The purpose of this study was to analysis of moving distance during games, time and heart rate for hockey games using GPS (global positioning systems) by positions in Korea national female athletes. The subjects were Korea national female hockey players (n=13) including 4 forwards, 4 midfields, and 5 fullbacks that participated in five Korea vs. Japan international games. All subjects were wearing GPS throughout the games. The results were as follows: Firstly, the average total travel distance per game was approximately 5.7km and higher in the second half. Physical movement in the games was not different from positions where 70% of physical movement was performed at low intensity and 30% at moderate and/or vigorous intensity, suggesting that the subjects; physical movement was performed at the appropriate level of exercise intensity. Secondly, during the game, the subjects performed physical movement faster than 11km/h for 22 minutes, indicating that the subjects could maintain their physical movement at a relatively faster speed throughout the games. In particular, midfields showed a greater amount of physical movement at moderate speed. Thirdly, the average exercise heart rate was 145bpm, which was equivalent to 60% of HRmax. The subjects maintained their average exercise heart rate greater than 150bpm (above 60% of HRmax) for 40 minutes during the games, indicating that the players had an ability to maintain physical movement at high intensity throughout the games. In conclusion, in spite of the fact that Korea national female hockey players have an ability to maintain physical movement at a relatively faster speed and higher intensity, their physical movement and performance are often affected. Therefore, it is necessary to develop and apply the specific interval training program for national female hockey players that can facilitate the faster recovery from the repetitive physical movement requiring power and speed at high intensity.

The purpose of this study was to investigate basal physical fitness and smash speed of elite national badminton players. To perform this study, total forty six korea national badminton player were participated : twenty two male players(age : 20.90±2.24years, height : 179.30±5.40cm, weight : 73.80±7.12kg, career : 11.27±1.88years) and twenty four female players(age : 19.45±1.95years, height : 167.83±4.36cm, weight : 61.39±3.60kg, career : 9.50±2.47years). Each subjects performed the 6 basal physical fitness trials : agility, muscular endurance, muscular strength, flexibility, balance and cardiorespiratory endurance. And the speed of badminton smash were analysis by using radar gun when players were standing smash success. To determine the difference between two groups, independent samples test was used. As a result, we found that there was a large difference male players and female players in basal physical fitness and smash speed. First, male players were significantly strong in agility(side step 10%), muscular endurance(repetitional jump 12%), muscular strength(left grasping power 3%, right grasping power 31%) and cardiorespiratory endurance(20m suttle run 31%). On the other hand, female players were relatively strong in flexibility(sit and reach 27%) and balance(standing on one leg with eyes closed 51%). Second, maximum smash speed show that male players were about 57km/h(24%) faster than female players(male : 247.72km/h, female : 190.37km/h). Based on the findings, we shall be applicable training program to improve flexibility, balance of male athletes and agility, muscular endurance, muscular strength, and cardiorespiratory endurance of female athletes. our results will be appliable to improve the athletic performances of national badminton players by the coaches in the future.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to section the stages of performance development based on the track and field athletes' performance records, derive the performance development span, which was a continuum of the development stages, and extract the psychological experience of the performance development span. METHODS In this study, 56 retired track and field athletes were provided with competition records, and 10 athletes participated in in-depth interviews. With the stage of performance development partitioned using long and short-term moving averages and regression slope in PRR, a continuous of performance development span was derived. To extract psychological experiences in the performance development span, a subject analysis was conducted after an in-depth interview. RESULTS First, the track and field athletes' performance development stage calculated short and long-term moving averages in the PRR. Based on the average difference in the regression slope of the initial 20% CPR in which the long-term moving average was not calculated, it was divided into beginning, rising, peak, and decline periods. Second, the performance development span was a continuum of the stage was of performance development, and the beginning period was 0 < PRR ≤ 7, it was a time when the competition record rises sharply. The rising period was 7 < PRR ≤ 60, which was a virtuous cycle time of growth athlete. The peak period was 60 < PRR ≤ 74, which was a time when the peak record was maintained. The decline period was 74 < PRR ≤ 100, which was a time when the competition record was downward. Third, throughout the performance development span physical intelligence of track and field athletes was based on their natural physical superiority, the technical skills rises and remains at its peak and then enters a downward trend. Competitional Intelligence aims to become personalization as it matures gradually while its competition management capability and game knowledge are immature. Psychological intelligence overcomes the initial psychological atrophy to form confidence, and after experiencing psychological burden at the peak, confidence decreases. In the environmental context, the competition record rises in the early stages, continues to rise, peaks, and enters a downward trend. CONCLUSIONS Track and field athletes' performance development span was implemented as a continuum of beginning, rising, peak, and decline periods, and the psychological experience of the performance development span formed a span of physical intelligence, competitional intelligence, psychological intelligence, and environmental context.
PURPOSE Blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive individuals is reduced by the accumulation of post-exercise hypotension (PEH) induced by a long period of training. This study aimed to investigate the effects of intensity of two different aerobic exercises with identical energy expenditure on post-exercise blood pressure and cardiovascular function in prehypertensive men. METHODS Eleven prehypertensive men in their 30s participated in two trials repeatedly. In the first trial, the exercise was moderate in intensity and continuous (MICE) with 70% of VO2max, and the exercise in the second trial was high-intensity interval exercise (HIIE) with 50% and 90% of VO2max. Each exercise was performed for 30 min, and the variables related to BP and cardiovascular function were measured at certain times for 1 hr during the recovery phase. RESULTS Our main findings are as follows: (1) Systolic blood pressure was significantly lower at 30 and 45 min of recovery time than the baseline in the HIIE trial, and systolic blood pressure was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 10, 15, and 30 min of recovery time. (2) The rate pressure product was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15, 30, 45, and 60 min of recovery time. (3) The heart rate was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15, 30, 45, and 60 min of recovery time. (4) Stroke volume was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 30 min of recovery time. (5) Cardiac output was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 min of recovery phase. (6) Total vascular conductance was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 and 30 min of recovery phase. (7) Total peripheral resistance was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 and 30 min of recovery phase. CONCLUSIONS The HIIE shows a higher cardiovascular stress than MICE; however, HIIE contributes to the augmentation of PEH and improvement of cardiovascular function. Therefore, HIIE rather than MICE should be suggested in BP control and enhancement of cardiovascular function in prehypertensive males.
Purpose A number of start-ups in the form of introducing sports contents in Korea as a new market are in progress, and appropriate support for each step is needed to increase the chances of a success. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to explore the entrepreneurial process of introducing and spreading newly created or developed sports content into a new market, Korea, by focusing on the innovation diffusion process model. Methods To derive the results, a qualitative research method was used, data were collected through in-depth interviews, literature search, and observation methods, and analyzed through categorization and itemization in stages based on content analysis results. Results Looking at the results, content recognition and problem identification were derived in the exogenous shocks stage, and the organization unity of internal and external stakeholder was confirmed in the formal coalition of opinion leaders stage. At the stage of internal communication between the opinion leaders of the social system, the expert communication in the same or similar field and external area appeared and the indirect experience also derived. In the decision to select a specific innovation stage, activities to belong to an international organization, to establish a new organization, and to secure idle space appeared, and at the stage of recruitment and/or the establishment of boundary spanners, efforts to secure internal and external human resource within the organization and to build an organization form appeared. In the stage of develop and introduce the innovation, online communication channels were established. In the stage of using mass media outlets, media articles, lectures, and academic conferences were used, and in the stage of actual diffusion of an innovation, experience and education programs were conducted, competition and exhibitions were held, venues were built, and actual international competitions were participated. At the stage of decisions to continue, discontinue, or re-invent the existing innovation must occur, evaluation was made by personnel inside and outside the organization. Conclusions It is possible to increase the success of start-up by creating a support system that can fill the necessary parts for each stage of start-up based on the derived activities for each stage.
Purpose Based on Haidt's social-intuitionist theory, this study analyzes the differences in ethical decision-making between sport athletes and the general public in order to understand the ethical judgment tendencies of athletes and examine the determining factors influencing their judgment from the perspective of their environment. In so doing, this study hopes to motivate education for enhancing ethical consciousness as well as institutional policy. Methods To this end, 200 elite athletes in their twenties registered for more than 10 years at the Korean Sports Association and 200 college students in their twenties from five universities in Seoul were selected for comparison. Response trends for each item were analyzed by percentage, and differences between groups were confirmed by the χ2 test method. Results The results are as follows. First, in general ethical situations, athletes usually showed a compulsory ethical view that emphasized principles, whereas in a sports situation, they showed a double consciousness and revealed a very strong consequential ethical view which put much emphasis on outcome. Second, athletes strongly maintained a Confucian ethical view that recognized ethics as a norm compared to the general public and, as a result, it was found that paternalism was relatively stronger than rationalism in their ethical decision making. Third, athletes regarded other people's thoughts and group interests as important criteria for ethical decision-making rather than individual thoughts and interests, and showed a group-centered mindset which emphasized group harmony and relationship. Fourth, while the general public viewed excellent athletes as those with excellent skills and good personality, and valued their morality, athletes thought relatively little of the influence and importance of morality in their success. Finally, it was found that coaches and managers were fundamental to the formation of the athlete’s moral view. Conclusion An in-depth understanding of sports participants' ethical awareness should come first in order to enhance ethical consciousness in sport. I hope this study will work as a catalyst for research which approaches athletes' ethical consciousness from a socio-cultural context.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the official world records of UIPM in the last 3 years to find out the relationship between the score characteristics of fencing, swimming, equestrian, and laser-run events in the final rankings and to analyze the relative importance of each event. Methods For 3 years, from 2017 to 2019, a total of the data were collected, the final rankings, fencing conversion scores, swimming conversion scores, equestrian scores, and laser-run conversion scores for all male and female athletes who participated in the UIPM Level 1 World Cup and World Championships(1,197 finals and 2,173 qualifiers). The Multiple regression analysis was used to establish the relationship between the response(subjective) variable and the conversion score of the four explanatory(independent) variables. Results The results were compared by qualification (n = 2173) and final (n = 1197) by dividing into male (n = 1179) and female (n = 1591), and the fencing score was qualifications (male β= -.691, female β= -.533) and the finals (male β= -.632, female β= -.632), it showed the greatest influence in all. On the other hand, the swim score showed the lowest impact on both qualifications (male β=-. 021, female β=-.196) and finals (male β=-. 087, female β=-. 207). The fencing event plays a major role in passing the qualifiers and is a big variable for good performance in the finals. On the other hand, in the case of swimming scores, both men and women had the lowest impact on the final ranking, and there is a limit to the final performance of swimming scores in both qualifiers. Conclusion In conclusion, it is necessary to analyze and systemize the fencing skills of the world’s best athletes, including Korean athletes, to improve the Korean fencing athletes' performance, and through such scientific analysis, a system that enables fast and flexible responses to the upcoming Olympic. Additionally, even though the importance of all sports should be levelled due to the characteristics of modern pentathlon, relative importance is biased toward fencing and swimming events are neglected. Therefore, it is deemed necessary to conduct a follow-up study on whether the scoring system in modern pentathlon consists of a scoring system that supports the records of each event and the upper and lower scoring system.





Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the moderate to vigorous physical activity(MVPA) and sedentary time measured by accelerometer. Furthermore, the level of physical activity and adherence rate of physical activity guideline(PAG) were compared with the self-reported questionnaire. Methods The MVPA, sedentary time, and adherence rate of PAG according to age and sex were examined to people who agreed to wear accelerometers among the participants of the 2014-2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. To compare the relationship between accelerometer and self-reported questionnaire, Chi-squared test and Spearman correlation analysis were performed. Results The MVPA of the accelerometer-total(AT) was 40.6 minutes/day for men and 31.1 minutes/day for women. Sedentary time was 502.9 minutes/day for men and 498.9 minutes/day for women. The MVPA of accelerometer-bout(AB) estimates was 16.4 minutes/day for men and 14.2 minutes for women. On the other hand, the MVPA of the self-report was 95.8 minutes for men and 64.3 minutes for women, and the sedentary time was 471.2 minutes for men and 455.2 minutes for women. The adherence rate of PAG was 55.6% of the self-report, 56.1% of the AT, and 21.4% of the AB. The correlation between self-report and accelerometer was statistically significant(p < 0.01), but showed a weak correlation coefficient(rho=0.112-0.351). There was no association between AB and self-report(p < 0.01). The sensitivity and specificity of the self-report were 71.3% and 48.6%, respectively. The positive and negative predictive values of the self-report were 27.5% and 86.1%, respectively. Conclusions As a result of this study, self-reported physical activity level by questionnaire had more MVPA and less sedentary time than the accelerometer-determined physical activity. In addition, the adherence rate of the PAG differed from accelerometer and self-report. The difference was significantly increased when comparing AB with the self-report. Therefore, great care must be taken when interpreting accelerometer and self-report questionnaire. Further research will be needed on specific methods that can be used by complementing the two measurement tools.
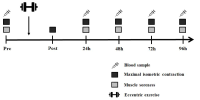
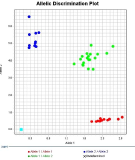
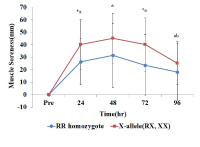
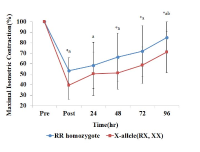
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to examine the change of muscle damage markers after maximal eccentric exercise and to verify the difference of recovery according to ACTN3 gene polymorphism. [Methods] Fifty healthy males participated in this study. Subjects performed 25 times/1 set (total 2 set) maximal eccentric contractions of the elbow flexor muscles on a modified preacher curl machine with a between-sets rest time of 5 min. Maximal isometric contraction (MIC) was measured 6 times (pre, post, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). Muscle soreness (SOR) was measured 5 times (pre, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). Blood samples were collected 5 times (pre, after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h). ACTN3 gene polymorphisms were identified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Data were analyzed using a 2-way repeated measure ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni test. [Results] Analysis of ACTN3 gene polymorphism revealed the following distribution: 22% RR (n=11), 50% RX (n=25), and 28% XX (n=14). Individuals were classified into the RR homozygote group (n=11) and the X-allele group (n=39). MIC showed a significant difference between groups and interaction (p<.05). The groups differed significantly in MIC at 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h after exercise and the X-allele group decreased more than the RR homozygote group. The groups differed significantly in muscle soreness and interaction (p<.05). SOR in the X-allele group was significantly higher than in the RR homozygote group at 24 h after exercise. Although blood CK activity was lower in the RR homozygote group than in the X-allele group, but there was no significant difference between the groups (p>.05). [Conclusion] The RR homozygote group showed lower muscle strength reduction rate, muscle soreness and blood CK activity than the X-allele group. This indicates that RR individuals have a lower risk of exercise-induced muscle damage than those with an X-allele.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the technique and power of the Korean national athletes and international athletes in the start phase of the 500 m speed skating to improve the performance and to understand the relationship between the biomechanical variables affecting the record. Method The subjects were 8 Korean national athletes (Korean athletes) and 6 international athletes (international athletes). For the three dimensional motion analysis, 5 high-speed cameras were used to capture the 40 m start phase of the athletes participating in the international competition. The variables selected for analysis were the kinematic chain, 100 m net time, time to 9 strokes, horizontal position of center of mass after 2.5 sec, range of motion of trunk, knee, push-off angle, net power output, total power loss. Results The correct kinematic chain ratio of Korean athletes was 61.2%, which was lower than 76.0% of international athletes. The time to 9 strokes was 2.82±0.25 sec for Korean athletes, which was significantly lower than 2.53±0.11 sec for international athletes (p=.001). The range of motion of the push-off angle was 60.15±2.75° for Korean athletes, which was significantly lower than 64.76±2.55° for international athletes (p=.001). The net power output was 887.2±269.9 W for Korean players and 1103±264.1 W for international players (p=.021). The variables related to the 100 m net time were the horizontal position of center of mass after 2.5 sec (r=-.956, p=.001), the net power output (r=-.931, p=.001), and the total power loss (r=-.904, p=.001). Conclusion In order to improve the start performance of Korean athletes, it is necessary to maximize the efficiency of skating through skill training to use the correct kinematic chain. Also power enhancement training is needed to improve leg power because the net power output related with 100 m net time.

