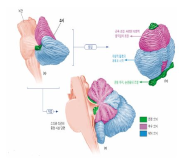
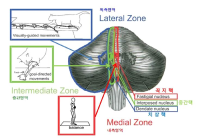
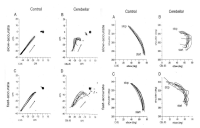
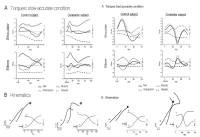
The cerebellum is one of the major parts of the brain involved in the motor control including motor coordination, muscle tone, balance, and the learning of motor skills. The purpose of this review paper was to explore of pathophysiology, anatomical function and neurophysiological mechanism for cerebellum. For this, we sought to examine of previous study related cerebellar disease. Specifically, this paper suggested that motor deficiency of limb movements, coordination, gait/posture balance, adaptation of during movement execution through information proprioception or kinaesthesia, and motor planning and programming of cerebellar patients. We expect that this review will be able to offer the useful information to research. For example, movement scientists will provide an academic information about cerebellar ataxia. Patients and their families will provide relevant information to the daily life (e.g., management and rehabilitation exercise).




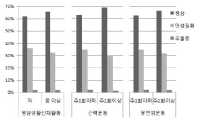
This study examined the association between physical activity (PA) and the prevalence of chronic disease and chronic depression. Additionally, the relationships between PA and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among general population, categorized by healthy, chronic disease and depression were investigated. Cross-sectional data includes 9,739 participants (4,351 males, 5,659 females, over 19 years old) who completed physical activity, chronic disease and HRQoL questionnaires from The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Complex samples frequency, descriptive, cross-tab and logistic analysis were used. Estimated prevalence of chronic disease and depression were significantly different between PA levels and frequency. Based on odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI), participating in lower levels of daily PA including less resistance and flexibility exercise were associated with an increased likelihood of chronic disease. Less frequency of resistance PA was also associated with an increased likelihood of depression. Estimated prevalence of HRQoL was different according to PA in the healthy and chronic disease populations. Adjusted OR and confidence intervals represented through lower levels of daily PA and less frequency of resistance PA were associated with an increased likelihood of poor HRQoL in the chronic disease population. No significant OR between PA and HRQoL in the depression population was observed.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between physical activity and depression according to the presence of disease. Methods A survey and basic assessment were conducted for 2,754 (Male=1,025 and Female=1,729) aged 40 and over who participated in the rural-based cohort study. The survey included physical activity, depression scale and disease preservation. The basic assessment measured height, weight, and body fat percentage. The measured data were analyzed by using logistic regression to examine the relationship between physical activity and depression prevalence. Results First, physical activity reduced the prevalence of depression by 33% and 51%, respectively, in the general population and in patients with the disease. Second, physical activity once or twice per week reduced the prevalence of depression in patients with disease by 51%, and at least three physical activities reduced the prevalence of depression by 37% in the general population and 33% of patients with disease. Third, physical activity less than 150 minutes per week reduced the prevalence of depression in patients with disease by 43%, and physical activity of more than 150 minutes and less than 300 minutes per week reduced the prevalence of 43% of the general population and 52% of patients with disease. Physical activity over 300 minutes per week had a 38% reduction in the prevalence of depression in the general population. Conclusions This study suggests that the level of physical activity suggested by the ACSM guidelines is appropriate to reduce the prevalence of depression. In addition, the patients with the disease was found to be effective with less frequency and amount of physical activity than the general person.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of continuous exercise and the accumulation of short-duration exercise for 12 weeks on body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease indices in overweight men in their 30s. METHODS Participants in the continuous exercise group (CE; n=13) performed a circuit exercise program of 30 min/session, 3 sessions/week for 12 weeks. Participants in the accumulation of short duration exercise group (ASE; n=12) performed the same exercise time of 30 min per day, divided into three sessions of 10 min. Body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease indices were measured pre- and post-test and were compared by utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. RESULTS 1) Regarding body composition, body weight, body mass index, skeletal muscle mass, waist circumference, and fat mass decreased significantly, while hip circumference increased significantly in the CE group. Waist circumference and skeletal muscle mass decreased significantly, while hip circumference increased significantly in the ASE group. 2) Regarding physical fitness, right grip strength, sit and reach, sit up, and maximal oxygen uptake increased significantly in both groups. 3) Regarding hypertension indices, there were no significant differences in both groups, but they showed a tendency to improve. 4) Regarding hyperlipidemia indices, triglycerides (TG) decreased significantly in both groups, and total cholesterol (TC) decreased significantly in the CE group. 5) Regarding diabetes indices, there were no significant differences in both groups, but a tendency to improve was noticed. 6) Regarding arteriosclerosis indices: TG/high density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio decreased significantly in both groups, and the TC/high density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio decreased significantly in the CE group. CONCLUSIONS We concluded that both the accumulation of short duration exercise and continuous exercise can be effective in improving body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease in overweight men.
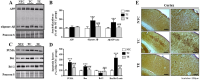
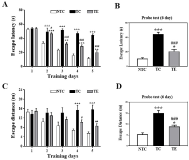
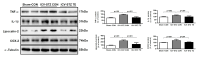
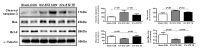
Purpose The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of treadmill exercise on mitochondrial quality control in the APP/sw transgenic mice model of Alzheimer's disease(AD). Methods The experimental mice were divided into non-tg-control (NTC, n=10), tg-control (TC, n=10), and tg-exercise (TE, n=10), and treadmill exercise was conducted for 12 weeks (15m/min, 60min, 5 times/week). And then, we measured the cognitive function using MWM and the brain cortex was evaluated to determine whether any changes in the oligomer Aβ, apoptotic-related factors, mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis. Results As a result, treadmill exercise significantly reduced oligomer amyloid and also had a positive effect on proteins (PUMA, Bax, Bcl-2) associated with apoptosis. In addition, through the treadmill exercise, PINK-1 decreased, and increased parkin, showing that active inhibition of mitophagy has been partially relaxed. It has been confirmed that the key autophagy markers LC3 and p62 significantly reduce p62 expression in TE group compared to TC group, and that LC3-II/LC3-I ratio tended to decrease, although not significant, increasing the activity of mitophagy. Next, proteins related to mitochondrial biosynthesis (SIRT-1, PGC-1α, Tfam, and COX-IV) have been identified, and the treadmill exercise has confirmed that the expression of all proteins has increased in part. Finally, cognitive has been shown to improve cognitive by shortening both swimming distance and time through treadmill exercise. Conclusions Thus, our finding suggested treadmill exercise alleviates cognitive dysfunction by improving mitochondrial quality control(mitophagy, mitochondrial biogenesis) and neuronal cell death via reducing amyloid accumulation, which may play a role in a preventive strategy for AD.

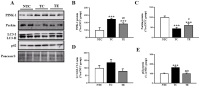
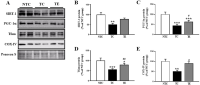
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of regular vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) level, aging- and lifestyle disease-related blood components in middle-aged women. Methods The participants were recruited from a total of 19 physically healthy people aged 50-59 years, and were randomly divided into vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise (VIAE, n = 10) and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (MIAE, n = 9) group. The participants were performed vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise three times a week for eight weeks, and body composition measurement, graded exercise test, blood collection were performed before and after. Results Mean exercise time was significantly longer in the MIAE group than in the VIAE group. The V̇O2max was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. Body weight, BMI, and body fat percentage were significantly lower than pre both groups. The BDNF concentration was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. The dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-s) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentration were significantly higher than pre both groups. The free fatty acid and triglyceride concentrations were significantly lower than pre both groups, and HDL-C concentrations were significantly higher than pre both groups. Conclusions Vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise not only increases maximal oxygen uptake and blood BDNF level in middle-aged women, but also induces positive changes in aging-related hormones and lifestyle-related blood variables.

[Purpose] The study was designed to examine the effects of a 10-week sports climbing training on body composition and surrogate indices of major lifestyle disease in obese elderly women. [Methods] Twenty elderly women, whose percent body fat was over 35%, were randomly assigned into one of two groups, i.e., sports climbing training group (TR: n=10) and control group (CON: n=10). The subjects in TR completed sports climbing training program with 5.8 and 5.9 of difficulty, at 11-13 of ratings of perceived exertion (RPE), 60 min/session, three sessions/wk for 10 weeks. Independent variables regarding body composition and major lifestyle disease, i.e., hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis, were measured and compared between two groups as well as between two tests simultaneously using a repeated two-way ANOVA. [Results] Regarding physique and body composition, there were significant interactions between group and test in body weight, body mass index, fat mass, and percent body fat. These variables decreased significantly in TR. 2) Regarding indices of hypertension, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure, and pulse pressure decreased significantly in TR. Regarding indices of dyslipidemia, triglyceride decreased significantly in TR. Regarding indices of atherosclerosis, TG/HDL-C ratio decreased significantly in TR. [Conclusions] It was concluded that the 10-week sports climbing training would be beneficial for reduction of body fat despite its’ influence on fat-free mass was limited, and would also contribute on improving surrogate indices of hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis in obese elderly women. Future research investigating the effects of various period, intensity, duration, and frequency of sports climbing training would be warranted.

Purpose The study was designed to compare physical fitness, indices of lifestyle disease, and biochemical property of muscle according to sarcopenia and obesity in elderly women. Methods One hundred elderly women were alloted to one of four groups, i.e., sarcopenia+obesity (SO: n=20) group, sarcopenia (S: n=20) group, obesity (O: n=29) group, and normal (N: n=31) group. Criterion for sarcopenia was 'appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM)/height2<5.4 kg/㎡', and criterion for obesity was 'percent body fat>35%'. Dependent variables regarding physical fitness, lifestyle disease, and biochemical property of muscle were measured and compared among four groups. Results 1) Regarding daily living fitness, grip strength, upper arm flexion, sit-and-reach, up and go, and VO2max in SO group and S group were significantly lower than N group. Regarding isokinetic function, peak torque and average power in SO group and S group were significantly lower, and relative values to body weight in SO group and O group were significantly lower than N group. 2) Regarding hypertension, resting HR and RPP in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Regarding diabetes mellitus, fasting plasma glucose and HOMA-IR in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Regarding hyperlipidemia, HDL-C in SO group and O group were significantly lower than S group and N group. Regarding atherosclerosis, TC/HDL-C ratio and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. 3) Regarding biochemical property of muscle, IL-6 in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Conclusion It was concluded that physical fitness was declined in sarcopenia elderly, and that relative value of isokinetic function, indices of lifestyle disease, and inflammation markers were deteriorated in obesity elderly. Especially, the decline and deterioration of physical fitness and indices of lifestyle disease were even more severe in the elderly who had the both status. Therefore, the efforts should be made to prevent and improve sarcopenia and/or obesity.

The purpose of this study was to explore the effects of 6-week treadmill exercise on inflammation and neuronal cell death in the hippocampus of intracerebroventricular (ICV) streptozotocin (STZ)-injected Alzheimer's disease (AD) rats. The experimental animals were divided into Sham-CON group (n=10), ICV-STZ CON group (n=10) and ICV-STZ TE group (n=10). The treadmill exercise was conducted for 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week, for 6 weeks. First, in a water maze test, it turned out that the time and distance of finding an escape platform significantly increased in the ICV-STZ CON group as compared to those in the Sham-CON group. In contrast, it turned out that the time and distance of finding the escape platform significantly decreased in the ICV-STZ TE group in which the treadmill exercise was carried out as compared to those in the ICV-STZ CON group. The expression of marker of astrocytes, Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) increased in the ICV-STZ CON group as compared to that in the Sham-COM group, but that in the ICV-STZ TE group decreased as compared to that in the ICV-STZ CON group. Regarding inflammatory reactions, it turned out that the expressions of TNF-α, IL-1β, Lipocalin-2 and COX-2 increased in the ICV-STZ CON group as compared to those of the Sham-CON group, but it turned out that those of the ICV-STZ TE group decreased as compared to those of the ICV-STZ CON group. Regarding neuronal cell deaths, the expressions of caspase-3 and Bax increased in the ICV-STZ CON group as compared to the Sham-CON group, but it turned out that the expression of Bcl-2 decreased, and the neuronal cell deaths increased. However, it turned out that the neuronal cell deaths decreased in the ICV-STZ TE group in which the treadmill exercise was carried out as compared to that in the ICV-STZ CON group. Therefore, it turned out that the treadmill exercise showed positive effects on improving cognitive ability by reducing inflammatory reactions and inhibiting neuronal cell deaths in the rats with AD. In other words, aerobic exercise like treadmill exercise can be applied as an effective alternative to improve symptoms of AD.


PURPOSE The United Nations (UN) has proposed 17 Sustainable Development Goals and has been extending its efforts to achieve them. Sport can be linked closely to the third goal, which is related to health and well-being. Therefore, this study aimed to explore and to analyze individual's changed sport activities during the COVID-19 pandemic, focusing on ways to achieve health and well-being related goals through sport. METHODS A qualitative research method was employed, and in-depth interview methods were used for data collection. For data analysis, categorization and itemization were used along with content analysis. RESULTS Looking at the derived results, in the context of an infectious disease such COVID-19, sport activity patterns have changed due to reasons such as stadiums or facilities, interpersonal reasons, fear, inconvenience, staying healthy, increase in leisure time, and individual preferences. CONCLUSIONS Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the indicators of health and well-being related SDGs are exhibiting a downward trend. At this point, it is necessary to find a way to achieve the goal through sport that can participate voluntarily for the purpose of pursuing pleasure.