study should be undertaken to examine the effects of wearing safeguard devices on hitting intensity and hormone secretion and concentrations, that closely associated with body fluid and ion balance during Kumdo exercise and/or training.

PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of different resistance training structures on basic physical fitness, 1-repetition maximum (1RM), and isokinetic shoulder and knee muscle functions in male college students. METHODS Forty college students were divided into four groups: control group (CG, n=10), compound set training group (CSG, n=10), pyramid set training group (PSG, n=10), and superset training group (SSG, n=10). Excluding CG, each group performed a different resistance exercise method at an intensity of 60~80% 1RM for 60~90 min, three times a week for eight weeks. To compare the effects of resistance training structures, we confirmed body composition, basic physical fitness, 1RM, as well as isokinetic shoulder and knee functions. RESULTS Results indicated that the PSG exhibited the most significant improvement in relative peak torque in isokinetic shoulder and knee testing compared to the other groups. Additionally, all exercise groups positively affected back strength, 40m sprint, and 1RM compared to the CG, although no significant differences were observed among exercise groups. CONCLUSIONS The findings suggest scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of pyramidal resistance training in improving isokinetic shoulder and knee muscle functions in male college students.