PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to explore violence in the Korean sports world and examine the reality of sports violence in the past and present by reflecting the voices of the field and academia through an in-depth analysis. METHODS First, through a systematic literature analysis, the essential problems of sports violence that have been discussed in academia were explored. Next, based on this, perception was explored by applying a multi-case study method to an in-depth analysis of the opinions of experts in academia and the field. Finally, by deriving the research results and discussing them, implications for this study were provided. RESULTS First, the essential problem of sports ethics was the change in sports ethics perception that was different from the sports ethics problem caused by the diversification of victoryism. Second, the essential problems of sports violence were ethics and sports ethics in society with different standards, and the unaltered perception and culture of sports ethics. Third, the problems and causes of sports violence were institutional changes and practical limitations of physical violence, control of the possibility of violence, insensitive verbal violence, cyber violence as a new form violence due to changes in the times, and rationalizations of bystanders. CONCLUSIONS This study is expected to serve as a catalyst for the field and academia by exploring the phenomenon of sports violence in more depth through the problems of violence by type and its causes according to the changing times.
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the associations between accelerometer-measured physical activity and both cardiometabolic disease risk factors and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. METHODS We performed a retrospective cohort study with age-sex matched case-control using data from the 2014-2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, which was administered to South Korean adults (n=320). Individuals were categorized into quartiles based on accelerometer-measured moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA). Demographic and physical characteristics, waist circumference, visceral adiposity index, blood pressure, lipid profiles, and TG/HDL-C were observed. The associations between MVPA status and cardiometabolic disease risk factors as well as metabolic syndrome were determined using multiple logistic regression. RESULTS For the waist circumference, SBP, DBP, MBP, visceral adiposity, triglyceride, and a surrogate estimate of insulin resistance, the Q1 and Q2 groups had higher means compared with the Q3 and Q4 groups. HDL-C was higher in the Q3 and Q4 groups compared to the Q1 and Q2 groups. Odds ratios for cardiometabolic disease risk factors and metabolic syndrome decreased in a curvilinear manner with the increasing quartile of MVPA. CONCLUSIONS Adults with higher MVPA participation were strongly associated with cardiometabolic disease risk factors and metabolic syndrome.
Purpose This study is to investigate the human rights violations of Semi-professional team athletes. Methods The subjects of the survey were 4,069 people in total of 56 sports athletes from teams. than, 1,251 athletes who agreed to provide personal information (635 males and 616 females) were sampled. The survey tool consisted of a total of 76 questions asking about violence, sexual violence, and general characteristics of semi-professional athletes. Results were frequency analysis, cross-analysis, and multiple response analysis. Results Despite being an adult athlete in the semi-professional Team's Workplace Sports Team, life controls were severe in the sports team and human rights violations, such as verbal and physical violence, were widely observed, and sexual harassment and sexual violence were not small. The main perpetrators were the leaders and senior players, and the venue was the training ground. The players were in an environment where they were forced to respond passively for fear of hierarchical, collective atmosphere and personal disadvantages, and were blind spots for labor rights in terms of contracts and treatment. Conclusion To human rights violations of semi-professional athletes as the structural problems of the Korean sports. It is necessary to strengthen human rights education by the workplace movement department and conduct regular human rights surveys, and legal institutionalization to establish a disciplinary information system for perpetrators. In addition, by enacting guidelines for human rights in the sports world, a system should be prepared so that the victims can actively express their intentions.
Purpose The purpose of this studied to improve athletes’ performance through sports psychological skills training and counseling of a male canoe player in high school. Methods One male high school athlete in J area was interviewed for sports psychological skills training and counseling, and interviewed athletes and coaches diagnosed the potential psychological problems of athletes. Through this process, the athlete gained the ability to control anxiety about the game and strengthened the attention-focused ability to increase his confidence and set a goal for improving concentration. For effective training, sports psychological counselors, athletes, and coaches met once a week to create a routine. and participated in direct training on a boat with the coach every week. Sports psychological skills, anxiety about competition, and self-management of athletes were measured before and after to confirm the effectiveness of training of athletes' psychological skills. Results As a result, athletes' psychological skills and anxiety decreased, their confidence increased, and their concentration, which was diagnosed as an urgent problem of athletes, improved. Conclusions psychological skills of athletes, psychological shortcomings of players were reinforced, thus enhancing the athletes' performance. This suggests the effectiveness and necessity of training in sports psychological skills. It is hoped that continued support will serve as an opportunity to diagnose potential psychological problems of student athletes and apply them to training to contribute to improving their performance.
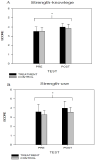
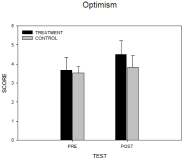
Purpose The goal of this study was to investigate the application effect of strength-based positive psychology intervention to elite archers. Methods Total of 20 elite archers participated in this study. Treatment group consisted of 10 elite archers participated in the strength-based positive psychology intervention for 8 weeks. Each individual responded the questionnaires in pre- and post-treatment sessions. Data were analyzed by repeated-measure ANOVA. Furthermore, archers participated in the program responded to in-depth interviews. Results According to the results, participants in strength-based positive psychology intervention showed that significantly increased strength knowledge, strength use, and optimism in the post–treatment compared to the pre-treatment session while control group did not show significant changes. In addition, archers perceived that there were positive effect on thinking ·coping and their self-confidence and self-esteem enhanced after participating the program. Conclusion The results of this study suggested that strength-based positive psychology intervention has positive impact on athlete’s wellbeing and perception of individuals strength and can be applicable to different sports field.

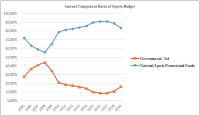
Purpose This study focused on analyzing the policies regarding operation of Sportstoto, a sole legal sports betting business in Korea. Methods In order to fulfill the research goal, literature review on reports, articles, and statistics from Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism, National Gambling Control Commission, Korean Sports Promotion Foundation, and other precedent studies was conducted. Results Currently Sportstoto fails to maintain its competitiveness due to inconvenient betting process, lack of product diversification, and low payout rate, resulting in the growth of illegal sports gambling. In addition, governmental aid for sports budget has diminished consistently, while at the same time the revenue cap regulation for betting industry restrains the development of Sportstoto and disturbs the gathering of sports budget, which appears to be a policy contradiction. Moreover, there are no specific guidelines for the expenditure of Sportstoto revenue which function as a budget. Conclusions This study suggests three ideas to overcome these problems. First is the alleviation of regulation in non-monetary area so that Sportstoto can improve its competitiveness against illegal sports gambling. Second is the clear establishment of policy regarding sports budget, either to foster Sportstoto as a fundraising business, or to enlarge governmental allocation for the budget. Lastly, institutional management must be provided for the expenditure of Sportstoto revenue as to follow government’s sports policies.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of vibration therapy on the functional, imaging, and mechanical properties in elbow flexor after a single bout eccentric exercise. Methods Twenty-three untrained adults male participated in this study [CON(control)= 11, VT(vibration)= 12]. Volunteers performed 5-set of 6 maximal (90˚/s) eccentric contractions of the non-dominant elbow flexor on a isokinetic dynamometer. Vibration was applied using a side alternating vibratory platform (12 Hz frequency, 4 mm amplitude) with 3-set of 60 sec during 3-day after eccentric exercise. Results The VT group showed a reduction in exercised-induced muscle damage(EIMD) symptoms in the form of attenuating muscle swelling and echo intensity (P<.05) compared with the CON, mechanical properties were improvement (P<.05) compared with the CON. However, muscle soreness, range of motion and maximal voluntary isometric contraction were not significant (P<.05). Conclusion As currently practiced, vibration therapy after eccentric exercise may reduce EIMD by improving quality of the muscle, suggesting that this therapy is an effective strategy for EIMD.

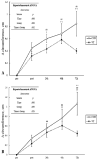
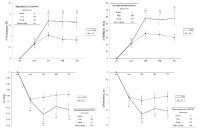
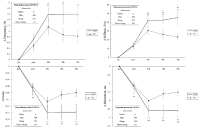
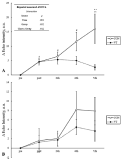

Purpose In general, motor imagery and action observation have been distinguished from each other. Recently, several studies demonstrated that combined approach to motor imagery and action observation can be more effective in motor learning. The present study examined the effects of observation learning combined motor imagery and action observation during acquisition basketball shooting skills. Methods We divided with control group, action observation group and observation learning group combined mental image and action observation in the three middle school. Action observation group provided the action observation program, and observation learning group was performed observation learning combined mental image and action observation training. All groups were perform basic basketball skills. Experimental intervention was performed for 10 weeks, and data analysis was performed 3 groups × 2 time repeated ANOVA. Results The results indicated that all group were improve after intervention, and subjects who participated in combined mental image and action observation was significant in the interaction effect on the front shoot. Moreover, the interaction effect on the motor imagery ability was significant. Conclusions These findings suggest that the use of observation learning combined mental image and action observation strategy potentially optimizes motor skills performance and motor image ability by incorporating motor imagery, especially when observing movements with intent to imitate.


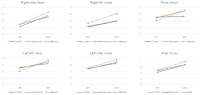
Purpose Sperm quality and function are reduced by environmental factors (e.g., obesity), leading to increased infertility worldwide. Therefore, the purpose of this review paper was to investigate the effects of obesity and exercise training on sperm quality and function in animal and human models. Methods In order to determine the effects of obesity and exercise on sperm quality, motility, morphology, testosterone, oxidative stress, inflammation, we reviewed previous literatures with MEDLINE, PubMed, and Scopus databases. Results The most important factor to control the sperm motility is calcium ion, which is performed by the protein of CatSper (Cation Channel of Sperm). Obese men showed the decrease of number, concentration, motility, and volume in sperm, resulting in delayed or failed fertility. However, regular exercise training increased sperm-mediated factors including number, motility, and morphology, and festicular function-mediated factors including sperm concentration and serum testosterone. Conclusions While obesity exacerbates sperm quality and function in men, regular exercise training with moderate intensity increases sperm number and motility and reduces oxidative stress and inflammation, leading to the improvement of men’s fertility.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of parents’ involved dance-sports program on a physical activity level and a fitness of children with a developmental disability and on their parents’ perception. Methods The participants were seven children with a developmental disability ranged between 8 and 16 years and seven parents of them participating in the dance-sports program during 90 minutes, 3 times per week for 8 weeks. The quantitative data (i.e., the physical activity level, the physical fitness, and the questionnaire) were collected before and after the intervention. Results The results showed that there was statistically significant difference of the parents’ perception on children’s participation in a physical activity [F=5.63, P<.04]. Although the experimental group showed increase trend, whereas the control group showed decrease trend, there was no statistically significant difference of the physical activity level and the physical fitness of the children with development disabilities. Conclusions Parent participated dance sports program seems to be effective on parents’ perception on children’s participation in a physical activity, physical activity level and the physical fitness of the children with a development disability in experimental group.