Purpose The purpose of this studied to improve athletes’ performance through sports psychological skills training and counseling of a male canoe player in high school. Methods One male high school athlete in J area was interviewed for sports psychological skills training and counseling, and interviewed athletes and coaches diagnosed the potential psychological problems of athletes. Through this process, the athlete gained the ability to control anxiety about the game and strengthened the attention-focused ability to increase his confidence and set a goal for improving concentration. For effective training, sports psychological counselors, athletes, and coaches met once a week to create a routine. and participated in direct training on a boat with the coach every week. Sports psychological skills, anxiety about competition, and self-management of athletes were measured before and after to confirm the effectiveness of training of athletes' psychological skills. Results As a result, athletes' psychological skills and anxiety decreased, their confidence increased, and their concentration, which was diagnosed as an urgent problem of athletes, improved. Conclusions psychological skills of athletes, psychological shortcomings of players were reinforced, thus enhancing the athletes' performance. This suggests the effectiveness and necessity of training in sports psychological skills. It is hoped that continued support will serve as an opportunity to diagnose potential psychological problems of student athletes and apply them to training to contribute to improving their performance.
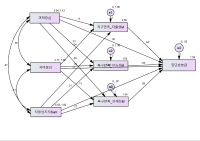
In sport context, the motivational climate created by significant others (e.g., coachs and peers) has been influences on the athletic-student's motivation, engagement, performance, and skill development. Collective efficacy is important for team performance because it influences a group's task choice, effort expenditure, persistence in the face of failure, and resistance to discouragement. This study was to examine the influence of peer motivational climate (i.e., task-involving and ego-involving motivational climate) and coach autonomous support for basic psychological need satisfaction and collective efficacy. In the study, participants were 289 athletic-students' of team sports. In the study then, questionnaire was assessed using by the correlation and path analysis. The results showed that task-involving motivational climate significantly predicted of collective efficacy, while ego-involving motivational climate were negatively predict to the collective efficacy. The results suggest the importance of considering peer influence in addition to coach influence when examining motivational climate in team sport.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to understand the athletic identity of youth football players and to trace its changing trend. METHODS Participants of this study included 93 players in 2005 and 94 players in 2021, who were in middle and high schools. All participants answered open-ended questionnaires. After the results of the inductive content analysis, the changing trend of the results was assessed. RESULTS The athletic identity of youth football players were collected from 811 raw data samples collected in 2005 and 741 collected in 2021 and categorized into 19 sub-categories and 5 categories. The results show a tendency to be specific to football. The athletic identity of a football player itself is weakening, being replaced by the identity of being a student. The role of the camp is also weakening, while more privacy and autonomy are allowed to the players. As a result, efforts to secure the players’ right to study were accepted by the players, and expected to decrease as camp life with limited privacy is on the decline, and as senses toward one’s physical competence are changing. CONCLUSIONS Sociocultural contexts, including changes in the system and social modifications, are reflected in the football player's athletic identity and its changes. The athletic identity of youth football players has changed from its 2005 version of unacademic camp life with limited privacy to the 2021 version, where the player leaves camp to be provided with privacy and attend classes.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine athletes’ psychological competition experiences. Methods For this study, 64 student athletes, attending universities located in Seoul and Chungcheongbuk-do, participated in the study by completing an unconstructed questionnaire. The data were analysed through content analysis method. Results As a result, 15 themes, such as morale loss, comparable performance levels, opponent irritation were collected and the themes were classified into three categories including objectives of psychological competition, requirements of psychological competition, and psychological battle. In match situations, athletes attempt to psychologically compete in order to achieve objectives such as opponent’s morale loss, induce carelessness, trigger agitation and anger, dispersion of attention, and distraction. Psychological competition among rivals is valid when the requirements, such as comparable performance levels, sensitivity to match situations, strong tenacity and confidence, understanding of opponent and oneself, mutual checks and balances, are met. Athletes attack and defend to win the psychological competition by utilizing opponents irritation, information distortion, unexpected behaviors, predicting and coping, pulling a poker face, exclusion of opponents, and self-focusing. Conclusion This study created a theoretical foundation for a profound understanding of athletes’ psychological competition, which is often found in sport fields. Furthermore, this study is meaningful in that it has raised a chance of interest concerning psychological interaction between players in match situations.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to verify their effectiveness as we develop and apply worksheets for improving life skills and resilience of collegiate Taekwondo athletes. Methods The study went through three stages: developing, applying, and evaluating. In the developing stage, literature review, expert meeting, and pilot test (n=25) were conducted to develop the worksheets. In the applying stage, 37 athletes participated in life skills program using the worksheets. Data were collected by survey and in-depth interview. In the evaluating stage, paired t-test, word cloud analysis, and inductive content analysis used to identify the effect of worksheets. Results First, the worksheets were composed of 3 stages (plan, acquisition, implementation) and 15 sessions including 12 factors of life skills. Second, the worksheets were applied in each phases such as planning, acquiring, and implementing. In the planning phase, they understood life skills knowledge and set goals. In the acquisition phase, students learned specific life skills’ strategies. In the practice phase, the acquired life skills were applied and practiced in real life and relationships. Third, the result of paired t-test showed that all the factors of life skills and 6 factors of resilience were significantly improved. In addition, word cloud and in-depth interviews revealed that the participants' cognitive and psychological changes were most prominent. Conclusions The life skills worksheets consists of 12 factors in 15 sessions and can be considered as an effective intervention tool for improving the resilience and life skills of collegiate Taekwondo athletes.

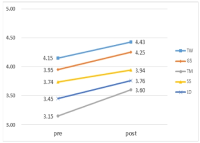
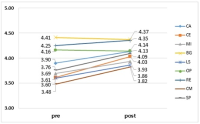









Purpose Based on Haidt's social-intuitionist theory, this study analyzes the differences in ethical decision-making between sport athletes and the general public in order to understand the ethical judgment tendencies of athletes and examine the determining factors influencing their judgment from the perspective of their environment. In so doing, this study hopes to motivate education for enhancing ethical consciousness as well as institutional policy. Methods To this end, 200 elite athletes in their twenties registered for more than 10 years at the Korean Sports Association and 200 college students in their twenties from five universities in Seoul were selected for comparison. Response trends for each item were analyzed by percentage, and differences between groups were confirmed by the χ2 test method. Results The results are as follows. First, in general ethical situations, athletes usually showed a compulsory ethical view that emphasized principles, whereas in a sports situation, they showed a double consciousness and revealed a very strong consequential ethical view which put much emphasis on outcome. Second, athletes strongly maintained a Confucian ethical view that recognized ethics as a norm compared to the general public and, as a result, it was found that paternalism was relatively stronger than rationalism in their ethical decision making. Third, athletes regarded other people's thoughts and group interests as important criteria for ethical decision-making rather than individual thoughts and interests, and showed a group-centered mindset which emphasized group harmony and relationship. Fourth, while the general public viewed excellent athletes as those with excellent skills and good personality, and valued their morality, athletes thought relatively little of the influence and importance of morality in their success. Finally, it was found that coaches and managers were fundamental to the formation of the athlete’s moral view. Conclusion An in-depth understanding of sports participants' ethical awareness should come first in order to enhance ethical consciousness in sport. I hope this study will work as a catalyst for research which approaches athletes' ethical consciousness from a socio-cultural context.
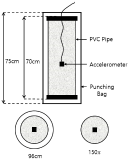
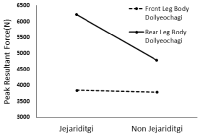
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the comparison of peak resultant force in taekwondo body dollyeochagi in accordance with Jejariditgi existence and the position of kicking leg. Methods Twelve students who majored taekwondo participated in this experiment. They have a forth dan(degree) black belt in taekwondo. The peak resultant force was measured 12 times(2 jejariditgi existence × 2 position of kicking leg × 3 times). Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures was used to analyze the data. Results There was significant difference in interaction effect of peak resultant force in taekwondo in accordance with jejariditgi existence and the position of kicking leg. And there was significant difference in main effect of peak resultant force in taekwondo in accordance with jejariditgi existence and the position kicking leg. Higher peak resultant force was shown in body dollyeochagi with jeariditgi as compared with non jejariditgi. And higher peak resultant force was shown in rear kicking leg as compared with front kicking leg. Conclusions The results show that jejariditgi is a factor affecting the peak resultant force. Comparison of peak resultant force in taekwondo body dollyeochagi in accordance with jejariditgi existence and the position of kicking leg will provide strategies for coaches and athletes to perform improved taekwondo dollyeochagi.


PURPOSE This study investigates the effectiveness of biomechanics information on intermediate golfers driver swing learning. It analyzes changes in center of pressure (COP) patterns, GRF Direction Inclination, driver performance, and learners psychological responses to determine the learning effects. METHODS Subjects were 32 right-handed male golfers (handicap 15-23) who had no difficulty in performing the golf driver swing (Full swing). Four groups were selected, BF (Biomechanics Feedback group), BVC (Biomechanics Verbal Cue group), CB (Combination group), and CT (Control group), and assigned randomly. Driver swing learning showed results after 6 weeks,and a transfer test was conducted 1 week after the completion of the learning. RESULTS Analysis of COP patterns and GRF Direction Inclination indicated changes in the BF, BVC, and CB groups. Furthermore, analysis of driver distance (m), club head speed (km/h), and ball spin rate (rpm) revealed that during the 6-week acquisition phase, all three groups (excluding the control group) showed improvements in driver distance, club head speed, and ball spin rate. However, there were no statistically significant differences among the groups. In contrast, the transfer test showed statistically significant differences among the groups, with the CB group exhibiting the highest driver distance. Learners' psychological responses during the learning process were trust, understanding, and satisfaction. The understanding factor was relatively higher in the CB and BVC groups compared to the BF group. CONCLUSIONS In summary, biomechanics information (BI) was effective in improving driver performance, and changesappeared in the COP pattern and GRF Direction Inclination, indicating a change in movement. Therefore, BI can be fully utilized for athletes or high-level advanced players and for motor learning for intermediate-level students.However, BI can only improve learning effects by strengthening learners' “understanding” when visual feedback forms and verbal cues are provided together.