PURPOSE This study aimed (1) to analyze the behavioral intention and use behavior among the consumers of online home training contents via YouTube by employing the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT); (2) to test the moderating effects of risk perception toward the coronavirus (COVID-19) infection, and 3) to test differential impacts of generational difference across millennial and baby boom generations. METHODS A total of 400 questionnaires were distributed, and 383 samples were used for the final analysis after excluding 17 incomplete responses. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 25.0 and AMOS 22.0. RESULTS It was found that (1) the performance expectancy, the effort expectancy, and the social influence had positive effects on behavioral intention; (2)the facilitating condition had negative effects on the use behavior; (3) the behavioral intention had positive impact on the use behavior. Moreover, the risk perception toward the COVID-19 infection did not have moderating impacts on the UTAUT model, whereas generational differences did. CONCLUSIONS Our results suggest that the marketing strategy that improves exercise performance, convenience, and social influencing factors may be key to home training customers' behavioral intention and use behavior. Furthermore, home training material makers should recognize that the features and infrastructure required for the two generations are distinct and develop a separate marketing strategy for each.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to analyze the effect size of the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT) in the sports field using a meta-analysis. METHODS After identifying related studies by using RISS, 22 articles were selected and used to analyze the relationship between UTAUT sub-factors (performance expectancy [PE], effort expectancy [EE], social influence [SI], and facilitating conditions [FC]) and intention to use via the comprehensive meta-analysis program. RESULTS The results are as follows: First, the effect size between PE and intention to use was 0.521. Second, the effect size between FC and intention to use was 0.514. Third, the effect size between EE and intention to use was 0.500. Finally, the effect size between SI and intention to use was 0.475. CONCLUSIONS Diverse strategies can be derived to increase consumers' intention to use in the sports field using the UTAUT model.
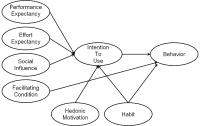
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the factor that influence the using behavior of online sport media by university students applying Unified theory of acceptance and use of technology 2(UTAUT 2). Methods The study performed a research survey using convenient sampling method. The sample was 235 university students who had experience with online sport media. The data were analyzed through frequency analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, and structural equation model using SPSS Windows ver . 20.0 and AMOS 20.0. Results The results showed that, firstly, performance expectancy and effort expectancy had a positive effect on intention to use, however, no significant influence on social effect on intention to use. Secondly, facilitating condition had positive effect on usage behavior. Thirdly, hedonic motivation had positive effect on intention to use. Fourthly, Habit had positive effect on the intention to use and usage behavior. Lastly, intention to use had positive effect on usage behavior. Conclusion Based on the conclusion of this study, online sports media companies should provide useful and convenient viewing experience by providing personalized services, and should apply various attraction strategies to habitually use sports online media.

PURPOSE This study aimed to explore the structural relationships between technology-related factors and the intention to use baseball data, drawing upon the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) and technology readiness (TR). METHODS Survey data from 203 Korean professional baseball players were used in frequency, reliability, correlation, and confirmatory factor analyses as well as structural equation modeling. RESULTS Positive TR positively influenced performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, and conditions facilitating baseball data use. Negative TR did not significantly impact performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, and conditions facilitating baseball data use. Performance expectancy, effort expectancy, and facilitating conditions were found to positively influence data use intention, while social influence did not significantly impact data use intention. CONCLUSIONS The findings suggest that increasing performance expectancy, effort expectancy, and facilitating condition factors could be key to enhancing the intention to utilize baseball data.