PURPOSE This study aimed to develop physique and basic physical fitness evaluation criteria for middle school soccer players, providing a foundation for training and player development to be used by coaches in the field. METHODS The study involved 440 middle school soccer players (Grade 1=178, Grade 2=132, and Grade 3=130). Measurements were conducted on seven physique and ten basic physical fitness factors. Measurement results were organized using Windows Excel 2021 and descriptive statistics were performed using Windows SPSS 26.0. Based on the descriptive statistics of the measurement results, the Cajori 5-Grade evaluation method was applied to establish evaluation criteria for each grade and fitness component. RESULTS The study results provide evaluation criteria for middle school soccer players based on the measured data, considering grade, physique, and basic physical fitness. CONCLUSIONS The criteria established in this study are expected to be widely utilized by coaches in the field to set training goals for areas such as player selection, development, injury prevention, and rehabilitation.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the moderate to vigorous physical activity(MVPA) and sedentary time measured by accelerometer. Furthermore, the level of physical activity and adherence rate of physical activity guideline(PAG) were compared with the self-reported questionnaire. Methods The MVPA, sedentary time, and adherence rate of PAG according to age and sex were examined to people who agreed to wear accelerometers among the participants of the 2014-2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. To compare the relationship between accelerometer and self-reported questionnaire, Chi-squared test and Spearman correlation analysis were performed. Results The MVPA of the accelerometer-total(AT) was 40.6 minutes/day for men and 31.1 minutes/day for women. Sedentary time was 502.9 minutes/day for men and 498.9 minutes/day for women. The MVPA of accelerometer-bout(AB) estimates was 16.4 minutes/day for men and 14.2 minutes for women. On the other hand, the MVPA of the self-report was 95.8 minutes for men and 64.3 minutes for women, and the sedentary time was 471.2 minutes for men and 455.2 minutes for women. The adherence rate of PAG was 55.6% of the self-report, 56.1% of the AT, and 21.4% of the AB. The correlation between self-report and accelerometer was statistically significant(p < 0.01), but showed a weak correlation coefficient(rho=0.112-0.351). There was no association between AB and self-report(p < 0.01). The sensitivity and specificity of the self-report were 71.3% and 48.6%, respectively. The positive and negative predictive values of the self-report were 27.5% and 86.1%, respectively. Conclusions As a result of this study, self-reported physical activity level by questionnaire had more MVPA and less sedentary time than the accelerometer-determined physical activity. In addition, the adherence rate of the PAG differed from accelerometer and self-report. The difference was significantly increased when comparing AB with the self-report. Therefore, great care must be taken when interpreting accelerometer and self-report questionnaire. Further research will be needed on specific methods that can be used by complementing the two measurement tools.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of continuous exercise and the accumulation of short-duration exercise for 12 weeks on body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease indices in overweight men in their 30s. METHODS Participants in the continuous exercise group (CE; n=13) performed a circuit exercise program of 30 min/session, 3 sessions/week for 12 weeks. Participants in the accumulation of short duration exercise group (ASE; n=12) performed the same exercise time of 30 min per day, divided into three sessions of 10 min. Body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease indices were measured pre- and post-test and were compared by utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. RESULTS 1) Regarding body composition, body weight, body mass index, skeletal muscle mass, waist circumference, and fat mass decreased significantly, while hip circumference increased significantly in the CE group. Waist circumference and skeletal muscle mass decreased significantly, while hip circumference increased significantly in the ASE group. 2) Regarding physical fitness, right grip strength, sit and reach, sit up, and maximal oxygen uptake increased significantly in both groups. 3) Regarding hypertension indices, there were no significant differences in both groups, but they showed a tendency to improve. 4) Regarding hyperlipidemia indices, triglycerides (TG) decreased significantly in both groups, and total cholesterol (TC) decreased significantly in the CE group. 5) Regarding diabetes indices, there were no significant differences in both groups, but a tendency to improve was noticed. 6) Regarding arteriosclerosis indices: TG/high density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio decreased significantly in both groups, and the TC/high density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio decreased significantly in the CE group. CONCLUSIONS We concluded that both the accumulation of short duration exercise and continuous exercise can be effective in improving body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease in overweight men.
Purpose The current study investigated the effects of exercise information using social network service(SNS) to identify changes of physical activity and psychological variables among inactive college students. Methods Inactive college students(30 experimental group, 30 control group) were voluntarily participated in the 12-weeks intervention. During this period, the experimental group received exercise information through SNS. And all study participants’ physical activity, stages of physical activity, self-efficacy, motivation, and perceived benefits and barriers were measured at the pre, mid and post intervention. Frequency analysis, chi-square test, 2-way ANOVA RM were conducted to analyze data obtained in the study. All procedures were performed by using SPSS 23.0. Results The exercise information intervention using SNS during 12 weeks had a positive effect on the stages of physical activity of inactive college students, and there were statistically significant differences. In addition, physical activity, perceived benefits and barriers, self-efficacy, motivation positively improved after the intervention, but there were no statistically significant differences between experimental and control group. Conclusions The present study suggests that psychological strategies using various SNS programs have positive effects for inactive college students to increase physical activity and its related psychological variables.
The aim of the study was to examine the tracking of body composition and physical fitness in boys and girls for 6 years. Thirty-seven boys and girls participated throughout the study. All measurements were performed annually. Body height, body weight, circumferences and skinfold thicknesses were measured and skeletal maturity was assessed. Body composition and bone mineral density were measured by DXA. Nine physical fitness tests were administered. Results of the study showed that there are significant interaction effects of time and group for body height(p<.01), waist circumference(p<.001), and skinfolds at triceps(p<.01), suprailiac(p<.01), thigh(p<.001) and medial calf(p<.01). All anthorpometric variables except skinfold thickness increased during the study period. Significant interaction effects of time and group were found for percent body fat(p<.05) and bone mineral density(p<.01). Percent body fat and fat tissue increased in boys from 7 to 11 years, then decreased in 12 years. Lean tissue(p<.001), bone mineral content(p<.001) and bone mineral density(p<.001) increased both in boys and girls throughout the study. There were significant interaction effect of time and group on sit and reach, standing long jump and sit-ups. In conclusion, percent body fat and fat tissue increased until 11 years, lean tissue and bone mineral density increased throughout the study both in boys and girls.


Purpose The study examined the effects of a 12-week high intensity circuit training (HICT) on abdominal fat, physical fitness, blood lipids, and insulin resistance in middle-aged obese women. Methods Thirty obese women, aged 32-48 yrs, were recruited and randomly assigned to either HICT group (TR; n = 15) or control group (CON; n = 15). Subjects in the TR group participated in HICT of which resistance exercise and aerobic exercise were performed with a duration of 40 min/session and 3 sessions/wk for 12 weeks, whereas subjects in the CON group were asked to maintain their normal life patterns. Dependent variables included abdominal fat area, body composition, physical fitness, blood lipids profiles, and insulin resistance index. Analysis of variance with repeated measures with Bonferroni corrections was used to compare the outcomes between two groups. Results Main findings of the present study were as follows: 1) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant reductions in overall (i.e., body mass index and percent body fat) and abdominal obesity (i.e., waist circumference, total abdominal fat area, visceral fat area, subcutaneous fat area, and visceral fat area-subcutaneous fat area ratio), 2) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant improvements in health-related physical fitness (i.e., muscular strength, muscular endurance, muscle power, flexibility, balance, and cardiorespiratory endurance), and 3) compared to the CON group, the TR group had significant improvements in fasting lipids, glucose, insulin, and insulin resistance. Conclusions The current findings of the study suggested that HICT would be an effective exercise intervention to improve metabolic complications associated with obesity and poor physical fitness in obese middle-aged women.



[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to determine the influence of complex exercise and chromium supplement on healthe-related physical fitness, appetite regulating hormones, and diabetes risk factors in obese elementary school students. [Methods] The subjects were 32 obese elementary students over 25 kg/m2 to BMI, 8 complex exercise with high chromium supplement group (CE+HC), 8 complex exercise with low chromium supplement group (CE+LC), 8 complex exercise with placebo group (CE+PL), and 8 placebo group (PL). The subjects have performed the exercise program for 70 minutes a day and 3 times a week with aerobic and anaerobic exercise during 12 weeks. Also, low and high chromium supplement group took a peel 50 ug and 400 ug respectively at the same time and place. [Results] There were significant decreases in body fat to CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) and significant increase in muscle mass compared with CE+PL (p<.05). However, there were no significant differences in body weight, BMI, muscular strength, muscular endurance, and flexibility between groups. For appetite regulating hormones, there is a significant difference to ghrelin in CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) and there were significant differences to glucose and insulin significantly decreased in CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) in diabetes risk factors. [Conclusion] In conclusion, there were positive responses for body composition and diabetes risk factors for the twofold cases through complex exercise and high chromium supplement, but not for physical fitness and appetite regulating hormones.
This study was designed to investigate the effects of increment of physical activity for 12 weeks through aerobic exercise training or change from own vehicle to public transportation for commuting on physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function in middle-aged men. Forty-four subjects, aged 30-50 yrs, were randomly assigned to either one of three groups, i.e., aerobic exercise training group (TR: n=14), change to public transportation group (PT: n=15), or control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR performed aerobic exercise for 30 min per sessions, three sessions per week, subjects in PT changed from their own vehicle to public transportation for commuting, and subjects in CON maintained their life patterns during the same intervention period. Physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function were measured at pre- and post-test, and the data were analyzed by repeated two-way ANOVA. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables related to physical fitness improved significantly in TR. Right grip strength, standing long jump, side step test, and sit-and-reach improved significantly in PT. 2) Although there were no significant changes in all variables related to insulin resistance, the variables tended to be improved in TR and PT. 3) TNF-α decreased significantly in TR and PT. IL-6 and CRP tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. 4) ALT decreased significantly in PT. AST and γ-GT tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. It was concluded that the 12 weeks of change to public transportation as well as aerobic exercise training would be beneficial for physical fitness and inflammatory markers. These interventions also would be possible to improve insulin resistance and liver function. The increment of physical activity through change from own vehicle to public transportation was found to be equally beneficial for health promotion compared to aerobic exercise.
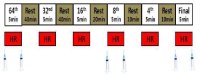
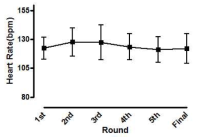
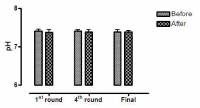
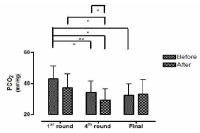
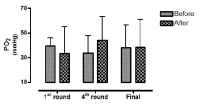
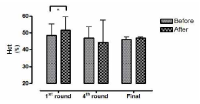
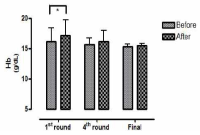
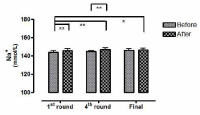
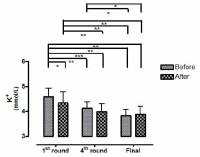
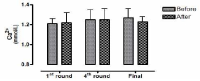
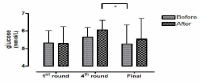
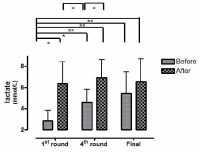
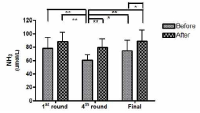
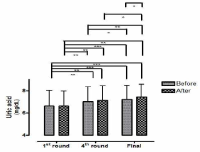
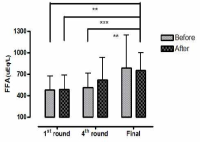
This study aimed to examine the change of the indices in blood gas, ions, and by-products of fatigue substances and components in collegiate elite Kumdo competitors, who carry out a number of competitive games during one day tournament event. Subjects were carried out total 6 simulated, but followed same conditions and rules of actual competition, with providing similar inter-game break time. Eight well trained male competitors, who had awarded from national wide competitions, voluntarily participated in this study and revealed 51.5(±8.8) mL·kg-1min-1 of maximal oxygen consumption and 12.4(±5.1) % body fat. TWOWAY ANOVA (tournament round vs. pre & post each game) was adopted to test whether the mean differences were existed, and the interaction between individual factors and main effect within each factors were analyzed. Statistical significance was set at Alpha (α) = .05. While there were no significant changes in blood hydrogen ion concentration (i.e., pH) and partial pressure of oxygen (PO2), partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) significantly decreased as the tournament games were repeated. The level of hemoglobin and hematocrit were significantly elevated only during the 1st round of tournament. Na+ was significantly increased but K+ was decreased. Ca2+ concentration however, was not significantly altered. Although the changes of blood glucose level did not show any consistent patterns, free fatty acid (FFA) concentration was increased after completed each game compared to prior to initiate the each game. Blood NH3, lactic acid, and uric acid concentration increased at immediately after each game, and the pattern was maintained throughout the tournament round continued. These results reflected that the repeated participation of the tournament may cause the accumulation of the by-products of fatigue substances in blood and alteration of various ion components and energy substrates. Accordingly, the ways of reducing the physical fatigue and providing adequate energy source inter-tournament games needs to be necessarily considered for successful Kumdo competition. Data obtained from this study could valuable for searching the effective training and management methods to improve the performance and reduce the fatigue of the professional elite Kumdo competitors.

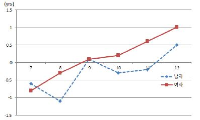
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate conditioning management and perception in Korea Ladies Professional Golf Association golfers and elite amateur female golfers. METHODS Physical characteristics and performance-related factors were investigated through a short version of the conditioning questionnaire consisting of 16 questions on five factors, surveying 129 female professional golfers and 174 elite amateur female golfers. The components of the questionnaire included physical fitness (four questions), injury (four questions), nutrition (three questions), mental (three questions), and performance strategy factors (two questions). Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 23.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). An independent t-test was used for comparison between groups. RESULTS Physical fitness-related factors showed significant differences in all four questions between groups (p<0.001–0.031), injury-related questions showed significant differences between groups in three questions (p<0.001–0.003), and one nutrition-related question was different between groups (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS Differences were seen in conditioning management factors recognized between professional and elite amateur female athletes. Future research on conditioning questions and differences in effects according to actual performance will be needed.