Purpose The purpose of this study is to examine effects of professional baseball home fans' perception of the community on their recognition of stadium spaces. Methods The subjects of the survey were home fans of baseball. A total of 600 questionnaire(100 fans each team: DOOSAN, LG, SK, LOTTE, HANHWA and KIA) were collected and 510 copies were used as the final analysis data. Collected data was processed by using SPSS 21.0 program. T-test, one-way ANOVA, correction analysis and multiple regression analysis were conducted to test hypothesis. Results There were significant differences of perceptions on community such as perceptions on sense of belonging; favored teams, perceptions on active involvement; gender and favored teams, perceptions on pride of the home town; gender, favored teams and glasses for viewing, and perceptions on classification; educational level and favored teams. There were significant differences of perceptions on stadium spaces such as perceptions on historicity; favored teams and viewing experience, perceptions on authenticity; favored teams and viewing experience, and perceptions on symbolism; age, favored teams and glasses for viewing. Among home fans' perceptions of their community, sense of belonging and pride of the home town had positive effects on their perceptions on historicity among perceptions of stadium spaces, while perceptions of classification had negative effects on them; sense of belonging and pride of the home town had positive effects on both perceptions of authenticity and symbolism. Conclusions The findings indicate that there is a close relationship between the community and professional baseball stadiums, and it is necessary to commonly enhance sense of belonging and pride of the home town for the community in order to promote positive perceptions on stadiums.
PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze factors associated with physical activity (PA) in older adults based on social ecological theory. METHODS Secondary analysis was conducted using raw data from the 2021 Community Health Survey. after excluding 129 non-responses in the PA domain, a total of 74,363 individuals were included in the final analysis. A total of eight factors, including personal (level of depression, history of falls), relational (relationships with neighbors, living alone), community (satisfaction with the local community system, safety), and environmental factors (living environment, natural environment), were selected in accordance with the key points of social ecological theory. To analyze social ecological factors related to the PA of older adults, we conducted a decision tree analysis using Chi-square automatic interaction detection (CHAID). RESULTS The average PA level among older adults was approximately 136 minutes, but the mode and median were both 0 minutes. A total of 20.2% of older adults met the physical activity recommendations, while 79.8% did not. According to the first split of the decision tree, living alone was the most relevant factor associated with the PA of older adults, followed by depression and falls. Older adults living alone, with a depression score of 10 or higher, and who had experienced a fall within the past year, were least likely to meet the PA recommendations. CONCLUSIONS This study urgently suggests that PA programs should target older adults living alone, experiencing depression, and falls.
PURPOSE This study developed and tested a theoretical research model delineating the relationships between sports consumers’ team identity and their response to regional identity, sense of community, and community contributions. METHODS To achieve the purpose of this study, a total of 1,196 spectators who attended professional baseball games were surveyed. For the data analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, convergent validity, discriminate validity, and composite reliability were performed to confirm the validity and reliability of the scale through AMOS 24.0. Research model and hypothesis testing were conducted using structural equation modeling, which used data from ten different professional baseball team area contexts. RESULTS The results provide empirical evidence of the positive influence of sports consumers’ regional identity and sense of community on team identity toward community contributions in sporting event area contexts. CONCLUSIONS This study confirmed the role of regional identity and sense of community in building professional sports team identities and community contributions.
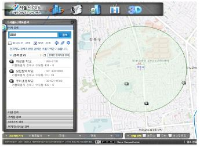
This study measured the accessibility of public exercise facilities within a residental area of a metropolitan community and examined how the accessibility can affect physical activity participation of residents. Initially, a total of 639 residents, who were aged between 19-70, visited Metabolic Syndrome Management Center of the Community Public Health Center, and registered for a Obesity Clinic Program, was listed as potential subjects. And those who responded to Physical Activity Questionnaire were selected for the analyses (n=92, 14.3% of 639). The relationships between physical activity level and accessibility to public exercise facilities were analyzed. Objective distance to public facility was related to ‘volume of participation to vigorous physical activity(r=.209)’, 'total volume of participation to physical activity(r=.206)’. And perceived distance to public facility was related to ‘volume of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.235)’. perceived transport time to public facility was related to ‘duration of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.239)’, ’volume of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.306)’, and ‘volume of participation to total physical activity(r=.273)’. In contrast, the difference between objective distance to public facility and perceived subjective distance to the facility was negatively related to ‘duration of participation to moderate-intensity physical activity(r=-.221)’. The perceived numbers of public facility was positively related to ‘frequency of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.237)’, ‘frequency of participation to walking(r=.273)’, ‘volume of participation to walking(r=.251)’ and 'total volume of participation to physical activity(r=.252)’. The predictor of 'total volume of participation to physical activity was perceived numbers of public facility(R2=.153, p=.046). The results revealed that the subjective accessibility to public health facilities was more influential to physical activity participation than the objective accessibility. Further research was warranted while using diverse populations as well as considering a inclusion of environmental factors.


The purpose of the study is to find the impact of social and economic factors in physical activity of children and youth. This study utilized the data from 4th Korean Children and Youth Panel Study(KCYPS), and the analysis were carried out based on the starting sample of 2,009 from ‘the elementary 4 panel’ and 1,978 from the ‘middle school 1 panel’ and 1,984 from the ‘high school 1 panel’, 5,971 full data were used in the final analysis. Data were processed using hierarchical regression analysis and it was statistically validated at the significance level of 0.05. First, Pearson r and Spearman ρ showed that all variables are statistically significant correlations. Second, among the first factors of personal and family characteristics, household income level(B=.113), family composition(B=-.049) and parental education (B=.060) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, parental education (B=.027) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Third, among the second factors of community-level characteristics, Gini coefficient (B=-.810), wealth concentrating (B=.120) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, the Gini coefficient (B=-0.315) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Additional factors that determine the coefficient of variation in the level 2 were found to be 0.623 and 0.001 respectively. Therefore, second factors of community-level characteristics are added such as Gini coefficient, wealth concentrating were explained to children and youth exercise time during physical activity 62.3%(p<.01) and subjective evaluation of physical education in grades 0.1%(p<.01). predictive power to

Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship among the social responsibility (economic responsibility, community cultural activity and social contribution activity), the image of the club, and the assets (image, reliability, attitude and loyalty) of the mother company. Methods The objectives of this research were the home fan in “2018 Shinhan Bank My Car KBO League.” A survey was conducted for 350 home fans of SK Wyverns who gathered in Incheon SK Happiness Dream Baseball Ground to watch the games of SK Wyverns vs. Samsung Lions held from April 6 (Fri.) to April 8 (Sun.). Data processing was done with PASW Ver. 18.0 and AMOS 18.0. Results Firstly, among the sub-factors of social responsibility, economic responsibility, community cultural activity and consumer protection had significant influence on the team image. Secondly, the team image had meaningful influence on the mother company image. Thirdly, the mother company image had significant influence on the mother company trust, mother company attitude and mother company loyalty. Fourthly, the mother company trust had significant influence on the mother company loyalty. Fifthly, the mother company attitude had significant influence on the mother company loyalty. Conclusions The mother companies of professional baseball clubs, too, will have to seek various ways for joint working with professional baseball clubs while actively supporting the activities of the professional baseball clubs being aware that professional baseball clubs give positive effect to the mother companies.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to find out whether they can contribute to the revitalization of urban communities. Methods This study conducted in-depth interviews and focus group interviews to collect qualitative data. The collected data were analyzed through the domain analysis and the classification analysis. Results The roles of sports club managers in leadership and network intermediaries were very important in the accumulation of social capital. The formation of staff members who work for the managing and activating sports clubs has created trust and satisfaction with the sport. Their activities contributed to the formation of social capital in sports clubs and played an important role in revitalizing sports clubs. Conclusions Sports club managers performed important roles in building trust and network with the club members and even other clubs through their leadership. These management activities are possibly contributed to the creation and accumulation as social capital. Therefore this research also showed the possibilities of extension to local community of the social capital through sports clubs.
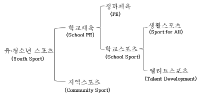
Purpose and Methods The purpose of this study is to clarify the concepts of ‘youth sport policy’ and policy areas as an alternative to school physical education concept and to provide a core conceptual framework for the development and implementation of youth sports policy in the future. Results The notion of youth sport policy is a process of seeking rational decision-making and optimal alternatives to solve the social problems associated with sports participation of youth in elementary school(aged 6 years) to high school(aged 18 years). The concept of 'youth sport' can reflect modern culture rather than 'school physical education' and it can be seen as more future oriented for lifelong participation in sports. The areas of youth sport policy are classified into physical education, school sport, and community sport. Physical education refer to the physical education classes operated by the Ministry of Education, and the school sport refers to the sports activities that take place throughout the school. Community sport is sports activities that are carried out outside the school by the choice of youth, which is the area where cooperation between the public sector and the private sector is needed. Conclusion In conclusion, healthy and active life for youth is required to establish cooperative governance of related organizations in order to ensure proper linkage between youth sport policy areas. Through this, it is necessary to solve the social problems of youth and promote their lifelong enjoyment of sport more consistently, efficiently and effectively.

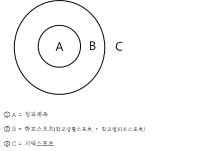
PURPOSE This study aimed to categorize consumers’ subjectivity on public value of citizen professional football club. METHODS Q-sample and Q-classification charts were developed based on theoretical background of the public value of citizen football clubs, and in-depth interviews with consumers were conducted using the Q-methodology. Q-classification and Q-factor analyses were conducted by selecting local residents as P-samples. RESULTS The public value of citizen football clubs was confirmed as ‘Type I: club-city win-win’, ‘Type II: social integration’, and ‘Type III: culture-led’. These types are contrary to previous studies that mainly focused on management and marketing, such as financial profitability and soundness, regional economic impact, and commercial value. This is the result of examining the public value of the citizen football club from based on the subjectivity of consumer, and it differs from that in previous studies. CONCLUSIONS This study reconfirmed the specificity and role of citizen football clubs in commercialized professional sports. It showed that citizen clubs must adopt organizational goal and operation method that are different from profit sports organizations (clubs).
PURPOSE This study investigated the associations between physical fitness and fall efficacy with thigh circumference in elderly women with osteopenia/osteoporosis. METHODS A total of 166 female participants aged 76.3±5.0 years with –1.0≥T-score of femur neck bone mineral density were voluntarily recruited from local community centers. The participants were classified as low 25%, middle 50%, and high 25% groups based on their thigh circumference. Physical fitness measurements, including strength, flexibility, aerobic endurance, and balance were measured with a standardized protocol. The Korean version of the fall efficacy scale (K-FES) was used to assess fall efficacy. Logistic regression analysis was used to estimate odd ratio (OR) of poor physical fitness and low fall efficacy according to thigh circumference levels. RESULTS In terms of physical fitness, the middle 50% group (OR=0.430, 95% CI=0.194-0.953) and high 25% group (OR=0.129, 95% CI=0.049-0.343) had significantly higher linear trend for poor physical fitness compared to the low 25% group (reference), (p<0.001). In fall efficacy, the middle 50% group (OR=0.279, 95% CI=0.119-0.656) and high 25% group (OR=0.100, 95% CI=0.036-0.275) had significantly higher linear trend for low fall efficacy compared to the low 25% group (reference) (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS The current findings suggest that maintaining high thigh circumference via regular physical activity and diet may contribute to attenuation of decreased risk for poor physical fitness and low fall efficacy in elderly women with osteopenia/osteoporosis.