PURPOSE This study aimed to: 1) compare the differences in static lower-extremity alignment (SLEA) between female ballet dancers (BD) and non-ballet dancers (NBD); 2) investigate the differences among gesture leg (GL) and supporting leg (SL) in BD and dominant leg (DL) in NBD; and 3) compare limb asymmetry between groups. METHODS Twenty-nine female BD and 20 NBD were recruited for this study. The quadriceps, tibiofemoral, rearfoot, and genu-recurvatum angles, tibial torsion and varum, and navicular drop height were measured. An independent t-test was conducted to compare SLEA and limb asymmetry between groups. One-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni post-hoc tests were performed to determine the differences among the GL, SL and DL. RESULTS BD showed lower quadriceps and rearfoot angles, less tibial varum and navicular drop, and greater tibiofemoral angle (p<.005) than NBD. BD showed less quadriceps angle asymmetry but greater tibial torsion asymmetry (p<.01) than NBD. GL and SL in BD showed differences in quadriceps, tibiofemoral, rearfoot angle, tibial torsion and navicular drop compared to NBD. CONCLUSIONS Repetitive dance movements can transfer varying forces to the GL and SL, potentially contributing to SLEA asymmetry. An intervention strategy that can reduce SLEA asymmetry in BD is needed, as is the identification of elements of ballet training that contribute to maintaining a normal SLEA.
PURPOSE This study aimed to verify the influence of imposter syndrome tendencies in athletes on their achievement goal orientation, and regulatory focus. METHODS Data collected from 413 athletes through surveys were analyzed using SPSS version 27.0 and AMOS version 21.0 to assess reliability and validity, conduct independent sample t-tests, perform correlation analysis, and conduct multiple regression analyses. RESULTS The findings revealed significant sex-based differences in imposter syndrome tendencies, achievement goal orientation, and regulatory focus. Moreover, significant correlations were observed between sub-factors of imposter syndrome, achievement goal orientation, and regulatory focus. Imposter syndrome tendencies had varying effects on achievement goal orientation, with the discount factor significantly influencing approach orientation, the fake factor significantly affecting avoidance orientation, and fear factors significantly impacting self-avoidance. Additionally, imposter syndrome tendencies influenced regulatory focus, as the discount factor significantly affected both promotion focus and prevention focus, while fake and fear factors significantly influenced prevention focus. CONCLUSIONS This study underscores the importance of athletes' imposter syndrome tendencies as significant contributors to psychological variables related to motivation, including achievement goal orientation and regulatory focus.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to synthetically explore different communication strategy patterns that are dependent on the events and stakeholders, which include professional sports players, teams, and the associations. METHODS Using the Python program, we performed web crawling and machine learning algorithms to analyze news articles for our research analyses. In particular, 696 articles on driving under the influence (DUI) of alcohol were gathered and subject to descriptive scrutiny; a total of 782 sentences were selected for the analysis. Also, among the 509 articles on illegal gambling, 484 sentences were analyzed. Moreover, 50 frequently reported words were extracted from these sentences to assess their frequencies through the word cloud method for concrete visualization. Then, the data were mapped in order to systemically understand the communication strategy patterns for each case, which were dependent on the stakeholders and timing of the event. RESULTS The empirical results revealed that in case of unethical events of driving under the influence that were reported in the news, most of the subjects chose an apology strategy immediately, but for illegal gambling reports, the parties involved rarely respond and it was difficult to find specific strategy patterns among the subjects. CONCLUSIONS The present study reveals that when professional sports teams were exposed to transgression, depending on the characteristics of the event and stakeholders, they chose different communication strategies involving fan characteristics for the event and subjects. Ultimately, they chose different strategies dependent on their fans’ involvement.
PURPOSE Sport pedagogy (SP) has established itself as a subdiscipline in Human Movement Studies since the 1970s. It has become an academic labyrinth as a result of its rapid flourishing. Most researchers are extremely confused about this disorderly research complex. This study aimed to evaluate the characteristics of SP in stages in the western (mostly English speaking) countries. METHODS Analysis of literature published in English from 1990 to 2022. RESULTS The developmental versions were divided as follows: SP1.0 is positivistic in nature, SP2.0 is multi-paradigmatic as it includes all paradigms, and SP3.0 (current version). Many academic journals have been launched, and a variety of books on divergent topics are being published. Currently, research has exploded. In SP3.0, research performed by British scholars are notable in terms of number and quality, overpowering those by scholars in the USA and other countries. Youth sport and sport coaching are regarded as new legitimate areas. Additionally, signs for SP4.0 have been indicated. CONCLUSIONS In order to find way outs in the SP labyrinth, it is necessary to recognize the current research trends in international SP.
Purpose The current study investigated the effects of exercise information using social network service(SNS) to identify changes of physical activity and psychological variables among inactive college students. Methods Inactive college students(30 experimental group, 30 control group) were voluntarily participated in the 12-weeks intervention. During this period, the experimental group received exercise information through SNS. And all study participants’ physical activity, stages of physical activity, self-efficacy, motivation, and perceived benefits and barriers were measured at the pre, mid and post intervention. Frequency analysis, chi-square test, 2-way ANOVA RM were conducted to analyze data obtained in the study. All procedures were performed by using SPSS 23.0. Results The exercise information intervention using SNS during 12 weeks had a positive effect on the stages of physical activity of inactive college students, and there were statistically significant differences. In addition, physical activity, perceived benefits and barriers, self-efficacy, motivation positively improved after the intervention, but there were no statistically significant differences between experimental and control group. Conclusions The present study suggests that psychological strategies using various SNS programs have positive effects for inactive college students to increase physical activity and its related psychological variables.

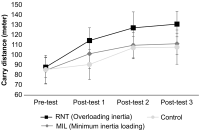
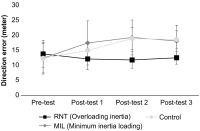
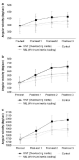
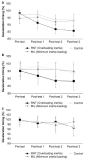
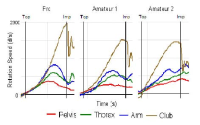
[Purpose] We examined the influence of reactive neuromuscular training (RNT) on golf swing coordination. RNT aims to induce proper coordinative movement by exaggerating the performer’s mistakes. Therefore, we applied RNT using inertia overloading to golfers who have problems with kinematic sequence during a golf swing. [Methods] To examine the effect of 12 weeks of RNT on golf swing coordination, we employed a ball tracking system (launch monitor) and motion analysis system (inertia sensors) were taken on four consecutive periods (pre-test and post-tests 4, 8, and 13 weeks later). Thirty Korean male cadets were divided into three groups based on inertial loading and practiced 7-iron golf swings combined with specific group tasks twice per week. [Results] At pre-test, most participants reached maximal angular velocity near the impact timing (95-100%). However, the deceleration timing of the maximum angular velocity of the proximal segments gradually moved toward mid-downswing as the training sessions proceeded, with the RNT group ultimately outperforming the two control groups. Additionally, the RNT group showed a significantly higher maximum angular velocity in the thorax and wrist. [Conclusion] Our results suggest that RNT can be sufficient to elicit and effective whole-body coordination pattern. Considerable follow-up research is needed on the use of RNT for various sports tasks and the effects of expertise on RNT results.




Purpose The purpose of this study is to calculate the ranking of vault players in artistic gymnastics by individual and by country using the PageRank algorithm. The purpose of this study is to provide basic data that can be used in gymnastics events by comparing the performances of historical vault players with those of previous Olympic competitions. Methods The data collected for this purpose is a score of 117 vault players based on the results of the Olympic final event published in the International Gymnastics Federation (FIG). For data analysis, PegeRnak algorithm was used for calculating the ranking of vault players using MS-Excel and NetMiner. Results The results are as follows that. First, the PageRank algorithm is possible to calculate for historical vault players' rankings. Specifically, the ranking of vault players for historical Olympic calculated by PageRank ranked as Gervasio Deferr from Spain (ESP) at 1st, Alexei Nemov from Russia (RUS) at 2nd, and Klaus Koste from Germany (GDR) at 3rd. Second, Network of vault players' ranking is separated by each generation of Olympic games. Conclusions As a conclusions, it is possible to calculate national ranking of vault games of gymnastics by using PageRank algorithm.




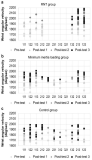
The objective of this study was to reveal the characteristics of lower extremity motions of middle-aged women in accordance with their walking speed, and also to suggest elements of improving functions of walking-shoe for the improvement of gait stability. Total 30 healthy middle-aged women were asked to walk in their preferred speed and also speed 20% faster than that. Using the 3D motion capture system and the plantar pressure measuring system, the characteristics of lower extremity motions were measured. For the analysis on differences in motions between preferred and faster speeds, the paired t-test was performed. At this time, the significance level was set up as α=.05. The walking in faster speed showed the greater ground contact angle than walking in preferred speed while its gait stability was low. Also, the faster walking showed the bigger plantar pressure, and especially, the pressure on the great toe was high. It would be necessary to improve functions of shoes for the gait stability and dispersion of pressure on feet while fast walking.

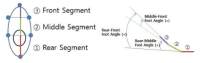

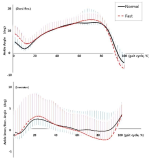

PURPOSE This study aimed to characterize the kinematic variables of stair climbing in adult women by analyzing the effects of varying heel heights on their climbing behavior. METHODS A total of 24 adult women (age: 22.08±1.28years; height: 160.43±4.30cm; weight: 54.10±6.39kg) participated in this study. All subjects wore the same type of high heels with heights of 1cm, 5cm, and 7cm while performing stair climbing on stairs measuring 18cm in height. Ten infrared cameras (200Hz) and ground reaction force sensors (1000Hz) were set up on the stairs, along with an 8-channel electromyography system (1000Hz) to analyze the maximum moments at each joint and the muscle activation during stair climbing. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 27.0 (IBM., USA). All variables underwent the Shapiro–Wilk normality test, with repeated measure analysis of variance or the Friedman test applied based on the results. Post hoc tests were conducted using the LSD test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test. RESULTS Our study found four key findings. First, a significant decrease in maximum dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, inversion, and adduction moments of the ankle joint was observed with increasing heel height. Second, the maximum extension, adduction, and external rotation moments of the knee joint significantly decreased as heel height increased, while the maximum abduction and internal rotation moments significantly increased. Third, the maximum flexion, extension, and abduction moments of the hip joint significantly increased with higher heel heights. Fourth, muscle activity of the rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, and gastrocnemius decreased with increasing heel height compared to walking; however, muscle activity in the tensor fasciae latae increased. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study suggest that as heel height increases, the risk of injury may rise due to limited ankle use and increased moments in the knee and hip joints, potentially leading to muscle strength imbalances in adult women, particularly through the overuse of specific muscles.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of accelerated rehabilitation exercise on physical fitness, lower extremity isometric strength, and blood variables in older adult women diagnosed with degenerative osteoarthritis. METHODS A total of 29 older adult women diagnosed with degenerative osteoarthritis residing in G city participated in the study, and 19 participants, excluding dropouts, took part in the experiment. They underwent exercise twice a week for 60 minutes per session over a period of 12 weeks. Pre- and post-experiment, the older adult fitness assessment (SFT), lower extremity isometric strength, and blood variables were measured. Data analysis was performed using SPSS 25.0, and paired sample t-tests were conducted to examine the effects before and after exercise. RESULTS The study results showed significant differences in body mass index (BMI) before and after exercise (p<0.05), and the older adult fitness assessment (SFT) showed significant differences in all items (p<0.01). Lower extremity isometric strength showed significant differences in absolute (Nm) and relative (%BW) values of 20° right flexion muscle (p<0.01). In terms of blood variables, significant differences were observed in creatine and ESR before and after exercise (p<0.01). CONCLUSIONS This study’s results suggest that regular physical activity and rehabilitation exercise programs can positively impact the muscular strength, cardiovascular endurance, exercise function, and blood composition of older adult women diagnosed with degenerative osteoarthritis. It is indicated that conducting future research, including periodic exercise programs, could be beneficial in promoting sustained exercise participation.