PURPOSE Sporting events constitute attractive platforms for providing participants with unique experiences. This study was aimed at investigating the structural relationships among perceived sporting event quality, image, trust, satisfaction, and loyalty of small-scale golf tournament participants. METHODS The questionnaire was structured in five dimensions: sporting event quality (4 sub-dimensions and 13 items), image (3 items), trust (3 items), satisfaction (3 items), and loyalty (4 items). A total of 217 amateur golfers from four Ecolian public golf clubs (Gwangsan, Jechon, Jeoungsun, and Younggwang) during the golf tournament participated in this study. Factor, reliability, validity, and structural equation model analyses were performed utilizing SPSS 24.0 and AMOS 24.0. RESULTS This study indicated that sporting event quality in a small-scale sporting event was the crucial factor of image, trust, and satisfaction, which, in turn, significantly impacted loyalty. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study contribute to theoretical understandings of sporting event quality factors that predict sport consumers’ image, trust, and satisfaction in the context of sports and leisure. Additionally, this study offers practical suggestions for administrators who develop marketing strategies for small-scale sporting events.
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to determine the influence of complex exercise and chromium supplement on healthe-related physical fitness, appetite regulating hormones, and diabetes risk factors in obese elementary school students. [Methods] The subjects were 32 obese elementary students over 25 kg/m2 to BMI, 8 complex exercise with high chromium supplement group (CE+HC), 8 complex exercise with low chromium supplement group (CE+LC), 8 complex exercise with placebo group (CE+PL), and 8 placebo group (PL). The subjects have performed the exercise program for 70 minutes a day and 3 times a week with aerobic and anaerobic exercise during 12 weeks. Also, low and high chromium supplement group took a peel 50 ug and 400 ug respectively at the same time and place. [Results] There were significant decreases in body fat to CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) and significant increase in muscle mass compared with CE+PL (p<.05). However, there were no significant differences in body weight, BMI, muscular strength, muscular endurance, and flexibility between groups. For appetite regulating hormones, there is a significant difference to ghrelin in CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) and there were significant differences to glucose and insulin significantly decreased in CE+HC compared with CE+PL (p<.05) in diabetes risk factors. [Conclusion] In conclusion, there were positive responses for body composition and diabetes risk factors for the twofold cases through complex exercise and high chromium supplement, but not for physical fitness and appetite regulating hormones.
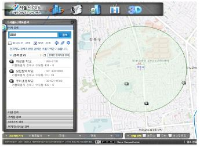
This study measured the accessibility of public exercise facilities within a residental area of a metropolitan community and examined how the accessibility can affect physical activity participation of residents. Initially, a total of 639 residents, who were aged between 19-70, visited Metabolic Syndrome Management Center of the Community Public Health Center, and registered for a Obesity Clinic Program, was listed as potential subjects. And those who responded to Physical Activity Questionnaire were selected for the analyses (n=92, 14.3% of 639). The relationships between physical activity level and accessibility to public exercise facilities were analyzed. Objective distance to public facility was related to ‘volume of participation to vigorous physical activity(r=.209)’, 'total volume of participation to physical activity(r=.206)’. And perceived distance to public facility was related to ‘volume of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.235)’. perceived transport time to public facility was related to ‘duration of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.239)’, ’volume of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.306)’, and ‘volume of participation to total physical activity(r=.273)’. In contrast, the difference between objective distance to public facility and perceived subjective distance to the facility was negatively related to ‘duration of participation to moderate-intensity physical activity(r=-.221)’. The perceived numbers of public facility was positively related to ‘frequency of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.237)’, ‘frequency of participation to walking(r=.273)’, ‘volume of participation to walking(r=.251)’ and 'total volume of participation to physical activity(r=.252)’. The predictor of 'total volume of participation to physical activity was perceived numbers of public facility(R2=.153, p=.046). The results revealed that the subjective accessibility to public health facilities was more influential to physical activity participation than the objective accessibility. Further research was warranted while using diverse populations as well as considering a inclusion of environmental factors.


The purpose of this study is to examine the level and difference of sport personalitys of middle school students depending on their quality of sport participation. According to prior research(박정준, 2012; Beller & Stoll, 1996), we decided that faithfulness, cooperation, justice and consideration are the sub-components of sport personalities. The reliability and validity of the Sport Personality Index Questionnaire was verified through Cronbach's α test and confirmatory factor analysis. The survey was conducted from students (n=768) in an urban area of Seoul, thereby level and differences of sport personality were analysed by t-test, one-way ANOVA, and frequency analysis. As a result, male students had higher sport personalitys than female, with regard to the participants'grade, frequency and duration of sports involvement. Disparities of gender and grade were revealed due to the frequency and duration of their sports participation. Regarding the effectiveness of sports activities, school-directed sports activities such as the after school sports programs or mandatory sports club activities had barely influenced building sport personality. In order to build students'sports personalities, specific strategies are sorely needed to increase girl's participation and to enlarge opportunity for regular and consistent participation of middle school students. Moreover, in order to develop participants'sport personality within school-directed sports activities, those programs'development and implementation should be deliberately approached with pedagogical intention and organization.

The purpose of this study was to examine the current status of school sport club(SSC) participation and to explore relationship between school sport participation and positive youth development. In order to do this, a survey was conducted with 403 elementary, middle, and high school teachers who are currently taking charge of SSCs, and also individual interviews were conducted with 22 students. In addition, the youths' developmental asset questionnaire was administered with 412 middle school students. The survey results from 403 teachers showed that SSCs have potential to contribute to positive youth development because teachers are placing an emphasis on character development as well as physical and social development through SSC activities. In addition, participants who regularly participate in physical activities had higher internal and external developmental assets than non-participants or irregular participants. Specifically, students participated in SSC more than twice a week had higher internal and external assets than students participate once a week. In addition, participants who engage more than one hour per session had higher internal and external assets except constructive use of time and social competence. Discussion and implications for organizing SSCs to provide developmental contexts and contents for positive youth development were provided.
PURPOSE This study focuses on the experiences of novice tennis enthusiasts in Korea, aligning with the rising popularity of tennis as a burgeoning cultural phenomenon. METHODS Employing an ethnographic approach, we included eight participants with <5 years of tennis, in addition to three auxiliary participants. RESULTS The primary findings of this study are as follows: First, novice tennis players from the MZ generation actively employ tennis as a means of personal expression, sharing their tennis-related fashion and experiences on SNS. Second, most novice tennis players report a sense of detachment from the traditional club-centric tennis culture, gravitating toward casual court usage, spontaneous activities, and flexible membership structures. F inally, despite their modest technical proficiency, they avidly engage in knowledge-based consumption, displaying a profound grasp of tennis-related information. CONCLUSIONS These findings provide valuable insights into comprehending this burgeoning cultural phenomenon in Korean society, stemming from the escalating interest in tennis, and can serve as a valuable benchmark for establishing development strategies for tennis.
PURPOSE Recreation specialization theory, which is characterized by a unique development process and progress, has been found to have varied pathways that develop in different patterns based on each dimension of recreation specialization. This study aimed to investigate how each sub-dimension of specialization changes as the degrees of experiential participation (frequency, period, and intensity of participation) and goods investment (expenditure) of the scuba divers increase. METHODS In the summer of 2021 (May-August), a purposive sampling method was used to collect samples from young scuba divers, and 278 copies of valid data were used for the final analysis. Frequency analysis, descriptive statistical analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, curve estimation analysis, and hierarchical regression analysis were performed using SPSS 24.0 and AMOS 24.0 ver. RESULTS The findings were as follows. First, the quadratic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the scuba divers’ participation intensity and cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations based on experience. Second, the cubic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the participation period, frequency of participation, and cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations of scuba divers. Third, the cubic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the expenditure cost of scuba divers and the cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations in the center of the goods. As the period, frequency, and expenditure of scuba diving participants increased, the relevant cognitive, behavioral, and affective specializations did not progress in a linear manner; instead, they went through an intermediate maintenance stage and developed to a higher level. CONCLUSIONS Progressive and meaningful consumption of experiences and goods further promotes recreation specialization. Any future follow-up study should identify a trade-off point in the development of the recreation specialization in a step by step manner.
Impact of 9-week strength training of racing cyclist candidate during training camp on body composition, racing cyclist specific fitness, and racing cycle performance was examined. Two by two (cyclist experience, y/n and strength training (ST) participation, y/n) experiment design was employed. A total of 20 candidates participated and divided evenly into four groups; 1) experienced cyclist participating ST (CST), 2) non-experience cyclist participating ST (nCST), 3) experienced cyclist no participating ST (CnST), and 4) non-experience cyclist no participating ST (nCnST). Two programs were introduced; 1) non ST containing, pre-existing program emphasizing on sprint and acceleration training and 2) new-program containing ST and sprint and acceleration training. CST and nCST participated the latter program. Before and after the 9-week training, body composition, racing cyclist specific fitness, and racing cycle performance was tested. After 9 weeks, all groups decreased body weight(p<0.05), body fat content(p<0.05), body mass index, and CST and nCST increased lean body mass(p<0.05). Muscular strength measures such as grip strength, low back strength, 1RM of bench press, 1RM of squat, and anaerobic capacity improved after 9 weeks in all groups(p<0.05). The magnitude of changes was greater in order of CST, nCST, CnST, nCnST. Time trial of 200 meter sprint was faster after 9 weeks in all groups except CnST while 500 meter sprint was improved only in nCnST(p<0.05). After 9 weeks, regardless of previous cyclist experience, those who participated in ST ranked high places at racing cycle competition. Both training programs for the candidates improved body composition and racing cyclist specific fitness. When strength training was added to pre-existing training program emphasized on sprint and acceleration, the racing cycle performance was enhanced. Strength training for racing cyclist is highly recommended to improve their racing performance.
PURPOSE This study examined the cultural experiences of tennis club members that have changed due to COVID-19, specifically emphasizing the accepted culture within these clubs. METHODS Seven tennis club members, with over five years of experience, active participation in two or more clubs, and a history of active participation, were interviewed using in-depth interviews and a semi-structured questionnaire. RESULTS Firstly, the tennis club members accepted the “no contact” culture that has emerged since COVID-19. Secondly, social distancing made getting together in large groups difficult, and tennis club activities became more limited. This has led to weakening the tennis club community, which is different from what we have seen before. Lastly, the growing interest in non-traditional content has led to an increase in participants enjoying tennis through social media. The information and experiences gained through social media have changed the perception of coaching. CONCLUSIONS The cultures that tennis players have adopted due to COVID-19 are expected to continue in the future. The findings from this study may provide evidence for understanding the changing culture of sports in the future.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to apply a life skills program to student-athletes and statistically verify the changes in life skills of the experimental and control group. METHODS Participants were 34 high school Taekwondo athletes (Mage=17.71). They were divided into 18 in the experimental group and 16 in the control group. For eight weeks, the experimental group participated in the life skills program after training and the control group participated in only training as usual. Data were collected by using Life Skills Scale for Student-Athletes (LSSSA), and the participants of two groups filled out the LSSSA before and after the program application. The collected data were analyzed by using repeated measure analysis of variance (ANOVA), and partial η2 (eta squared) was calculated to present the effect size. RESULTS The interaction between time and group was statistically significant in goal setting, coping with stress, positive thinking, and managing emotion among sub-factors of life skills. Partial η2 was interpreted as having a large effect size as it revealed the range of .22 to .51. Therefore, comparing before and after participating in the program, the life skills score of the experimental group among the two groups was significantly improved. CONCLUSIONS Student-athletes who participated in the program experienced positive changes in life skills than those who did not participate in the program.