
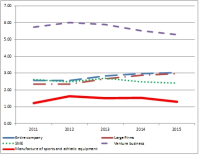
Purpose In recent years, competition among companies has become more and more important to maximize the competitiveness of companies by improving their productivity through technological innovation. Increasing competitiveness through technological innovation is becoming an essential requirement for survival of companies. In order for companies to innovate, it is necessary to spend R&D investment and the government is strengthening various policy supports to do this. Athletic equipment industry classified as manufacturing industry in sports industry. In this study, considering the fact that manufacturing industry occupies a large part of Korea's R&D investment, we compared R&D intensities with athletic equipment industry and other industries. We also examined whether R&D investment has affected firm performance. Methods The data used in the analysis were extracted from KIS-DATA with KSIC codes of companies classified as sports and athletic goods manufacturing industry in the 9th Korean Standard Industrial Classification of National Statistical Office. The analysis period is five years from 2011 to 2015 to look at the current status. Looking at the number of companies extracted by year, it was 42 in 2011, 45 in 2012, 46 in 2013, 48 in 2014, and 39 in 2015. Results Research showed that the intensity of R&D of athletic equipment industry was 1.22% in 2011, 1.63% in 2012, 1.51% in 2013, 1.53% in 2014 and 1.30% in 2015. This was lower than the manufacturing industry, which was a category of athletic equipment industry, and lower than that of similar small and medium sized enterprises. The correlation between R&D intensities and the sales growth rate of firms showed a positive correlation in 2011 and 2015, but the correlation is not strong. Conclusion R&D investment in athletic equipment industry was not actively taking place, and R&D investment did not have a significant effect on the performance of the company.


This study aimed to analyze the patterns of service return and the 3rd stroke in relation to the winning and losing points in Badminton men's doubles matches. Especially the comparison of the patterns between rally point and service server game systems was made. Video records of 12 top elite teams were analyzed. As a result, there were significant differences in the total stroke patterns between the rally point system and the server game, and there was a higher offensive stroke tendency. After classification of situations with ‘after the service trial’ and ‘after the service return’, there were high number of winning ratio and offensive stroke in the after the service situations. There were no significant difference in the winning/losing points and winning ratio when the types of 3rd shot attempts were analyzed. I case of the win and lose in service return, there was a significant difference in the server game while not in the rally point system. Offensive stroke ratio in the server’s return categories and the service return strokes’ categories, and was no difference in shots after the return of service in the server team. From the investigation of offensive stroke ratio and winning ratio, there was a high ratio in the rally point system game but no difference in the server game. When aggressive service return took place, rally point system had higher winning ratio, but the server game system did not display such characteristic. Based on these results, recommendations of service anticipation and aggressive plays for Korean Men's doubles game have been suggested.


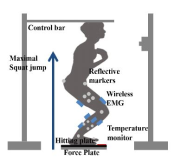
The human foot is only part that directly contact between the body and the external environment, and is ideally positioned to provide sensory information to the Central Nervous System (CNS) during static and dynamic tasks. Through cutaneous mechanoreceptors located in the dermis, the foot is able to recognize touch pressure and vibration stimuli, which provide important feedback information used for the fine coordination of movements. The purpose of this study is to quantitatively examine the effect of changing the foot cutaneous sensory by temperature stimulus on maximal performance and muscle activation using wavelet technique. Sixteen healthy subjects volunteered to participate in this study (Male: Age 21.4±2.4years; Height 174.7±5.3츠; Weight 70.6±5.2kg; Female: Age 20.5±0.6years; Height 163.2±3.1cm; Weight 55.6±4.8kg). Sensory pressure thresholds were determined for the plantar surface of the foot using monofilament. Kinematic, kinetic and EMG data which relative to maximal performance were collected while squat jumping in each temperature condition(cool 12-15℃ normal 28-30℃ hot 45-48℃). Maximal jump height was significant higher in normal condition. Vertical GRF in normal condition showed higher peak value the other conditions. And then EMG signal were significant different between temperature conditions during maximal performance. By changed sensory feedback on temperature, one can alter maximal performance and muscle activation pattern. Cutaneous feedback is important in performance and neuromuscular control, and temperature changes significantly influence on lower extremity during maximal squat jump performance of healthy subjects.





This study has been conducted to develop methods and techniques for the analysis of data related to baseball performance using the winning and losing games. The purposes of the study were to examine differences of athlete performance for semi playoff, playoff, and Korean professional baseball series and to develop optimal forecasting model for the short term series. Data used in the study were taken from Korean professional baseball association. Three data sets including semi play off from 1982 to 2012, play off from 1989 to 2012, and Korean series from 1982 to 2012 were used. To compare athlete performance by winning and losing games for short-term series t-test was applied. This study created new parameters by weighted value through the equalization process to calculate skill related variables as a predicted variable. Three predicted models such as discriminant, binary logistic regression and artificial neural network models were developed to clarify the suggested models. The results showed that the number of significant parameters increased as the series continued. In particular, a variable related to error was added as a significant variable at the Korean Series. A third base hit in the play-off and a second base hit were also added as significant parameters in the play-off and the Korean series, respectively. In addition, W/L a major variables affecting a given technology area, the pitching PO, PO, the inertia, KS, the pitching, respectively. An artificial neural network model was finally selected with the highest accuracy and lowest input of estimated parameters in the semi play-off. In the play-off, artificial neural network model that applied technical area parameters by specialist criteria had better accuracy rate than two others. In the Korean series, artificial neural network model that created estimation parameters by applying all parameters was chosen as the final model. When the overall accuracy level of semi-play off, play off and Korean series was figured out, binary logistic regression model had higher accuracy of classification than discriminant model, but artificial neural network model had the higher accuracy of classification than binary logistic regression model.


PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the effects of motion analysis and image training using self-modeling with visual cues on the skill performance, imagery, and sports confidence of adolescent female soccer players. METHODS The participants were elite soccer players from two girls’ high school soccer teams divided into an experimental group (D girls’ high school, n=16) and a control group (I girls’ high school, n=13). The experimental group underwent motion analysis and image training when performing penalty kicks, short kicks, and long kicks using self-modeling with visual cues, while the control group underwent training using self-modeling videos without visual cues. Before and after the training, the evaluation score was calculated according to kick performance, and the imagery and sports confidence factors were measured. For the statistical analysis of all collected data, descriptive statistics, the Friedman test, the Mann-Whitney U test, and two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance were used. RESULTS First, on the motion analysis using self-modeling with visual cues, the experimental group’s penalty kick and short kick scores were improved and differed significantly, but no significant change was noted in long kick score. Second, as a result of image training using self-modeling with visual cues, all visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability factors of the experimental group improved except for the auditory factor, and the interaction effect was confirmed. In addition, the stated sports confidence of the experimental group was improved and the interaction effect confirmed. CONCLUSIONS The analysis of kick motion using self-modeling with visual cues was effective for the penalty kicks and short kicks of adolescent female soccer players. Moreover, this study confirmed that the analysis of kick motion improved the visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability sub-factors of imagery and significantly affected the players’ stated sports confidence.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the difference and consistency of kinematic variables for each athlete by selecting the official records of the world's elite female triple jumpers to evaluate the performance level. Methods Three athletes who won the prizes at the World Championships Daegu 2011 Women's Triple Jump were selected as the study subjects, and only the successful trials were used for analysis. Pearson's correlation analysis was conducted with the kinematic variables in the hop, step, and jump phase, respectively. Also, kinematic variables with statistically significant correlations between braking time and pushing time and related variables were described separately. The duty factor and support factor for the hop, step, and jump of support phases were calculated. Results The successful trials rate were 66.7% for Olha, 50% for Olga, and 83.3% for Caterine. In the last three stride distances of the approach run, Olha and Caterine had a “medium-long-short” pattern and Olga had a “long-short-medium” pattern. There was no difference in the duty factor value between hop and jump phases in the ‘hop-dominate’ technique type, but there was a difference in the jump phase in the ‘balance’ technique type, and the duty factor value in the step of both technique types was greater than that of hop and jump phases. As for the percentage of the support factor, Olha and Caterine had a characteristic that the percentage of braking time in step and jump phases was opposite. On the other hand, Olga had the same percentage for the hop and step phase, and a smaller percentage for the jump phase. Conclusion To increase the accuracy of the board touch-down, maintain a certain last stride(1SL) depending on the technique type. This consistency of the approach run increases reduces distance loss on the take-off board and increases the successful rate of each trial. The duty factor can judge both the performance level and the technique type of triple jump, and the support factor is a variable that can classify the technique types of hop, step, and jump phases. If both the relative time required for the triple jump and the variability of the support time(braking and pushing) for each phase are constant, the difference in records by trial will be small.

Purpose This study is a phenomenological research which tries to describe the subjective experience and to analyze multi-layered meanings, and it finds out the men's training experience and meaning. The purpose of this study is to investigate why the men do Yoga and what the subjective meaning of Yoga experience, and the study examines critically whether Yoga experience especially focused on women is against gender performance and dominant body discourse. Methods For the study, 6 middle & young-old aged men who do Yoga more than 6 months every week are selected as participants. Results The meaning of Yoga for middle & young-old aged men in their lives is as follows. First, it is hard for men to experience Yoga because of social and cultural background. Finding Yoga class which takes men's membership is difficult. Second, middle & young-old aged men's physical feature(interest in their health and disease) and personal background(women friendly daily life) become specific motivation to overcome the barrier to do Yoga. Third, Yoga is 'alterative training', not a training. Yoga is considered as a training which replaces the feature of training called men's sports previously. Fourth, Yoga has a meaning of 'healing' to have our own time. Fifth, Yoga is changed by itself in Yoga culture which is focused on women even though middle & young-old aged men do Yoga for a long time. Sixth, middle & young-old aged men realize that the feature of Yoga is not 'for only women', and they thought it is 'neutral training that men can do too.' Conclusion Consequently, the reason why middle & young-old aged men do Yoga is started from the motivation regarding physical characteristics and personal background, and the main purpose is to cure and to heal our bodies and mind. For them, Yoga means 'alternative training to fit their bodies' and 'their own time'. Moreover, old male adult's training experience and meaning are against gender performance in that it cause a crack in stereotyped gender sports area, but it is notable that there is no intention to resist the dominant gender body discourse.

Purpose: This study was to verify the relationship between coaching behavior(autonomy/controlling behavior), self-regulation motivation and performance. Method: 356 athletes (from middle to work and professional team) in individual and team sport completed coaching behavior scale developed by this researchers assessing autonomy and controlling coaching behavior perceived by players, Korea Basic Pyshoclogical Needs Scale (KBPNS) assessing basic psychological needs, Behavioral Regulation in Sport Questionnaire (BRSQ) assessing sports motivation level based on self-determination theory, and sport performance score. To estimate the relationship between coaching behavior, self-regulation motivation and performance, this study employed the structure equation modeling analysis. Results: The relationship between psychological needs, regulation motivation and performance showed that autonomy coaching behavior tend to reinforce competence and autonomy of player. These variables have a positive effect on more inner regulation motivation. Moreover, the intrinsic motivation through stimulation experience was a key factor leading to a positive performance by improving the performance strategy and skill of athletes. Conclusion: These results are meaningful as an empirical evidence that relationship between motivation and performance can be changed according to the type of coaching behavior, and that autonomous coaching behavior play an important role in maximizing the performance of player that provided theoretically form.

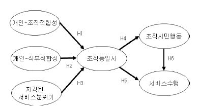
The purpose of this study is to empirically inquire into the relationship between a commercial sports center employee's person-environment fit(person-organization fit., person-job fit) & perceived service climate and organizational identification, organizational citizenship behavior and service performance through structural equation model analysis. For this purpose, this study conducted a questionnaire survey of 207 employees working at 12 commercial sports center(a facility in possession of more than 3 events). In an effort to verify the proposed structural model, this study used SPSSWIN Ver. 21.0 and AMOS 18.0. The research results are as follows: First, it was found that person-organization fit had an influence on organizational identification. Second, person-job fit was found to have an influence on organizational identification. Third perceived service climate was found not to have a positive influence on organizational identification. Fourth, organizational identification was found not to have a positive influence on organizational citizenship behavior, either. Fifth, organization identification was also found not to have a positive influence on service performance. Sixth, organizational citizen's action was found to have a positive influence on service performance.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the official world records of UIPM in the last 3 years to find out the relationship between the score characteristics of fencing, swimming, equestrian, and laser-run events in the final rankings and to analyze the relative importance of each event. Methods For 3 years, from 2017 to 2019, a total of the data were collected, the final rankings, fencing conversion scores, swimming conversion scores, equestrian scores, and laser-run conversion scores for all male and female athletes who participated in the UIPM Level 1 World Cup and World Championships(1,197 finals and 2,173 qualifiers). The Multiple regression analysis was used to establish the relationship between the response(subjective) variable and the conversion score of the four explanatory(independent) variables. Results The results were compared by qualification (n = 2173) and final (n = 1197) by dividing into male (n = 1179) and female (n = 1591), and the fencing score was qualifications (male β= -.691, female β= -.533) and the finals (male β= -.632, female β= -.632), it showed the greatest influence in all. On the other hand, the swim score showed the lowest impact on both qualifications (male β=-. 021, female β=-.196) and finals (male β=-. 087, female β=-. 207). The fencing event plays a major role in passing the qualifiers and is a big variable for good performance in the finals. On the other hand, in the case of swimming scores, both men and women had the lowest impact on the final ranking, and there is a limit to the final performance of swimming scores in both qualifiers. Conclusion In conclusion, it is necessary to analyze and systemize the fencing skills of the world’s best athletes, including Korean athletes, to improve the Korean fencing athletes' performance, and through such scientific analysis, a system that enables fast and flexible responses to the upcoming Olympic. Additionally, even though the importance of all sports should be levelled due to the characteristics of modern pentathlon, relative importance is biased toward fencing and swimming events are neglected. Therefore, it is deemed necessary to conduct a follow-up study on whether the scoring system in modern pentathlon consists of a scoring system that supports the records of each event and the upper and lower scoring system.




