PURPOSE This study analyzed the relationship among coaching behaviors, motivational climate, sports competence, effort, and failure tolerance as perceived by high school athletes. Additionally, it examined whether motivational climate, competence, and effort mediate the relationship between coaching behaviors and failure tolerance. METHODS Using questionnaires measuring autonomy-supportive coaching behavior, controlling coaching behavior, motivational climate, sports competence, effort, and failure tolerance, 365 high school athletes were surveyed. Using SPSS 28.0 and Amos 28.0 software, descriptive statistics and structural equation modeling were conducted along with the following types of analyses: reliability, correlation, confirmatory factor, convergent validity, and discriminant. Additionally, the bootstrap method was used to verify serial multiple mediating effects. RESULTS Autonomy-supportive behavior had a significant positive effect 1) on motivational climate, sports competence, and effort and 2) on failure tolerance. 3) Controlling coaching behavior had a significant negative effect on motivational climate and sports competence. 4) Motivational climate and 5) sports competence both had a significant positive effect on effort. 6) Effort had a significant positive effect on failure tolerance. Last, in the relationship between autonomy-supportive behavior and failure tolerance, motivational climate, sports competence, and effort showed partial mediating effects. CONCLUSIONS This study confirms the importance of coaches’ autonomy-supportive behavior in determining failure tolerance among adolescent athletes. Based on this information, counseling (educational) programs aimed at enhancing performance can be developed and provided in sports settings, thus fostering success among athletes.
Purpose Highly popular these days, eSport is inviting increasing scholarly attention and research. Scholarly work on eSport, however, remains focused on whether eSport is a “real” sport, that is, its sporting qualities and status, excluding ethical issues. This paper analyzes ethical issues about cognitive enhancement drugs often associated with eSport in order to suggest guidelines for resolving these issues. Methods First, environmental features of eSport are examined to find out types of cheating in eSport, as well as the ways eSport athletes are exposed to drugs. Next, ethical issues of cognitive enhancement drug use and why they are important are discussed, drawing upon multiple scholars. Last, this paper argues that the ban on drug use conventionally implemented in sport is not appropriate to eSport due to the characteristics of eSport. The paper concludes with possible future approaches to this issue. Results The ban lists administered by ESIC and WADA would not work for the need of eSport athletes and even run a risk of stunting the growth of eSport industries. It is thus important to think up an appropriate drug-related policy for eSport. Preemptive education for eSport athletes is also required to promote the ethical consciousness and judgment regarding drug use. Conclusions Insofar as eSport’s huge popularity leads to the increased status of eSport athletes, thereby exerting much influence on young people, ethical questions about eSport, drug use in particular, need to be urgently discussed for the sake of eSport’s wholesome development.
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine contemporary sports reality and its problems through the feature-length independent film <Not Out>, which focused on baseball, a popular sport, and highlighted its rather dark side. METHODS The researcher performed a textual analysis using the perspective of critical theory. RESULTS Gwang-ho was the hero of a walk-off hit in the national baseball competition final, who suffered from three career strikes during his third year of high school and thought that he had bright future ahead of him. Before the amateur draft, Gwang-ho boldly rejected the proposal of a trainee contract from a professional team (strike 1), then he was subsequently not selected in the amateur draft (strike 2), before he applied for the college entrance examination for baseball specialties, and was eventually rejected. (strike 3) In the end, he was able to enter college through a bribe given by his father (not-out situation). CONCLUSIONS <Not Out> is a film based on a true story, and it showcased the realities of elite sports by revealing the dynamics of society and school, where the main character responded with reluctance and indifference. This movie highlighted the realities of delinquency, violence, abusive language, bribe, and violations of the right to learn and how these have continued to evade the law despite being thought to be gone.
PURPOSE This study examined levels of safety knowledge and practice among recreational sports participants, focusing particularly on impacts of gender, age, injury experience, and exercise-level profile. In sports environments, understanding these factors is essential for developing targeted strategies to promote safe behaviors. METHODS Survey data from 7725 participants engaged in regular recreational sports activities were analyzed. Latent Profile Analysis was employed to categorize participants based on their injury experience and exercise levels, resulting in two profiles: Group 1 (moderate or severe injury experience with intermediate exercise levels) and Group 2 (mild injury experience with beginner exercise levels). Three-way ANOVA was then used to evaluate relationships between these profiles and safety knowledge and practice levels. RESULTS Results revealed significant differences across sex, age, and profile groups. Compared with women, men demonstrated higher levels of safety knowledge and practice, which were likely influenced by greater exposure to high-intensity sports and risk-taking tendencies. Adolescents exhibited the highest levels of safety knowledge and practice linked to structured safety education, but these levels declined in early adulthood and then increased again in middle age due to growing health awareness and preventive motivations. Furthermore, participants in Group 1 consistently showed higher levels of safety knowledge and practice than those in Group 2, highlighting injury experience’s role in shaping safety behaviors. CONCLUSIONS These findings underscore the importance of developing gender-specific safety education programs, age-appropriate interventions, and training initiatives tailored to beginning participants. Future research should evaluate these strategies’ long-term impact on safety practices and injury prevention in diverse sports settings.
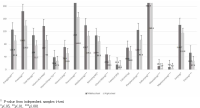
Purpose This study aimed to evaluate the nutrient intakes and diet quality of national youth badminton players participating in summer camp training in 2016. Methods Total of 40 middle school players and 60 high school players were included in the study. Two players with skipped meals were excluded from the final target. Food intake data for the 3-day using 24-hour recall method were obtained and analyzed using the CAN-pro 5.0 (Web ver. Korean Nutrition Society, Korea). Differences in nutrient intakes and diet quality were compared between middle school players and high school players using independent samples t-test. Results Intakes of vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin B6, folic acid, calcium, chloride, magnesium, and zinc in both groups were lower than (RNI) recommended intakes of KDRIs. On the other hand, intake of sodium significantly exceeded the recommended nutrient intake (RNI) of KDRIs in both groups. The NARs (Nutrient Adequacy Ratio) of vitamin C, vitamin B6, folate, calcium and zinc were less than 0.75 in both groups. The NARs of 11 nutrients except for folic acid were significantly lower in high school players. The MAR (Mean Adequacy Ratio) of middle school players was 0.78, significantly higher than 0.64 of high school players. The INQs (Index of Nutritional Quality) of vitamin C, vitamin B6, folic acid, calcium and zinc were less than 0.75 in both groups. The INQs of vitamin A, vitamin B6 and zinc were significantly lower in high school players. On the other hand, the total DDS (Dietary Diversity Score) of high school players was 3.88, significantly higher than 3.29 of middle school players. The DDS of fruit group as well as milk and dairy group were particularly low. Conclusions The results suggest that balanced diet managed by professional dieticians along with nutrition education should be implemented to improve nutrients intake and diet quality of national youth badminton players.
