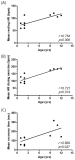
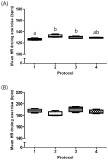
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate changes of the cardiovascular system by comparing heart rate (HR) and blood responses to exercise in younger and older adult dogs and to verify the value of dogs as aging model in exercise science research. Methods A total of 11 healthy beagles were divided into 2 groups according to age: younger adult dogs (1~2 years old, 7 animals) and older adult dogs (9~11 years old, 4 animals). Each animal exercised on the treadmill for 25 minutes, twice a week, and for 4 weeks. The exercise intensity was gradually increased by applying four different protocols. Resting HR, HR during exercise, and HR recovery time were determined as HR parameters. Biochemical analysis was performed on blood samples. The independent Student’s t-test and one-way ANOVA were used to analyze the mean difference of each variable. The associations between age and HR parameters were determined using Spearman‘s analysis. Results Older adult dogs showed higher HRs during rest and exercise than younger adult dogs. HR recovery time was significantly longer in older adult dogs than in younger adult dogs. A strong positive relationship was observed between beagles’ age and resting HR, HR during exercise, and HR recovery time, respectively. The heart rate response to the treadmill exercise was similar between the 1st week and 4th week in younger and older adult dogs. Exercise significantly reduced the white blood cell level in older adult dogs and increased the alkali phosphatase level in younger adult dogs. Conclusions The results of this study demonstrated that short-term treadmill exercise may have a positive effect on the aerobic capacity, inflammation, and bone formation, suggesting that dogs are valuable as aging model in exercise science research.

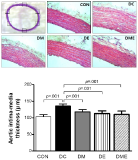
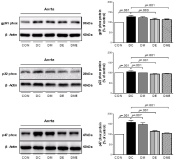
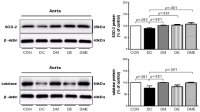
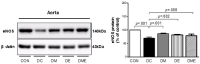
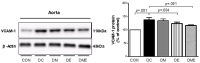
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment on NADPH oxidase, antioxidation and vascular function-related factors in aortic of D-galactose-induced aging rats. Methods To induce the animal model of aging, D-galactose was diluted in saline, and a dose of 100mg /kg was intraperitoneally injected into Sprague-Dawley rats once a day for a total of 10 weeks. Rats were divided into five groups: Control group (CON, n=9), D-galactose control group (DC, n=9), D-galactose+MitoQ group (DM, n=9), D-galactose+Exercise group (DE, n=9), D-galactose+MitoQ + Exercise group(DME, n=9), and treadmill exercise was conducted for 5 days/week during 8 weeks with gradual increase of intensity. MitoQ treatment was intraperitoneally injected at a concentration of 100μM/kg twice a week for 8 weeks during the research period. Results The result showed that treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment decreased the expression of NADPH oxidase level and increased antioxidant enzyme such as SOD-2, catalase. It lead to positive effects such as increasing the level of eNOS, a protein involved in vascular function while decreasing the level of VCAM-1. In addition, as a result, it showed the structurally reduced intima-media thickness. Conclusions It can be concluded that treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment are effective in ameliorating and treating vascular dysfunction resulting from aging.


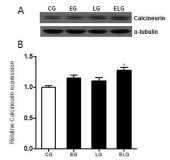
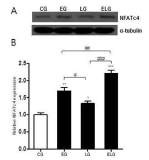
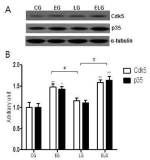
It has been reported that continuous exercise and bright light exposure improved resistance to stress and reduced depression and anxiety, which were attributed to enhancing neurotransmitter GABA exocytosis and stimulating neurogenesis. In this study, the effects of treadmill exercise and bright light exposure on the expression of GABAAreceptor activity, calcineurin and calcineurin calcium signaling pathway-depended NFATc4, neurogenesis-related protein Cdk5 and specific regulator factor of Cdk in neurogenesis p35 in the hippocampus of rats were investigated by western blot assay. The expression of GABAAreceptor, Cdk5 and p35 significantly increased in the exercise+light group compared to the control group and the light group. The expression of KCC2 and NFATc4 significantly increased in the exercise+light group compared to all the other groups. And the expression of calcineurin significantly increased in the exercise+light group compared to the control group. The overall results showed that exercise and bright light stimulated neurogenesis of the hippocampus in rats and had positive effects on improving the brain neuronal function.


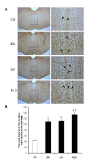
The main purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of treadmill exercise and bright light exposure on serotonin expression in rat brain. Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly assigned into four groups (n=9 in each group), specifically, control group (CG), exercise group (EG), light group (LG), and exercise+light group (ELG). Rats in EG were subjected to treadmill exercise (5 days/week, 30 min/day), LG rats exposed (5 days/week, 30 min/day, 10,000 Lux), ELG rats subjected to treadmill exercise in combination with exposure, and CG rats remained sedentary over a four-week period. We observed a significant increase in serotonin expression in the raphe obscurus nucleu and the midbrain of rats in EG, LG, and ELG, compared to CG. Interestingly, serotonin expression was significantly increased in ELG, compared to EG and LG in the raphe obscurus nucleu via immunohistochemistry. In the western blot, it showed a increased pattern in ELG, compared to EG and LG. The overall results showed that treadmill exercise and/or bright light had positive effects on serotonin expression in the brain. Therefore, we suggest that moderate exercise or exposure to bright light during a growth child may be beneficial in brain action.

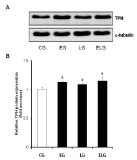

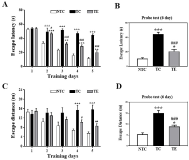
The purpose of this study was to explore the effects of 6-week treadmill exercise on inflammation and neuronal cell death in the hippocampus of intracerebroventricular (ICV) streptozotocin (STZ)-injected Alzheimer's disease (AD) rats. The experimental animals were divided into Sham-CON group (n=10), ICV-STZ CON group (n=10) and ICV-STZ TE group (n=10). The treadmill exercise was conducted for 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week, for 6 weeks. First, in a water maze test, it turned out that the time and distance of finding an escape platform significantly increased in the ICV-STZ CON group as compared to those in the Sham-CON group. In contrast, it turned out that the time and distance of finding the escape platform significantly decreased in the ICV-STZ TE group in which the treadmill exercise was carried out as compared to those in the ICV-STZ CON group. The expression of marker of astrocytes, Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) increased in the ICV-STZ CON group as compared to that in the Sham-COM group, but that in the ICV-STZ TE group decreased as compared to that in the ICV-STZ CON group. Regarding inflammatory reactions, it turned out that the expressions of TNF-α, IL-1β, Lipocalin-2 and COX-2 increased in the ICV-STZ CON group as compared to those of the Sham-CON group, but it turned out that those of the ICV-STZ TE group decreased as compared to those of the ICV-STZ CON group. Regarding neuronal cell deaths, the expressions of caspase-3 and Bax increased in the ICV-STZ CON group as compared to the Sham-CON group, but it turned out that the expression of Bcl-2 decreased, and the neuronal cell deaths increased. However, it turned out that the neuronal cell deaths decreased in the ICV-STZ TE group in which the treadmill exercise was carried out as compared to that in the ICV-STZ CON group. Therefore, it turned out that the treadmill exercise showed positive effects on improving cognitive ability by reducing inflammatory reactions and inhibiting neuronal cell deaths in the rats with AD. In other words, aerobic exercise like treadmill exercise can be applied as an effective alternative to improve symptoms of AD.


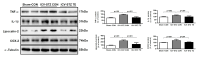
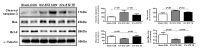

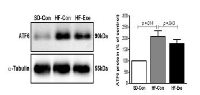
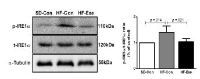
This study was to performed to the effect of 8-week endurance exercise influences on body weight, glucose tolerance and ER-stress in soleus of 16weeks Rats fed High-Fat diet. Rats were randomly assigned to 3 group; (1)Sprague-Dawley Control diet (SD-Con/n=4), (2)High-Fat diet Control (HF-Con/n=4), (3)High-Fat diet Exercise (HF-Exe/n=4). Exercise group ran on the treadmill for 30min/day at the level of 21m/min for 5days/week during 8weeks. Results showed that body weight and glucose tolerance of the HF-Con group was remarkably increased(p<.05) compared to other groups. However, HF-Exe group significantly decreased body weight and glucose tolerance compared to HF-Con group. Moreover, level of GRP78, ATF6, PERK and IER1⍺, which are main proteins of ER-stress were significantly increased in HF-Con group higher than other group, whereas HF-Exe group significantly decreased the expression of GRP78, ATF6, PERK and IER1⍺. Taken together, these finding suggested that the reduction of the body weight, glucose tolerance and unfolded protein response by treadmill exercise may represent a positive adaptation protecting against high-fat diet-induced ER stress.




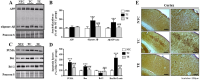
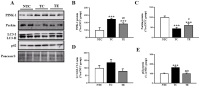
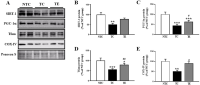
Purpose The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of treadmill exercise on mitochondrial quality control in the APP/sw transgenic mice model of Alzheimer's disease(AD). Methods The experimental mice were divided into non-tg-control (NTC, n=10), tg-control (TC, n=10), and tg-exercise (TE, n=10), and treadmill exercise was conducted for 12 weeks (15m/min, 60min, 5 times/week). And then, we measured the cognitive function using MWM and the brain cortex was evaluated to determine whether any changes in the oligomer Aβ, apoptotic-related factors, mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis. Results As a result, treadmill exercise significantly reduced oligomer amyloid and also had a positive effect on proteins (PUMA, Bax, Bcl-2) associated with apoptosis. In addition, through the treadmill exercise, PINK-1 decreased, and increased parkin, showing that active inhibition of mitophagy has been partially relaxed. It has been confirmed that the key autophagy markers LC3 and p62 significantly reduce p62 expression in TE group compared to TC group, and that LC3-II/LC3-I ratio tended to decrease, although not significant, increasing the activity of mitophagy. Next, proteins related to mitochondrial biosynthesis (SIRT-1, PGC-1α, Tfam, and COX-IV) have been identified, and the treadmill exercise has confirmed that the expression of all proteins has increased in part. Finally, cognitive has been shown to improve cognitive by shortening both swimming distance and time through treadmill exercise. Conclusions Thus, our finding suggested treadmill exercise alleviates cognitive dysfunction by improving mitochondrial quality control(mitophagy, mitochondrial biogenesis) and neuronal cell death via reducing amyloid accumulation, which may play a role in a preventive strategy for AD.

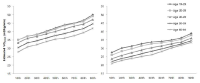
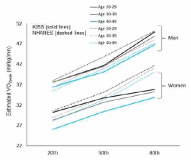
To provide the distribution of cardiorespiratory fitness including Bruce treadmill exercise time and estimated peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) and investigate association with cardiorespiratory fitness and metabolic syndrome, sedentary lifestyle, or education level among Korean adults. Analysis of data on 2,006 adults (19-64 yr) who had completed a maximal grade treadmill exercise test, from the Sports Institute of Sports Science Fitness Standards (KISS FitS) project 2014-2015. The mean maximal exercise time was 11’26’‘, 11’18’‘, 11’06’‘, 10’03’‘ and 8’51’‘ (minutes and seconds) for men 19-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59 and 60-64 years of age, respectively, for women, it was 9’49’‘, 9’09’‘, 8’42’‘, 8’01’‘ and 7’33’‘ for the corresponding age groups. The mean peak oxygen uptake was estimated as 42.3, 41.8, 41.2, 37.6 and 33.6 ml/kg/minute for men 19-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59 and 60-64 years of age, respectively, For women, it was 34.0, 31.8, 30.3, 28.0 and 26.4 ml/kg/minute for the corresponding age groups. A positive association between cardiorespiratory fitness level and education level was observed for both men and women. Furthermore, participants with sedentary lifestyle had a significantly lower cardiorespiratory fitness than participants with activity lifestyle. Finally, Men with moderate and high fitness level had 50% and 87% lower odds for the metabolic syndrome, and women had 48% and 50% lower odds for the metabolic syndrome, respectively, than the ones with low fitness level after adjustment for age, smoking, alcohol intake, and sedentary lifestyle. These results can be used to track future Korean assessments and to evaluated interventions. The differences in fitness status by education level, sedentary lifestyle or metabolic syndrome can also be used to develop health policies, program and educational services.

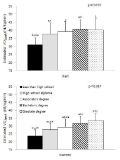
Purpose The aim of this study is to find how the pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise effect on the body composition, exercise performance ability, blood factor and obesity related hormone, and to verify the effect of pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise as an effective substance for obesity improvement. Methods This study selected 20 obese men in their twenties who has more BMI than 25kg/m2, and are applicable in 25% of the body fat, and randomly sampled group of 10 people for pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise (PYA), and 10 people for placebo intake and aerobic exercise (PLA). Intake of pyruvate and placebo was implemented for 10 weeks, 6 g a day, and aerobic exercise, treadmill exercise in the intensity of 50 ~ 60%’s target heart rate, was conducted for 10 weeks, 3 times a week, 60 minutes a day. To demonstrate the effect of pyruvate intake and aerobic exercise, all of the body composition, exercise performance ability, Lactate, and blood factor and hormone related to obesity were measured before and after the test in the same manner. Results The main results from this study are as follow; 1) In the case of body composition, in PYA, weight(p < .01), BMI(p < .05), body fat percentage(p < .01), and body weight without fat(p < .001) are reduced meaningfully. 2) In the exercise performance ability increased significantly in both PYA(p < .01) and PLA(p < .001) for V˙O2max, Also, in the case of distance during the exercise, PYA(p < .01) and PLA(p < .05) increased significantly in 15 minutes and PYA(p < .01) and PLA(p < .05) 30 minutes, but only in PYA from 45 minutes(p < .01) to 60 minutes(p < .05) 3) In case of Lactate, the significant decrease in PYA during stabilization and the significant increase in PYA after 30 minutes of exercise was not seen after 45 minutes 4) In the case of blood factor, HDL-C showed a meaningful decrease in PLA(p < .05) and Leptin showed a meaningful decrease in PYA(p < .001). Conclusions To sum up these results, it was more effective for the group of PYA which ingested pyruvate in improving obesity, even when the same aerobic exercise is conducted.

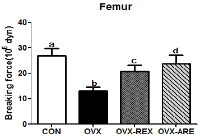
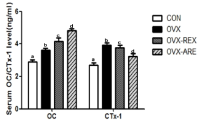
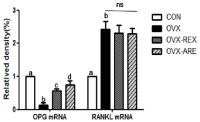
Purpose Osteoporosis is a systemic metabolic bone disease characterized by gradual decrease of bone mass and damage of the bone microstructure. In particular, postmenopausal osteoporosis is the most common type in women after menopause. This study aims to investigate the effects of combined exercise training on bone mineral density (BMD) and OPG/RANKL mRNA levels in ovariectomized rats. Methods A total of 40 Sprague-Dawley female rats were randomly divided into four groups: (1) CON (sham-operation, n=10), (2) OVX (ovariectomy, n=10), (3) OVX-REX (ovariectomy-resistance exercise, n=10), and (4) OVX-ARE (ovariectomy-combined aerobic and resistance exercise, n=10). Combined exercise training was performed on a treadmill and ladder adapted to rats in alternate days (4 days/wk, for 12 wk). Results Compared to the OVX group, all exercise treatments increased BMD and bone breaking force(p<0.05). In the bone turnover markers, serum C-terminal telopeptides of type-1 collagen (CTX-1) was significantly decreased in the exercise groups compared with OVX group and osteocalcin (OC) level was increased in the exercise groups (p<0.05). Additionally, in the exercise groups, expression of OPG mRNA was significantly increased compared with OVX group (p<0.05), and RANKL mRNA was slightly decreased but no significant between groups. Furthermore, OVX-ARE group showed more effects than OVX-REX group. Conclusions These results suggest that combined exercise may be a more effective therapeutic strategy to prevent and delay postmenopausal osteoporosis than resistance-only training.