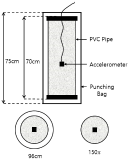
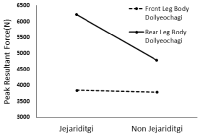
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the comparison of peak resultant force in taekwondo body dollyeochagi in accordance with Jejariditgi existence and the position of kicking leg. Methods Twelve students who majored taekwondo participated in this experiment. They have a forth dan(degree) black belt in taekwondo. The peak resultant force was measured 12 times(2 jejariditgi existence × 2 position of kicking leg × 3 times). Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures was used to analyze the data. Results There was significant difference in interaction effect of peak resultant force in taekwondo in accordance with jejariditgi existence and the position of kicking leg. And there was significant difference in main effect of peak resultant force in taekwondo in accordance with jejariditgi existence and the position kicking leg. Higher peak resultant force was shown in body dollyeochagi with jeariditgi as compared with non jejariditgi. And higher peak resultant force was shown in rear kicking leg as compared with front kicking leg. Conclusions The results show that jejariditgi is a factor affecting the peak resultant force. Comparison of peak resultant force in taekwondo body dollyeochagi in accordance with jejariditgi existence and the position of kicking leg will provide strategies for coaches and athletes to perform improved taekwondo dollyeochagi.


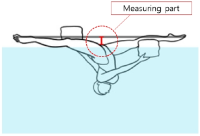
Purpose The purpose of this study is to compare the physical fitness levels among artistic swimmers in artistic swimmer national team trials. It is aimed to strengthen the physical fitness evaluation criteria of the national team and construct a physical fitness evaluation item suitable for an artistic swimming event. Methods A total of twenty two female elite artistic swimmers participated in this national team selection trial. Measurement list was performed body composition (Height, Weight, Body fat(%), Skeletal muscle mass, Lean body mass, BMI, Shoulder width, Arm span), Basic physical fitness (Push-up, Sit-up, Chin-up, Endurance of trunk backward extension and Sargent jump), Flexibility (Trunk backward extension, Shoulder flexibility, Frog position and Underwater split R, L) and Swimming test (100 m freestyle, 400 m freestyle). Data were analyzed by Independent t-test using SPSS Statistics ver 25.0. Results Age and skeletal muscle mass were significant difference between the two groups (p<.05). Also, 400 m swimming test was significantly different (p<.001). However, there were no significant differences in basic physical fitness and flexibility. Conclusions These results suggest that selected athletes are excellent not only in acting but also in physical fitness. Based on these results, it is necessary to construct a physical fitness items for the preliminary artistic swimming and to classify the physical fitness evaluation criteria according to the characteristics of the artistic swimmers.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the effect of a power-specific weight training program in order to improve the muscle strength of Korean national team’s freestyle wrestlers. Methods Participants were 13 male athletes in the national freestyle wrestling team. The period of the program was 6 weeks. Muscle strength, muscular endurance, muscle power, flexibility, agility, cardiorespiratory endurance, anaerobic power and isokinetic muscle function were measured. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 23.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). Paired t-test was conducted for comparison between pre-test and post-test score. Results There were significant difference and tendency in the leg isokinetic power and trunk isokinetic flexion strength. However, there was no significant difference in muscle strength, muscular endurance, muscle power, flexibility, agility and cardiorespiratory endurance. Conclusion The 6-week program focusing on the power-specific weight training indicated a significant difference not in every variable but in isokinetic muscle power, speed power and core strength. It is suggested that the training program was applied to the athletes less continuously and not in the long term because of frequent international games abroad and the need for losing weight. Consequently, a year-long training program with personalized methods should be developed to bring about more significant outcomes.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the lower extremity muscles activity during forward side step by soccer field ground types. Methods Fifteen elite high school soccer players participated in this study. Muscle activation patterns were recorded at 2000 Hz during forward side step task. Surface EMG of the tibialis anterior(TA), soleus(SOL), medial gastrocnemius(MG), lateral gastrocnemius(LG), peroneus brevis(PB) muscle was recorded, and the root mean square of the EMG was normalized, using a maximum voluntary isometric contraction(%MVIC). One-way repeated ANOVA was used for comparison among three soccer field ground types(natural grass, artificial turf, hard ground). Results Artificial turf displayed greater soleus and peroneus brevis activities compare to natural grass during forward side step task. Conclusions The relationship between increased soleus and peroneus brevis activation and greater incidence of injury in artificial turf versus natural grass requires further study. Soccer players routinely training on artificial turf for prolonged periods should be carefully monitored.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the differences in physique and physical fitness according to maturity between primary and middle school baseball players. Methods Participants were 112 elite youth baseball players (49 primary school; 63 middle school). Skeletal age estimated maturity. Physique (height, arm span, thigh volume), body composition (weight, muscle mass and body fat), physical fitness (strength, power, agility, flexibility, coordination, anaerobic power and aerobic power) were measured. An independent sample t-test was used to conduct verify the difference between physique and physical fitness according to maturity. Results The results of analyzing physical and physical fitness according to maturity showed that there was a significant difference (p<.05) between the early maturation group and on-time group in primary school baseball players, body fat percentage, muscle mass percentage, sit-up, anaerobic power and reaction time. There was a significant difference between the early maturation group and the on-time group in the middle school baseball players, weight (p<.05), thigh volume (p<.05), fat mass (p<.05), muscle strength (p<.01), power (p<.05) and coordination (p<.05). Conclusions In conclusion, the maturity of a growing baseball player may be influenced by the performance, so maturity status should be considered when judging the performance of a growing baseball player, especially a middle school baseball player.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to explore the trend of K league exodus and its factors. Methods Qualitative case study was conducted by selecting 9 footballers and 7 their agents as the participants who have migrated from South Korea to China and the Middle East. Results The factors of migration were categorized as three push and pull factors such as economy (individual income and club's profit), policy (employment for foreign and military service) and environment (markets in home and abroad). To understand sport migration in the economic factor, there should be the environmental condition (overseas market) to pay high salaries and transfer fee to individuals and their clubs, and at the same time, the domestic market should be relatively poor environment. In addition, this study overcame limitations of economic and environmental factors by classifying Asian quota system and military service into political factor, and found the specificity (local context) of K league. Conclusions In conclusion, this study can be regarded as the first empirical work on sport labor migration in Korea and valuable as basic data of follow-up studies.

[Purpose] This study aimed to investigate the structural relationships among event quality, spectators‘ destination image, country image, and behavioral intention in the international cycle competition, Tour de Korea 2017. [Methods] The questionnaire was structured in four dimensions: event quality (three sub-dimensions and twelve items), destination image (three items), country image (three items), and behavioral intention (four items). A total of 292 spectators from six hosting cities (Yeosu, Gunsan, Muju, Yeongju, Cheongju, and Seoul) during the event participated in this study. Factor analysis, reliability, validity, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling analysis were conducted utilizing SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0. [Results] This study indicated that event quality in an international sporting event was found to be the significant factor of spectators’ destination image and country image, which, in turn, significantly influenced the spectators’ intention to revisit to the place of the event and/or the event itself. [Conclusions] The findings of the present study contribute to theoretical understandings of event quality that predicts spectators’ behavioral intention and destination image in a global sporting event. Practically, this study also provides some important suggestions for practitioners who plan marketing strategies for international sporting events.

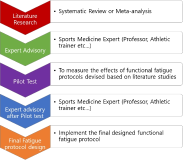
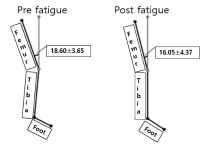
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of a functional fatigue protocol on lower extremity dynamic and static postural control. Methods A total of 20 physically active collegiate students participated in this study (ten males, ten females; age 22.5±2.7 years; mass 67.0±13.0 kg; height 168.0±8.9 cm). A unilateral stance with eyes closed for 10 seconds was performed to test static postural control using a balance force plate and single-leg drop landing on 30cm box was performed as a dynamic postural control test and captured using VICON motion analysis system. Results The results of this study showed an average heart rate of 176.3 beats/minute, an 18 rating on the perceived exertion scale, significant differences in blood lactate, and a static postural control deficit after fatigue as compared with before fatigue(p<.05). Dynamic postural control after fatigue changed landing strategy in the form of stiff landing. Knee flexion was decreased at initial contact and at peak vertical ground reaction force, also, both decreased valgus and internal rotation of knee joint. Conclusions This protocol may use for enhancing fatigue-endurance training as well as for inducing fatigue. Further, to ascertain a landing strategy, it is recommended to increase landing height to clearly observe changes in landing strategy.







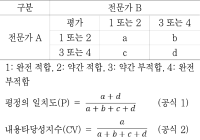
Purpose Common content knowledge(CCK) is composed of rules, techniques, and tactics. Such knowledge is a requirement for effective teaching of physical education (PE). There are, however, few validated tests of CCK. Thus, the purpose of this study was to develop a CCK test of soccer and evaluate the validity and reliability of the test using Rasch modeling (Rasch, 1980). Methods We developed thirty item common content knowledge test for soccer. Then, we used Rasch modeling to evaluate the validity and reliability of a test of soccer. Pre-service teachers (N=92) majoring in physical education and non-PE major (N=111) participated in this study. Results Thirty questions demonstrated good item-model fit. Moderately high internal consistency for person-ability and high internal consistency for item-difficulty are reported. Both Infit and Outfit statistics showed a good fit between the data and the Rasch model. Conclusions The analysis provides evidence to support the validity and reliability of this instrument as a CCK test of soccer. Limitations of the study were discussed and suggestions were provided to improve the test.

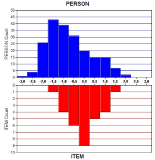
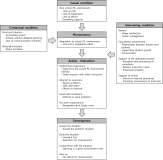
Purpose The purpose of this study is to explore the Instructor’s adaptation process of school P.E. environment in middle school sports club and to develop substantive level theory. Methods For this purpose, 17 sports instructors who had worked for more than 3 years at the middle school in Seoul were selected as research participants. The method of this study is the Grounded theory(Strauss & Corbin, 1990). Results The results of this study are as follows. First, as a result of open coding, the instructor's adaptation process of the school P.E. environment was organized into 104 concepts, 30 sub-categories, and 15 categories. Second, as a result of axial coding, a paradigm model for the adaptation process of the school P.E. environment was formed. Third, as a result of the selective coding, created the storyline of the adaptation process and made the core category, ‘instructor's adaptation process of the school P.E. environment in middle school’. Four types of adaptation process such as 'Acceptance type', 'Effort type', 'Compromising type' and 'Abandoning type' are derived through the formalization applied to the hypothesis of the core category. Conclusions Based on these results, the developed substantive level theory was evaluated and summarized.