PURPOSE For student-athletes to be able to successfully dedicate themselves to training and competition, the following key factors play an important role: The coach, team climate, and individual motivational characteristics. To test this hypothesis, the structural relationships between having a perceived autonomy support, a caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment were analyzed. METHODS Participants were 297 high school athletes registered with the Korea Olympic Committee (203 males, 94 females, Mage=17.88 years). Data were collected using sports climate questionnaires for autonomy support, caring climate scale, basic psychological needs scale, and sport commitment measurement. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling. RESULTS The model’s fitness was indicated by x2/df=2.797 (x2=106.288, df=38), CFI=.977, TLI=.967, RMSEA=.078 (90% CI=.061, .096). Examining the various path coefficients revealed that coach autonomy support had a positive effect on the athlete’s caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment. The caring climate had a significant effect on basic psychological needs, but did not have a statistically significant effect on sport commitment. Finally, basic psychological needs had a positive effect on sport commitment. CONCLUSIONS Coach autonomy support fosters a caring climate, and athletes who are able to perceive this are able to dedicate themselves to their sport since their basic physiological needs are met. Therefore, coaches should use appropriate coaching strategies to enhance athletes' autonomy and foster a caring climate, as both are essential factors for meeting athletes' psychological needs and promoting sport commitment.
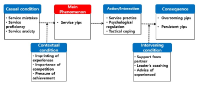
Purpose This study aims to investigate the experience of service yips in badminton players in depth through using grounded theory method. Methods We collected data from in-depth interviews with 14 participants in total, consisting of badminton players who experienced service yips, their doubles partners and coaches. The collected raw data were analyzed base on derive transcription, coding and paradigm models through grounded theory method. Results First, as a result, 59 concepts, 31 subcategories and 15 categories in regard to badminton service yips were deduced from open coding. Second, in axial coding, it was structured in a paradigm model by categories such as service yips, service mistakes, service proficiency, service anxiety, the imprinting experiences, the importance competition, the pressure of achievement, service practice, psychological control, tactical handling, support from partners, leaders’ coaching, advice from experienced ones, overcoming yips and persistent yips. Third, selective coding resulted in ‘Badminton service yips’ as the core category of this study. ‘Badminton service yips’ is a chronic performance impairment associated with badminton players making severe errors in swing motion on a service not intended by them that it is due to physiological or psychological symptoms such as hand tremors, overall body stiffness, arms stiffness, overstress, overanxiety, and concern over service mistakes. Conclusions We expect our study can be a theoretical foundation for understanding and explanation of ‘Badminton service yips’ and a useful reference for badminton players suffering from psychological difficulties caused by their service yips. The findings in this study should be considered for the development of potential strategies for overcoming the badminton service yips.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the optimal model for winning medal on vault event of men's gymnastics. Specifically, decision tree analysis was used to explore, first, for the optimal conditions for qualifying top 8th player that have high possibility into final round, and second, for the optimal model for obtaining the medal of the vault event. Methods Data were collected for five official competitions (Olympics, Asian games, and International championship, etc.) organized by the Federation of International Gymnastics (FIG) from 2013 to 2016. In this study, the data of 626 vault players were collected. Also all of these players performed 921 vault skills for qualifying round or final round. Five predictor variables for estimating for qualifying into the final round and for obtaining the medal of the vault event were selected; nationality, difficulty score, acting score, additional penalty score, final score. Results The results is as follows. Overall, it was confirmed that the optimal model for entering into the final round was the difficulty score of vault event. The optimal model for entering into the final round estimates 81.2% when condition would be the 5.6 or higher of difficulty score and 8.6 or higher of the acting score. The optimal model for winning medals was 86.7%, which means that when condition would be the 6.0 or higher of difficulty score and no additional penalty score. Conclusions This models can be used as a basic data for establishing a strategy for medal acquisition of vault event of gymnastics.



PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the occurrence of sports injuries among badminton national team candidates during training camps and to identify appropriate measures for players to effectively manage and respond to such injuries in the future. METHODS The participants consisted of 123 individuals who took part in national team candidate training camps for badminton in 2022 and 2023. Record sheets were utilized to document the athletes' thoughts and opinions related to exercise injuries during the training period. RESULTS Badminton national team candidates experienced exercise-related injuries in various areas, including the ankles, thighs, knees, hips, shoulders, and back. Female players had a higher incidence of lower body injuries compared to their male counterparts. Through interviews with players about these injuries, individualized approaches involving appropriate rest and training adjustments were found to be necessary; additionally, educating the players about rehabilitation strategies for exercise injuries is essential. CONCLUSIONS When conducting recreational training activities, it is important to avoid fostering excessive competitive attitudes. Additionally, if potential risks are present within the exercise environment, it is crucial to assess and address these with the utmost caution.