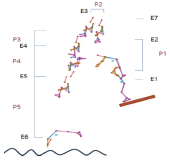
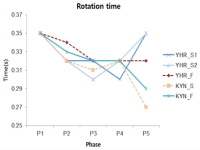
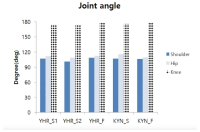
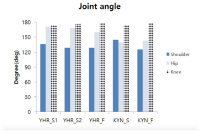
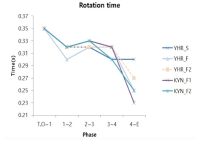
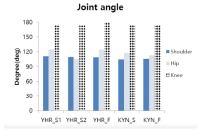
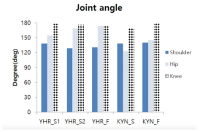
Purpose The purpose of this study is to overcome the shortcomings of 109C(Forward 4 ½ somersault) skill(Level 3.7) for two members of the men’s national diving team(YHR, KYN). Methods For qualitative analysis of the performed skill, three high-speed cameras and water-attached EMGs consisting of a total of ten placements were used. We instructed the two players to perform single-leg jump and double-leg jumps a total of three times each. Results The results of this study indicate that YHR and KYN appeared to increase their time or maintain the same time compared to the previous phase and displacement appeared higher when skill success occurred after the double-leg jump. The Shoulder & hip joints of YHR, KYN appeared larger in E2 and the hip joint of KYN appeared to increase in E1. Single-leg jump appeared similar or decreased the performed time of the previous phase in the last P5. YHR appeared larger only at a hip joint angle and KYN appeared smaller at the hip joint. The muscle activity(iEMG) of the two players appeared greater during skill failure than most of the muscles. Conclusions When perfectly performing 109C skills, the acquisition of medals in international competitions is possible. Therefore, in the future, it is necessary to study all of the variables that pertain to 109C.




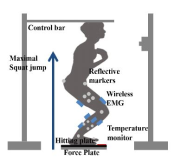
The human foot is only part that directly contact between the body and the external environment, and is ideally positioned to provide sensory information to the Central Nervous System (CNS) during static and dynamic tasks. Through cutaneous mechanoreceptors located in the dermis, the foot is able to recognize touch pressure and vibration stimuli, which provide important feedback information used for the fine coordination of movements. The purpose of this study is to quantitatively examine the effect of changing the foot cutaneous sensory by temperature stimulus on maximal performance and muscle activation using wavelet technique. Sixteen healthy subjects volunteered to participate in this study (Male: Age 21.4±2.4years; Height 174.7±5.3츠; Weight 70.6±5.2kg; Female: Age 20.5±0.6years; Height 163.2±3.1cm; Weight 55.6±4.8kg). Sensory pressure thresholds were determined for the plantar surface of the foot using monofilament. Kinematic, kinetic and EMG data which relative to maximal performance were collected while squat jumping in each temperature condition(cool 12-15℃ normal 28-30℃ hot 45-48℃). Maximal jump height was significant higher in normal condition. Vertical GRF in normal condition showed higher peak value the other conditions. And then EMG signal were significant different between temperature conditions during maximal performance. By changed sensory feedback on temperature, one can alter maximal performance and muscle activation pattern. Cutaneous feedback is important in performance and neuromuscular control, and temperature changes significantly influence on lower extremity during maximal squat jump performance of healthy subjects.





PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the risk factors for anterior cruciate ligament injury using the Landing Error Scoring System (LESS) and muscle activity during the drop vertical jump for overweight females. METHODS The body mass index was 18.5-22.9 kg/㎡ for normal weight females and 23-24.9 kg/㎡ for overweight females among 10 participants aged 20-30 years classified into groups of participants without any injury history and those who were right-footed. An automatic heigh-tweight machine, body composition analyzer, diagnostic imaging, electromyography with the LESS, and muscle activity analysis were used for measurements. The difference in muscle activity between the normal weight and overweight females was evaluated by independent t-test. RESULTS Overweight females had a smaller angle of knee bending during the drop vertical landing, leading to a smaller knee curve angle. In addition, they landed with an unbalanced foot touch on the ground inclined backward, thereby breaking the whole body balance. Overweight females had an incorrect posture compared with normal weight females, with higher LESS points. The muscle activity of the rectus femoris was higher than that of the biceps femoris, indicating a higher load on the muscle. CONCLUSIONS Overweight females take more load on the knee joint and cannot absorb the impact force properly. These results suggest a higher risk of anterior cruciate ligament injury in overweight females.

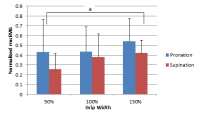
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of grip width and hand orientation on muscle activities of upper body during the lat pull-down. Methods Eight healthy men performed the 6 grip variations (3 grip width × 2 hand orientation) using an experimentally determined load of 70% of 1 repetition maximum. Five trials were analyzed for each grip type. Participants maintained a cadence of 2-second concentric and 2-second eccentric phases. The grip widths were normalized for each individual by using their biacromial diameter (100%), and then set the grip width 50% of biacromial diameter and 150% of biacromial diameter. Surface EMG of the latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major, infraspinatus, biceps brachii, triceps brachii, rectus abdominis, erector spinae and middle trapezius was recorded, and the root mean square of the EMG was normalized, using a maximum isometric voluntary contraction. Results Latissimus dorsi showed higher muscle activities in 100% grip width than those of 50% grip width. Pectoralis major and rectus abdominis showed higher muscle activities in 50% and 100% grip width than those of 150% grip width. Middle trapezius showed higher muscle activities in 150% grip width than those of 50% grip width. Conclusions Two-way repeated measures ANOVA for each muscle revealed that latissimus dorsi and middle trapezius (the posterior muscles of trunk) showed higher muscle activities in wide grip, on the other hand, pectoralis major and rectus abdominis (the posterior muscles of trunk) showed higher muscle activities in narrow grip.





PURPOSE This study aimed to characterize the kinematic variables of stair climbing in adult women by analyzing the effects of varying heel heights on their climbing behavior. METHODS A total of 24 adult women (age: 22.08±1.28years; height: 160.43±4.30cm; weight: 54.10±6.39kg) participated in this study. All subjects wore the same type of high heels with heights of 1cm, 5cm, and 7cm while performing stair climbing on stairs measuring 18cm in height. Ten infrared cameras (200Hz) and ground reaction force sensors (1000Hz) were set up on the stairs, along with an 8-channel electromyography system (1000Hz) to analyze the maximum moments at each joint and the muscle activation during stair climbing. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 27.0 (IBM., USA). All variables underwent the Shapiro–Wilk normality test, with repeated measure analysis of variance or the Friedman test applied based on the results. Post hoc tests were conducted using the LSD test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test. RESULTS Our study found four key findings. First, a significant decrease in maximum dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, inversion, and adduction moments of the ankle joint was observed with increasing heel height. Second, the maximum extension, adduction, and external rotation moments of the knee joint significantly decreased as heel height increased, while the maximum abduction and internal rotation moments significantly increased. Third, the maximum flexion, extension, and abduction moments of the hip joint significantly increased with higher heel heights. Fourth, muscle activity of the rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, and gastrocnemius decreased with increasing heel height compared to walking; however, muscle activity in the tensor fasciae latae increased. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study suggest that as heel height increases, the risk of injury may rise due to limited ankle use and increased moments in the knee and hip joints, potentially leading to muscle strength imbalances in adult women, particularly through the overuse of specific muscles.
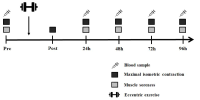
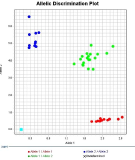
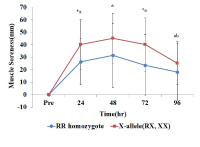
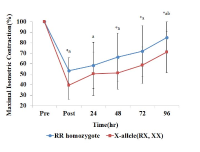
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to examine the change of muscle damage markers after maximal eccentric exercise and to verify the difference of recovery according to ACTN3 gene polymorphism. [Methods] Fifty healthy males participated in this study. Subjects performed 25 times/1 set (total 2 set) maximal eccentric contractions of the elbow flexor muscles on a modified preacher curl machine with a between-sets rest time of 5 min. Maximal isometric contraction (MIC) was measured 6 times (pre, post, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). Muscle soreness (SOR) was measured 5 times (pre, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). Blood samples were collected 5 times (pre, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). ACTN3 gene polymorphisms were identified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Data were analyzed using a 2-way repeated measure ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni test. [Results] Analysis of ACTN3 gene polymorphism revealed the following distribution: 22% RR (n=11), 50% RX (n=25), and 28% XX (n=14). Individuals were classified into the RR homozygote group (n=11) and the X-allele group (n=39). MIC showed a significant difference between groups and interaction (p<.05). The groups differed significantly in MIC at 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h after exercise and the X-allele group decreased more than the RR homozygote group. The groups differed significantly in muscle soreness and interaction (p<.05). SOR in the X-allele group was significantly higher than in the RR homozygote group at 24 h after exercise. Although blood CK activity was lower in the RR homozygote group than in the X-allele group, but there was no significant difference between the groups (p>.05). [Conclusion] The RR homozygote group showed lower muscle strength reduction rate, muscle soreness and blood CK activity than the X-allele group. This indicates that RR individuals have a lower risk of exercise-induced muscle damage than those with an X-allele.

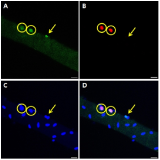
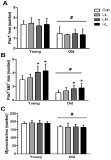
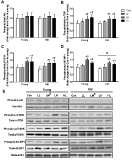
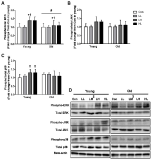
Purpose This is the first study to examine whether age impacts the response of single muscle fibers to high/low frequency and high/low volume electrical pulse stimulation. We performed in vitro experiments to evaluate the effect of low-frequency high-volume electrical pulse stimulation (EPS) on mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, and satellite cell activation in singles fibers of young and aged muscles. Methods Isolated single fibers from gastocnemius in 12-wk (n=21) and 72-wk (n=21) old male C57BL/6 mice were divided into four groups: 1) control (Con) received no EPS, 2) low-frequency low-volume EPS (LL), 3) low-frequency high-volume EPS (LH), and 4) high-frequency low-volume EPS (HL) were made to contract using independent EPS protocols. Satellite cell activation and anabolic pathway (mTOR and MAPK signaling) were measured before and after EPS. Results The number of quiescent (Pax7+/Ki67-) and active (Pax7+/Ki67+) satellite cells, myonuclear content and the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and ERK were higher in young when compared with old. However, regardless of age, LH and HL EPS significantly increased the number of activate satellite cells (142%, both) and phosphorylation of mTOR (129% and 133%, respectively), p70S6K (133% and 136%, respectively) and 4E-BP1 (140% and 129%, respectively) compared with Con. The protein expression of ERK phosphorylation only increased by LH EPS in both the young and old groups (123% and 125%, respectively). Conclusion Low-frequency high-volume EPS stimulated satellite cell activation and the mTOR signaling pathway in older similar to young muscle.

PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the lower limb muscle activity based on direction prediction presence or absence and gender during side cutting in healthy college students. METHODS The study participants included 14 healthy males and females (8 males; 6 females). All participants ran at full speed for a distance of 12m, and side-cutting was carried out at 45 degrees in a randomly indicated direction and in a fixed direction. Simultaneously, data regarding vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, and biceps femoris muscle activity of the dominant leg were collected using an electromyography sensor, and data regarding vertical acceleration were collected using an inertial sensor attached to the pelvis. A sync webcam was used for obtaining the initial contact of side cutting and the stance period time. During the 10 milliseconds (pre-activation) prior to the initial contact and 50% of the stance phase (loading phase), vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, and biceps femoris average muscle activity and hamstring to quadriceps ratio included as variables. RESULTS During the pre-activation and loading phase, the vastus medialis muscle activity of the male group was higher in the unexpected condition than in the expected condition. Furthermore, hamstring to quadriceps ratio was confirmed to be lower under unexpected condition compared to under expected condition during on loading phase. CONCLUSIONS The study results suggest that the risk of anterior cruciate ligament injury may increase with side cutting under unpredictable conditions. It is expected to provide useful information for identifying factors related to knee injury in the general population.

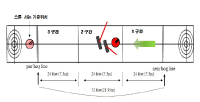
Purpose This is to provide essential data for training necessary for sweeping through the analysis of muscle activity generated at this time and how much sweeping and what trajectory moves the stone when the movement of the stone is controlled through sweeping. Methods To check and record the distance between the stones by checking the stop position of the stone made by sweeping each section, the length (progress distance) and width (progress direction) were recorded using a reference table and a record preparation table. With the EMG attached, a total of 60 sweeps were made 20 times each from the beginning of the section to the end of the section. Sweeping subjects were asked to sweep as much as possible under the same conditions in all three sections. Results As a result of the study, the muscle mobilization patterns of the 1st and 2nd sections of the stone with the faster speed and the 3rd section with the stone's slower speed appeared differently. It was confirmed that the sweeping motion of curling is a motion that is used evenly among the muscles of the upper extremity, and it can be verified that it is a suitable item for the development of upper body muscles. Also, the right deltoid's muscle activity rate during push and the right triceps brachii during pull was high. Conclusion Each section of the stone's sweeping effect is an exercise that has many variables, such as changes in atmospheric temperature and humidity, changes in ice temperature, temperature-size-number of pebbles, and the edge state-resilience of stones, etc. It is judged that experience can cope with these variables and requires training.

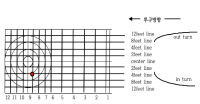

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the lower extremity muscles activity during forward side step by soccer field ground types. Methods Fifteen elite high school soccer players participated in this study. Muscle activation patterns were recorded at 2000 Hz during forward side step task. Surface EMG of the tibialis anterior(TA), soleus(SOL), medial gastrocnemius(MG), lateral gastrocnemius(LG), peroneus brevis(PB) muscle was recorded, and the root mean square of the EMG was normalized, using a maximum voluntary isometric contraction(%MVIC). One-way repeated ANOVA was used for comparison among three soccer field ground types(natural grass, artificial turf, hard ground). Results Artificial turf displayed greater soleus and peroneus brevis activities compare to natural grass during forward side step task. Conclusions The relationship between increased soleus and peroneus brevis activation and greater incidence of injury in artificial turf versus natural grass requires further study. Soccer players routinely training on artificial turf for prolonged periods should be carefully monitored.

