Purpose The purpose of this study is to examine effects of professional baseball home fans' perception of the community on their recognition of stadium spaces. Methods The subjects of the survey were home fans of baseball. A total of 600 questionnaire(100 fans each team: DOOSAN, LG, SK, LOTTE, HANHWA and KIA) were collected and 510 copies were used as the final analysis data. Collected data was processed by using SPSS 21.0 program. T-test, one-way ANOVA, correction analysis and multiple regression analysis were conducted to test hypothesis. Results There were significant differences of perceptions on community such as perceptions on sense of belonging; favored teams, perceptions on active involvement; gender and favored teams, perceptions on pride of the home town; gender, favored teams and glasses for viewing, and perceptions on classification; educational level and favored teams. There were significant differences of perceptions on stadium spaces such as perceptions on historicity; favored teams and viewing experience, perceptions on authenticity; favored teams and viewing experience, and perceptions on symbolism; age, favored teams and glasses for viewing. Among home fans' perceptions of their community, sense of belonging and pride of the home town had positive effects on their perceptions on historicity among perceptions of stadium spaces, while perceptions of classification had negative effects on them; sense of belonging and pride of the home town had positive effects on both perceptions of authenticity and symbolism. Conclusions The findings indicate that there is a close relationship between the community and professional baseball stadiums, and it is necessary to commonly enhance sense of belonging and pride of the home town for the community in order to promote positive perceptions on stadiums.

Purpose This study was designed to develop a team building program that helps freshmen student-athletes to adapt to college life and enhance team function and process and to examine the effects of this program. It could provide basic information of a team building program that effectively accelerates team function in the college team sports domain. Methods The program was developed through this process. First, an open-ended questionnaire was utilized to discover the needs of the program. Second, the results of needs of the program and important factors of team-building program were taken into consideration. Third, expert meetings were conducted. Consequently, the program consisted of three stages of total 10 sessions which was 90 min long. The questionnaires(Group Cohesion Questionnaire and Coach-Athlete Relationship Questionnaire), experience report, and program evaluation form were used as measures to identify the effects of the developed program. SPSS version 24.0 and inductive analysis were used to analyze the data. Results The results of this study are as follows. First, there was no statistically significant influence between developed program and the level of group cohesion. In contrast, the level of coach-athlete interaction was significantly increased. Second, the analysis of experience report revealed that this program reduced interpersonal conflict between team members and formed positive interpersonal relationship by mind of respect and consideration. Conclusion In conclusion, the hierarchical culture was strongly formed and team member suffered from the dual role of athlete and student in Korean college team sports. Thus, these should be resolved in order to enhance team function and process. As a results, this process could increase team performance as well as offer psychological stability to college student-athletes.

Purpose This study aims to explore migration factors of Korean male footballers who have moved from South Korea to Southeast Asian countries. Methods Qualitative case study was conducted with 9 footballers, 4 their agents and 2 K-league staffs as the participant. Results As a result, by regarding their migration as involuntary decision, this study could provide academic and practical discussion on sport labor migration. First of all, this study established theoretical framework for involuntary migration of the participants through ‘Push-Pull Theory’ which focuses on demand and supply on the labor force. Second, this study found that a local rule (FA compensation system) of Korean professional football league (K league) and hierarchical collectivist culture contributed to their migration, which has not been reported by previous studies focused on the voluntary migration of mainstream players and it reflected local context of K league. Conclusions In conclusion, this study confirmed that sport labor migration was also considered as social phenomenon and reflected a cross section of a particular society. Through the migration of athletes, we can provide a variety of viewpoint on economic (market) structure, related policy and system in a particular society, and understand migration motives in terms of agency (subculture).
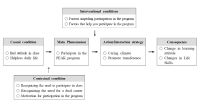
Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the process of participation in the PEAK program of collegiate athletes based on grounded theory. Methods In-depth interviews were conducted with 12 athletes from Y University who were registered in Korea Taekwondo Association. The collected data were analyzed by using the open coding, axis coding, and selective coding of the grounded theory, completed the paradigm model among the extracted concepts, and extracted the core categories through the story outline. Results As the result of data analysis, 'participating in the PEAK program' was found as the central phenomenon, and the causal situation was 'bad attitude in class' and 'helpless daily life'. The contextual conditions were 'recognition of the need for class participation and dual career' and 'motivation to participate in the program', and the intervening conditions were 'factors that hinder participation in the program' and 'factors that help program participation'. The action/interaction strategies were ‘caring climate’ and ‘promoting transfer’, and depending on the consequence, ‘learning attitude change’ and ‘life skill change’ appeared. Conclusion Participants improved their learning attitude through the PEAK program and confirmed the possibility of life skills transfer. It is hoped that this study can lead to implementation of various studies and discussions about life skills and transfer.

Purpose Sperm quality and function are reduced by environmental factors (e.g., obesity), leading to increased infertility worldwide. Therefore, the purpose of this review paper was to investigate the effects of obesity and exercise training on sperm quality and function in animal and human models. Methods In order to determine the effects of obesity and exercise on sperm quality, motility, morphology, testosterone, oxidative stress, inflammation, we reviewed previous literatures with MEDLINE, PubMed, and Scopus databases. Results The most important factor to control the sperm motility is calcium ion, which is performed by the protein of CatSper (Cation Channel of Sperm). Obese men showed the decrease of number, concentration, motility, and volume in sperm, resulting in delayed or failed fertility. However, regular exercise training increased sperm-mediated factors including number, motility, and morphology, and festicular function-mediated factors including sperm concentration and serum testosterone. Conclusions While obesity exacerbates sperm quality and function in men, regular exercise training with moderate intensity increases sperm number and motility and reduces oxidative stress and inflammation, leading to the improvement of men’s fertility.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the differences in physique and physical fitness according to maturity between primary and middle school baseball players. Methods Participants were 112 elite youth baseball players (49 primary school; 63 middle school). Skeletal age estimated maturity. Physique (height, arm span, thigh volume), body composition (weight, muscle mass and body fat), physical fitness (strength, power, agility, flexibility, coordination, anaerobic power and aerobic power) were measured. An independent sample t-test was used to conduct verify the difference between physique and physical fitness according to maturity. Results The results of analyzing physical and physical fitness according to maturity showed that there was a significant difference (p<.05) between the early maturation group and on-time group in primary school baseball players, body fat percentage, muscle mass percentage, sit-up, anaerobic power and reaction time. There was a significant difference between the early maturation group and the on-time group in the middle school baseball players, weight (p<.05), thigh volume (p<.05), fat mass (p<.05), muscle strength (p<.01), power (p<.05) and coordination (p<.05). Conclusions In conclusion, the maturity of a growing baseball player may be influenced by the performance, so maturity status should be considered when judging the performance of a growing baseball player, especially a middle school baseball player.

Purpose: This study was to verify the relationship between coaching behavior(autonomy/controlling behavior), self-regulation motivation and performance. Method: 356 athletes (from middle to work and professional team) in individual and team sport completed coaching behavior scale developed by this researchers assessing autonomy and controlling coaching behavior perceived by players, Korea Basic Pyshoclogical Needs Scale (KBPNS) assessing basic psychological needs, Behavioral Regulation in Sport Questionnaire (BRSQ) assessing sports motivation level based on self-determination theory, and sport performance score. To estimate the relationship between coaching behavior, self-regulation motivation and performance, this study employed the structure equation modeling analysis. Results: The relationship between psychological needs, regulation motivation and performance showed that autonomy coaching behavior tend to reinforce competence and autonomy of player. These variables have a positive effect on more inner regulation motivation. Moreover, the intrinsic motivation through stimulation experience was a key factor leading to a positive performance by improving the performance strategy and skill of athletes. Conclusion: These results are meaningful as an empirical evidence that relationship between motivation and performance can be changed according to the type of coaching behavior, and that autonomous coaching behavior play an important role in maximizing the performance of player that provided theoretically form.

[Purpose] This study evaluated the predictive power of Body Mass Index (BMI) for metabolic syndrome in older adults across pre-, during-, and post-COVID-19 periods, and examined the effects of metabolic syndrome factors on BMI by income level, aiming to inform elderly health management and crisis-related policies. [Methods] Data from 6,242 older adults (aged 65–80) were drawn from the 2019–2022 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Income was divided into quartiles, and time was segmented into pre-, during-, and post-pandemic periods. Multiple linear regression was used to assess the effects of metabolic syndrome factors (diabetes, abdominal obesity, low HDL, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia) on BMI by income and period. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis evaluated BMI’s predictive power for metabolic syndrome. Significance was set at .05. [Results] Abdominal obesity and low HDL consistently influenced BMI across all groups. In the lowest income group, hypertension increasingly affected BMI during and after the pandemic. BMI Area Under the Curve (AUC) values peaked during the pandemic in this group, while the highest income group showed stable predictive power. [Conclusion] The COVID-19 pandemic had a differential impact on the association between BMI and metabolic syndrome among older adults according to income level. In low-income older adults, the predictive power of BMI for metabolic syndrome increased during the mid-pandemic period, while it remained stable across all periods in high-income groups. Systematic health management programs and policy interventions targeting low-income older adults are required to reduce health disparities during public health crises.
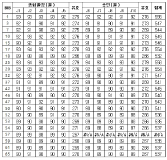
Purpose The purpose of this study is conducted to analyze the objectivity of the ski technical championships hosted by Korea Ski Instructor Association (KSIA) and to identify the error sources that affect the score of the competition. Methods To this end, we used the data from the 25th(2009) to 33rd(2017) ski technical championships held by the Korea Ski Instructor Association (KSIA). The data provided by Win Excel 2010 was used to sort out the missing data, such as abandonment, according to the data processing method. The collected data were analyzed by using SPSS 22.0 to calculate the mean and standard deviation of each season, event, and judges, and the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC). In addition, by using the single facet crossed design(p*j) of the generalizability theory’s G study, the variance component estimates for the participant(p) and the judges (j) are calculated, and the influence (%). Results As a result of the research, it was confirmed that the results of all the seasons and events from the 25th to the 33th events were very consistent, with the objective of .845~.986 higher than the recognition level of .80. In addition, the results show that the relative ratio of the judges to the error of the judging score is very low as a result of the error analysis through the dispersion component estimates. Conclusion In summary, the results of the KSIA evaluation are highly evaluated objectivity and have very low impact on the judges' errors.


Purpose The study was designed to investigate the effects of 12 weeks of circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation on physical fitness and metabolic syndrome. Methods Forty-one menopausal women were randomly assigned to one of three groups. i.e., combined circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation group (CT+T: n=14), L-tryptophan supplementation group (T: n=14), and control group (CON: n=13). The subjects in CT+T exercised three sessions per week and took 3g of L-tryptophan per day for 12 weeks. The subjects in T took 3g of L-tryptophan per day for 12 weeks. The subjects in CON were asked to maintain their life pattern for the same period of intervention. Physical fitness and metabolic syndrome-related variables were measured at pre- and post-test. The data were compared by utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. Results Main results of the study were as follows: 1) Standing long jump, one leg standing with eyes closed, sit-and-reach, sit-up, and maximal oxygen uptake increased significantly in CT+T. 2) Body weight, body mass index, waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, fat mass, and percent body fat decreased significantly in CT+T. 3) Total cholesterol decreased significantly in CT+T. 4) Fasting plasma glucose (FPG), fasting plasma insulin, and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in CT+T. FPG and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in T. 5) Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and rate pressure product decreased significantly in CT+T. DBP and MAP decreased significantly in T. 6) Number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased significantly in CT+T and T. Conclusion It was concluded that the circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation would have positive effects on physical fitness and metabolic syndrome, and that L-Tryptophan supplementation would have positive effects on metabolic syndrome by improving insulin resistance and hypertension in menopausal women.