Purpose The purpose of the study was to determine difference of body composition, bone mineral density and health-related fitness by physical activity level in young women. Methods A total of 90 women aged 19-29 years participated in this study. The subjects were divided into three groups (low, middle, and high level) according to the physical activity level estimated by bone-specific physical activity questionnaire(BPAQ). Body height and weight were measured. Body composition parameters including four sites of bone mineral density(BMD) were estimated by DXA (Hologic, QDR-4500, USA). Health-related fitness tests was assessed using sit & reach, grip strength, sit-ups, and VO2max. Statistical analysis was performed using SAS version 9.4. All data were presented in terms of means and standard deviations. One-way ANOVA was applied to determine difference of dependent variables by physical activity level. Duncan's multiple range test was used as a post-hoc test. The statistical significance level was set at p < .05. Results There were significant differences on body weight(F = 4.867, p = .01), body mass index(F = 5.053, p = .008) and fat-free mass(F = 8.364, p = .0001) among the three groups. Significant differences were found on whole body BMD(F = 16.730, p = .0001), lumbar BMD(F = 11.480, p = .0001), femur BMD(F = 42.182, p = .0001) and forearm BMD(F = 5.560, p = .005) among the three groups. There were also significant differences on sit and reach(F = 11.433, p = .0001), sit-ups(F = 17.972, p = .0001), VO2max(F = 3.106, p = .05) and duration of GXT(F = 7.479, p = .001). Conclusions There were differences on body composition, bone mineral density and health-related physical fitness by physical activity levels. Nevertheless, the questionnaire used in this study was not able to judge participation in various exercise types including aerobic exercise or resistance exercise. Therefore, in the future study, longitudinal study considering various types of physical activity and dietary intake will be needed.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate user perceptions regarding the mobile healthcare application of public health centers by using big data. METHODS The study data included 1,089 users’ reviews (from September 27, 2016 to December 23, 2021), which were analyzed using Python, Textom, KrKwic, UCINET 6, and the Net-draw program. RESULTS First, the evaluation of the application showed a higher number of “Good” responses (677 times) compared to “Bad” (329 times) and “Normal” responses (83 times). Second, network structures related to “Good” were “Like,” “Health care,” “Help,” “A sense of purpose,” “Grateful,” “Diet management,” “Exercise management,” “Easy,” “Recommendation,” “Satisfaction,” “Diet,” “Useful,” and so on. Third, network structures related to “Bad” were “Execution error,” “Request improvement,” “Question,” “Slow speed,” “Interlocking error,” “Lack of food type,” “Login error,” “Inconvenience,” “Delete and reinstall,” “Update error,” “Irritation,” “Connection error,” “Problem occurred,” “Direct input request,” “Not available,” “Waste of stars,” “Lack of function,” “Not enough,” “Stuffy,” “Lack of exercise,” and so on. Fourth, as a result of structural equivalence analysis, four clusters appeared: cluster 1 (negative function), cluster 2 (negative emotion), cluster 3 (positive function), and cluster 4 (positive emotion). CONCLUSIONS It is necessary to respond quickly in order to reflect on the users’ reviews, and active efforts are required to improve the program quality so that users can use it conveniently.
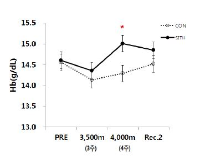
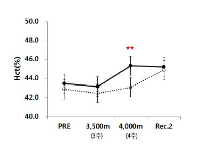
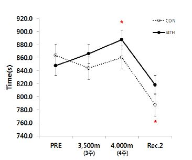
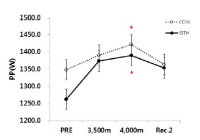
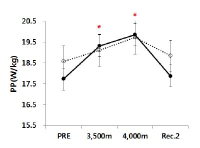
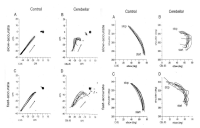
In this study, hypoxic exposure and training with regard to the current progress during the various models 'live and/or sleep high: train high' by way of 4 weeks in elite level tennis players. The experimental group which SITH(SIT with hypoxic) a 2,500m-4,000m to the graded elevation every 500m increased by the week five times a day, two times four weeks treated to a SIT (sprint interval training) and three hours of exposure in hypoxic chamber(simulated normobaric hypoxic). The CON(control) was conducted same period and methods without exposure to hypoxia that a SIT at sea level. As a results, the haematological variables were Hb and Hct compared Pre with the treatment at the end of 4,000 m(at 4 weeks) has been shown to significantly increased in both groups respectively(p<.05, p<.01; vs. Pre). Aerobic exercise capacity related variables that Time was SITH has been shown to significantly increased at 4,000 m(p<.05; vs. Pre). Also, VO2max was SITH has been showed increased in the same period a tendency(p=.072). Anaerobic exercise capacity related variables that PP(W) was both groups increased significantly at 4,000 m(p<.05; vs. Pre), and PP(W/kg) was CON group has been showed increased in the same altitude a tendency, whereas SITH group has been showed increased at 3,500m and 4,000m respectively(p<.05; vs. Pre). Therefore, this study was unlike previous studies with similar positive results as a follow-up study will be contribute to the attainment of a higher value.

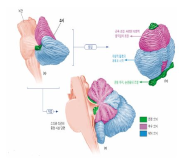
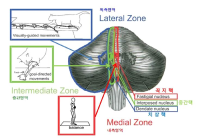
The cerebellum is one of the major parts of the brain involved in the motor control including motor coordination, muscle tone, balance, and the learning of motor skills. The purpose of this review paper was to explore of pathophysiology, anatomical function and neurophysiological mechanism for cerebellum. For this, we sought to examine of previous study related cerebellar disease. Specifically, this paper suggested that motor deficiency of limb movements, coordination, gait/posture balance, adaptation of during movement execution through information proprioception or kinaesthesia, and motor planning and programming of cerebellar patients. We expect that this review will be able to offer the useful information to research. For example, movement scientists will provide an academic information about cerebellar ataxia. Patients and their families will provide relevant information to the daily life (e.g., management and rehabilitation exercise).




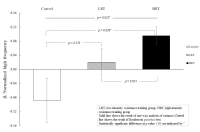
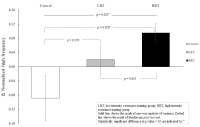
The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence of resistance training with different exercise intensities on heart rate variability(HRV) in habitual smokers. Twenty-eight healthy young smokers participated in this study were randomly divided into three groups; CON(control), LRT(low-intensity resistance training; 50% 1RM), and HRT(high-intensity resistance training; 70%1RM), respectively. LRT and HRT groups performed an 8-week resistance training(4 upper- and lower body exercises) using weight training machines, whereas CON group maintained their regular activities. All groups were evaluated basal body composition, hemodynamic parameters, HRV as autonomic nervous function, and muscular strength (1RM and isokinetic test) before and after the 8-week training. To assess the effect of 8-week training with different intensities on autonomic regulation, time and frequency domain indices of HRV were calculated from 5min R-R interval recording. As results, both LRT and HRT groups increased baseline 1RM and isokinetic strength compared to CON group. Meanwhile, high-frequency power reflecting parasympathetic activity was significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. In addition, normalized low frequency power(LF nu) indicating a shift of sympathovagal balance towards sympathetic predominance significantly decreased while normalized high frequency power(HF nu) which reflects vagal predominance significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. Furthermore, improved cardiac autonomic regulation and parasympathetic activation had significant association with increased muscular strength. Overall, the 8-week training has enhanced muscular strength in both training groups, particularly autonomic balance improved in young habitual smokers with high intensity resistance training.

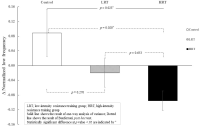
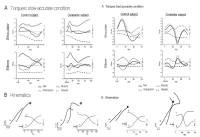
PURPOSE This study examined the effects of focus of attention on beginning golfers’ competitive anxiety and motor performance. METHODS Forty-eight college students with no prior golf putting experience were selected as participants and randomly assigned to internal-focus, external-focus, holistic-focus, and control groups (12 participants each). All subjects performed 5-m golf putting in acquisition, noncompetitive, and competitive situations. RESULTS In competitive situations, the internal-focus, holistic-focus, and control groups showed golf putting accuracy and consistency similar to those in noncompetitive situations, whereas the external-focus group’s golf putting accuracy and consistency were significantly lower in competitive situations than in noncompetitive situations. In addition, the holistic-focus group showed significantly higher golf putting accuracy than the control group in both competitive and noncompetitive situations. CONCLUSIONS Holistic-focus can be used effectively as a strategy for beginners to learn motor skills and reproduce learned motor skills when state anxiety increases. However, external attention focus cannot be considered a strategy to induce effective beginners’ exercise performance when competitive state anxiety increases.
PURPOSE This study aimed to explore ways to utilize augmented reality (AR) in school sports and leisure by examining the case of an elementary school sports club using augmented reality-based e-sports. METHODS A self-study approach and Eisner's(1995) educational criticism were utilized. Data including photos, videos, literature, and memory boxes related to the elementary school AR sports club were collected weekly during the school semesters from March 2023 to January 2024, spanning a total of 30 weeks. The data were analyzed following the stages of analysis by Elo & Kyngäs(2007). RESULTS Augmented reality can act as a personalized exercise coach by visualizing physical activity information. Through posture and movement analysis, education on physical strength and expression can be provided that is linked to home; it can also expand the range of sports experiences and create a new sports culture. In order to effectively utilize AR, edtech field experts must be trained, and content must be developed through cooperation between companies and schools. The educational effectiveness of the content must be verified and the management system must be inspected, and public facilities utilizing edtech must be expanded. CONCLUSIONS AR has endless development potential in school sports and leisure, but these will require active interest and support from educational authorities.
PURPOSE This study aimed to compare body composition, physical fitness, maximum muscle strength, and blood lactate concentration according to the level of aerobic capacity in Keirin cyclists. METHODS Forty-four Keirin cyclists participated in this study and were divided into three groups: the top 20% VO2max group (TG, n=9), the middle 20% VO2max group (MG, n=9), and the low 20% VO2max group (LG, n=9). The study measured body composition, physical fitness, maximum muscle strength, and blood lactate concentration in Keirin cyclists. Differences between groups were determined using one-way ANOVA analysis. RESULTS Body weight, percentage of body fat, and body mass index were significantly higher in the LG than in the TG and MG. The vertical jump and maximum muscle strength were significantly higher in the TG and MG than in the LG. Additionally, blood lactate concentrations immediately after exhaustive exercise and during the 5-minute recovery periods were higher in the LG than in the TG and MG. Moreover, the time to exhaustion, HRmax and maximum power were the highest in the TG. CONCLUSIONS Our findings suggest new information that levels of aerobic capacity in male Keirin cyclists might be a crucial predictor of cycling performance and recovery ability.
PURPOSE This study aimed to verify the criterion validity of the two-minute step test in older Korean adults, develop an equation for predicting VO2max, and verify cross-validation. METHODS A submaximal exercise test and the two-minute walk test were performed on 150 older adults (74 males and 74 females) aged 65 years or older. Correlation analysis was performed to confirm criterion validity. An equation for estimating VO2max was developed through multiple regression analysis, and cross-validation was confirmed by performing a correlation analysis between measured and predicted values of VO2max. RESULTS The correlation coefficient between VO2max and the two-minute step test was 0.457 (p<.001). The adjusted R2 of the developed VO2max prediction equation was 0.430 (p<.001), and the explanatory variables finally selected were sex, age, number of steps in the two-minute step test, and percentage of body fat. The correlation coefficient between the measured VO2max (19.08±4.36) and the predicted VO2max (19.73±3.36) was 0.654 (p<.001). CONCLUSIONS This study confirmed the criterion validity of the two-minute step test in older Korean adults, and the cross-validation of the developed VO2max prediction formula was verified. The explanatory variables of the prediction equation will be easy to apply in the field, and more meaningful results will be derived if the validity of the prediction equation developed for a larger number of participants is verified.
PURPOSE This study aimed (1) to analyze the behavioral intention and use behavior among the consumers of online home training contents via YouTube by employing the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT); (2) to test the moderating effects of risk perception toward the coronavirus (COVID-19) infection, and 3) to test differential impacts of generational difference across millennial and baby boom generations. METHODS A total of 400 questionnaires were distributed, and 383 samples were used for the final analysis after excluding 17 incomplete responses. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 25.0 and AMOS 22.0. RESULTS It was found that (1) the performance expectancy, the effort expectancy, and the social influence had positive effects on behavioral intention; (2)the facilitating condition had negative effects on the use behavior; (3) the behavioral intention had positive impact on the use behavior. Moreover, the risk perception toward the COVID-19 infection did not have moderating impacts on the UTAUT model, whereas generational differences did. CONCLUSIONS Our results suggest that the marketing strategy that improves exercise performance, convenience, and social influencing factors may be key to home training customers' behavioral intention and use behavior. Furthermore, home training material makers should recognize that the features and infrastructure required for the two generations are distinct and develop a separate marketing strategy for each.