Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a psychic energy management scale that construct a concept and based on extracted contents of structural validity and reliability of university athlete psychic energy management inventory. Methods To develop the scale, the researches were completed <research ⅰ; constructing sub-factors of Psychological Energy Management, ⅱ; developing scales of psychic energy management, ⅲ; verifying validity of psychic energy management>. The results shown are a follows. Results The psychic energy management inventory contents of the university athlete were categorized into five categories ; team energy, game energy, environment energy, leisure energy and body energy. Through statistical procedures and factor analysis, the psychic energy management inventory was developed with 4 factors 18 items (coach energy 4 question items, game/environment energy 6 question items, colleague energy 4 question items, body energy 4 question items). Conclusion Convergent validity and discriminant validity was demonstrated through the external validity, the multi-group analysis confirmed the structural equivalence of the scale between the school grades.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to develop a non-face-to-face self-regulation training program for middle and high school student-athletes through the conduct of a group online video counseling session, as well as to verify the effectiveness of such a tool. METHODS Based on the models of Zimmerman(2000) and Han Si-wan (2008), the 12-session non-face-to-face self-regulation training program consisting of interactions involving cognitive, emotional, and behavioral factors was developed and used on a 16-member experimental group. Additionally, self-regulation and mental toughness questionnaires were given to each member before and after the program, and the results were compared with the results of a 17-member control group. Since a qualitative evaluation was conducted, recorded training contents were organized into a text file; after which, a step-by-step coding procedure was performed, and then meanings and themes were identified and categorized. RESULTS Quantitative analysis found that the volitional inhibition mode of the control group decreased significantly; this was in comparison to the increase in the self-regulation mode of the experimental group. In addition, among the seven sub-factors of the mental strength test of the experimental group, a significant increase was found in the post-test of self-belief, attention control, emotional regulation, resilience, and optimism factors. As a result of qualitative data analysis, they complained of difficulties in the early stages of participation, but gradually recognized their problems and searched for changes, showed changes in cognition, emotion, and behavior as they approached the end of the study period. CONCLUSIONS It can be said that the non-face-to-face self-regulation training program helped student athletes improve their school life and performance by driving positive cognitive, emotional, and behavioral changes.
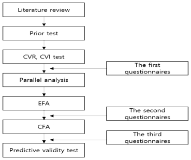
The purpose of this study was to develop an instrument that measures participantsʼ satisfaction in sports instructor training programs. The instrument development process includes focus group interviews, parallel analysis, and validity and reliability tests. Data were collected from 897 participants from three regular training sessions and were analyzed primarily using SPSS and MPlus software. The results indicated that the service satisfaction of sport instructor programs has an underlying three sub-factors, including ʻadministrative supportʼ, ʻcurriculum contentsʼ, and ʻlearning environmentʼ. This study can provide helpful information to managers in improving their respective sport instructor training programs.

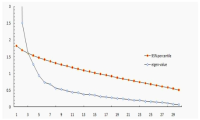

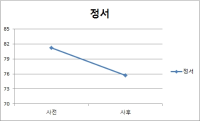
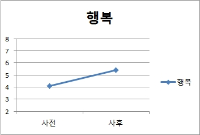
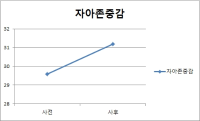
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of positive psychological intervention program on mood state, self-esteem and happiness of university student athletes. Methods The participants were 10 university student athletes. The measures utilized the Profile of Mood States(POMS), self-esteem inventory and happiness questionnaire. Positive psychological intervention program was developed by previous studies, participants interview and expert discussion. The positive psychological intervention program were managing life, self-esteem enhancing program, being optimistic, positive emotion program, gratitude, forgiveness, communication skill training program, habit/routine making program and action strategy development. The data were analyzed by SPSS 20.0. Results These results were as followings. Firstly, positive psychological intervention program decreased total mood disturbance(TMD) of university student athlete. Secondly, positive psychological intervention program improved self-esteem of university student athletes. Lastly, positive psychological intervention program increased happiness level of university student athletes. Conclusion Training and education system should be established in which a positive psychological intervention program can be applied to university student athletes.


Purpose This study was conducted to investigate the appropriateness of the concept of condition for athletes and to conceptualize condition in a way suitable for field and then to produce a tool to test condition that reflects usability. Methods 30 college athletes and national athletes with more than 5 years of experience were selected. In the conceptual review stage, the appropriateness of the concept of condition was verified. In the conditional element collection stage, the condition concept reflecting usability was extracted. In the development stage of the conditional questionnaire, a condition questionnaire was developed in consultation with the data provider to reflect usability. Results Previous studies on the condition of athletes were complicated and the necessity for consideration of usability was raised. As a result of conceptualization with consideration of the application to the sport scene, condition in a scene is summarized into both physical and psychological states. As a result of the appropriateness evaluation of the tool that produced the condition inspection tool reflecting the condition element based on universality and peculiarity of conditionality, the athletes evaluated that the condition inspection tool properly reflects condition, is easy to apply and can be used for condition control. Conclusion The development and application of psychological testing instruments reflecting usability will accelerate the application of sports psychology in the appropriate direction. The reflection of usability will contribute not only to the reliability and validity of the psychological testing tools used in the field of sports psychology, but also to the improvement of the possibility of intervention by leaders and athletes, the convenience of development procedures, and the utility of response results.

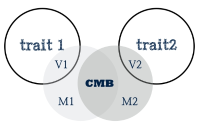
Common Method Biases(CMB) is not the matter of measuring tools but the various errors caused by measurement. One of the procedural remedies to overcome these errors is the separation of measurement. However, according to the analysis of the papers published in sports psychology academic journals during the last ten years, the papers used the separation of measurement were just 24 papers of total 197 papers and most measurement were the questionnaires of Likert scale. So this research introduces the Situational Judgment Test(SJT) which can measure the psychological variables using different method except for the questionnaires of Likert scale and describes the developing process and the existing research results. In addition to this, on the basis of the Situational Judgment Test(SJT) developed in the area of sports, it suggests that the scoring key methods which is applied both the distance score and order score show better the validity compare with methods using only the distance score.

PURPOSE This study examined the effect of sports life skills and life skills transfer of student-athletes and coaches, applying Actor-Partner Interdependence Model (APIM). METHODS Korean student-athletes and coaches from middle and high school sports teams participated in this study. There were 300 student-athletes (Mage=15.44, SD=1.64; male=218, female=82), with an average of 5.46 (SD=2.40) years of athletic career. Meanwhile, 33 coaches were (Mage=39.70, SD=8.36; male=26, female=7), with an average of 13.52 years of coaching career (SD=10.01). Measures included the Life Skills Scale for Student-Athletes (LSSSA; Jang et al., 2020) and Korean Life Skills Transfer Survey (KLSTS; Lim et al., 2018). Descriptive analysis, correlation, and APIM were undertaken by using the SPSS and AMOS programs. RESULTS First, the correlation between athletes’ and coaches’ life skills was not significant. Second, athletes’ life skills significantly affected their life skills transfer, similar to coaches’ life skills significantly affecting their life skills transfer. Fourth, coaches’ life skills did not significantly influence athletes’ life skills transfer, and the converse was not true either. CONCLUSIONS This study verified the effect of life skills development for two groups of athletes and coaches, on transfer in sports, and attempted statistical verification of whether it affects sports life skills and transfer between athletes and coaches. Although no statistically significant results were found in the partner effect, it is meaningful in that, it provided important implications for conducting a follow-up study on the relationship between athletes and coaches. In other words, it is expected to be a cornerstone for research on building a new model, along with investigating the interactive relations between athletes and coaches on life skills in the sports field.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop the sport 5C scale of the Korean version. Methods The participants were 772 high school students from 17 to 19 who participated in sport regularly. The validation of Sport K-5C followed a three-step validation procedure through substantive stage, structural stage, and external stage. Results First, In the substantive stage, Sport K-5C consisted of 50 items with 5 factors. Second, in the structural stage, although Sport K-5C was explored as 24 items with 4 factors by EFA, but as a result of CFA, Sport K-5C was confirmed as 24 items with 5 factors. Third, the external stage provided additional validity through correlations of tests with other questionnaires which are similar concept and opposite concept, and group differentiation. Conclusions Sport K-5C is composed of 5 factors and 24 items. The factors are Caring, Character, Confidence, Competence, Connection. This scale can be used to provide an objective evaluation of positive development of youth in sport and physical education context.
