Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between physical activity and depression according to the presence of disease. Methods A survey and basic assessment were conducted for 2,754 (Male=1,025 and Female=1,729) aged 40 and over who participated in the rural-based cohort study. The survey included physical activity, depression scale and disease preservation. The basic assessment measured height, weight, and body fat percentage. The measured data were analyzed by using logistic regression to examine the relationship between physical activity and depression prevalence. Results First, physical activity reduced the prevalence of depression by 33% and 51%, respectively, in the general population and in patients with the disease. Second, physical activity once or twice per week reduced the prevalence of depression in patients with disease by 51%, and at least three physical activities reduced the prevalence of depression by 37% in the general population and 33% of patients with disease. Third, physical activity less than 150 minutes per week reduced the prevalence of depression in patients with disease by 43%, and physical activity of more than 150 minutes and less than 300 minutes per week reduced the prevalence of 43% of the general population and 52% of patients with disease. Physical activity over 300 minutes per week had a 38% reduction in the prevalence of depression in the general population. Conclusions This study suggests that the level of physical activity suggested by the ACSM guidelines is appropriate to reduce the prevalence of depression. In addition, the patients with the disease was found to be effective with less frequency and amount of physical activity than the general person.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a comprehensive model for facilitating and hindering factors about girls' participation in physical activities. Methods Based on systematic analysis, 26 foreign journals published from 2005 to 2016 were comprehensively analyzed. The journals were directed to facilitating and hindering factors of girls' physical activities. A model was developed by categorizing various factors in the previous studies, and by conceptualizing those categories, and by creating visualization of relations between the categories. Results Seven facilitating factors are referred to as 'SPORTS', including ‘Self-recognition’, ‘Physical environment’, ‘Opportunities’, ‘Relationship’, ‘Treatment’, and ‘Social supports’. In contrast, nine hindering factors are conceptualized as 'INCAPABLE' which includes 'Internalized gazes’, ‘Negative feedback’, ‘Competitiveness’, ‘Alternativeness’, ‘Perceived danger’, ‘Appearance’, ‘Bad feeling’, ‘Lack of opportunities’, and ‘Effeminate norms'. Conclusions It is suggested that the girls' physical activity patterns vary depending on whether the girls subjectively interpret the physical activity or girls are being objectified by other's evaluation. And those individual, relational, and environmental levels are needed to strengthen the subjectification of girls.


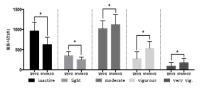
Active participation in Moderate to Vigorous Physical Activity(MVPA) is the indicator of healthy development for adolescents. However, Korean adolescents’ MVPA have continuously declined, and Korean adolescents have lower levels of MVPA compared to adolescents in other countries. Considering this issue, the purpose of this study is to examine the effectiveness of SPARK M-SPAN program to promote adolescents’ MVPA in P.E. classes and to understand how the promotion of adolescents’ MVPA occurs. To collect data, this study used Sequential Mixed Method and GT3X accelerometers. A total of 168 adolescents (84 in an experimental group and 84 in a control group) participated in this study for the quantitative data analysis, and six students and a teacher were interviewed for the qualitative data analysis. Paired t-test showed that students in SPARK P.E. classes experienced the significant decreases of sedentary behaviors(-339.6 sec) and low intensity P.A.(-96.9 sec) at p<.05 and the significant increases of moderate(+99.3 sec), vigorous(+252.4 sec), and very vigorous intensity P.A.(+84.7 sec) regardless of gender difference at p<.05 except for female students’ moderate intensity P.A.. The qualitative data analysis showed that SPARK classes gave students positive learning environments and led them to experience enjoyment and achievement-orientated learning Key teaching strategies of SPARK program and future research suggestions were provided in the discussion section.

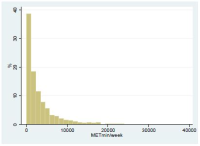
Recent studies focus on Metabolic Equivalent Task (MET) to measure levels of and areas of peoples’ physically active lifestyle because MET more readily translate peoples ’subjectively perceived physicality into standardized scores. MET also allows researchers to clearly understand the relationships between peoples’ physicality and psychological variables. Thus, the purpose of this study was to understand the levels of and areas of MET among Korean middle school students and to analyze the relationships between MET scores and physical self-efficacy. A total of 278 questionnaires were analyzed using SPSS 18.0. Exploratory factor analysis, descriptive analyses, and regression analyses indicated that middle school students’ physically active lifestyle occurred in the order school, leisure, housework, and transportation areas. Female students did more physical activity in the areas of housework and transportation, compared to male students. In contrary, male students did the majority of physical activity in the areas of school and leisure. Physical self-efficacy affected students’ MET scores, especially for vigorous intensity activity. With regard to gender differences, physical self-efficacy affected male students’ MET scores in the area of leisure while female students’ MET scores were affected in the areas of school and housework. The results were discussed in light of methodological and pedagogical perspectives, and future research suggestions were provided in the discussion.
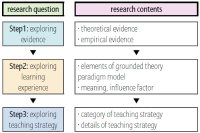
Purpose The purpose of this study was to understand learning experiences deeply and to prepare practical teaching strategies by reflecting the voices of the field. Methods For this, I used the logic and techniques of 'the grounded theory'. In particular, I used ‘the grounded theory paradigm model', which enables a holistic and systematic analysis of specific experiences to explore learning experiences and teaching strategies. I selected 10 male and female students who participated in art and physical activities as research participants. I collected data through literature review, in-depth interviews, and expert meetings, and analyzed using open coding, axial coding, and selective coding. Results First, I explored “the learning experience of art and physical activities in free-semester system", according to the elements of grounded theory paradigm model. It is composed of the ’causal condition’, ‘contextual condition’, ‘central phenomenon’, ‘interventional condition’, ‘interaction strategy’, and ‘results’. Second, based on this, I conducted "the teaching strategies for art and physical activities in free-semester system". These are composed of 'expansion strategy', 'diversity strategy', 'spontaneity strategy', and 'immersion strategy'. Conclusions The results of this study suggest that art and physical activities in free-semester system are leading to a positive change extended from the planned goals. In addition, various variables are structurally intertwined, and thus, it is considered that more strategic and systematic efforts are required in various dimensions for the successful application.


The purpose of this study was to examine whether the difference between ingestion of nutrition supplements for 8 weeks can regulate physical activities and fatigue recovery. Fifty one middle-aged women participated in this study and were divided into placebo, ingestion of 20g energy supplement and ingestion of 40g energy supplement groups. Energy supplement mainly consists of carbohydrates and proteins. All subjects take in this supplement one time per a day for 8 weeks. Physical activity and fatigue recovery were measured before and after ingestion of energy supplement for 8 weeks by using the Wingate anaerobic and a blood tests. In the Wingate anaerobic test, the peak power(p<.01) and average power(p<.05) were significantly increased in ingestion of 20 and 40g supplement groups compared to the placebo group. Although concentrations of lactate and growth hormone in the blood didn’t show a significant differences among groups, blood concentrations of cortisol and ammonia were further enhanced in ingestion of 20 and 40g supplement groups compared to the placebo group(p<.001). The results of present study provide evidence that energy supplement mixed with carbohydrates and proteins may be effective to increase physical activity as well as to reduce blood concentration of fatigue-related factors after exercise.
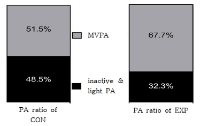
PURPOSE This study conducted a longitudinal analysis of physical activity levels and characteristics of middle-school boys and girls over a three-year period before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. METHODS This study used a sequential mixed-methods research design. In the quantitative study; three-dimensional accelerometers were used to measure weekly physical activity and sedentary time over three years (2019, 2020, and 2021) among 33 middle-school boys and girls, and the data were analyzed using repeated measures analysis of variance. In the qualitative study, data were collected and analyzed through focus group interviews with five participants. RESULTS The quantitative study indicated a significant increase in sedentary behavior and significant decrease in low-intensity activity and MVPA during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. In the second year of the pandemic, no significant difference was observed in sedentary behavior, low-intensity activity, and MVPA compared to the data collected in the first year. During the pandemic’s first year, qualitative study identified the following physical activity problems: “lockdowns,” “sedentarization of leisure,” and “reduced structured physical activity.” The following reasons were identified for the lack of improvement in physical activity during the second year: “intensified sedentary lifestyle habits,” “weak social networks,” and “lack of energy to exercise.” CONCLUSIONS The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a significant decrease in physical activity and a significant increase in sedentary behavior among middle-school students in South Korea, and even as the environments for physical activity have recovered, the physical activity problems of the early stages of the pandemic have not improved.
Purpose The current study investigated the effects of exercise information using social network service(SNS) to identify changes of physical activity and psychological variables among inactive college students. Methods Inactive college students(30 experimental group, 30 control group) were voluntarily participated in the 12-weeks intervention. During this period, the experimental group received exercise information through SNS. And all study participants’ physical activity, stages of physical activity, self-efficacy, motivation, and perceived benefits and barriers were measured at the pre, mid and post intervention. Frequency analysis, chi-square test, 2-way ANOVA RM were conducted to analyze data obtained in the study. All procedures were performed by using SPSS 23.0. Results The exercise information intervention using SNS during 12 weeks had a positive effect on the stages of physical activity of inactive college students, and there were statistically significant differences. In addition, physical activity, perceived benefits and barriers, self-efficacy, motivation positively improved after the intervention, but there were no statistically significant differences between experimental and control group. Conclusions The present study suggests that psychological strategies using various SNS programs have positive effects for inactive college students to increase physical activity and its related psychological variables.

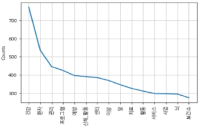
Purpose The purpose of this study is to introduce the basic concepts and procedures for topic modeling and to explain topic modeling to news articles about dementia-related physical activities. And it is also to discuss the possibility of using topic Modeling in the field of physical education. Methods In this study, the LDA algorithm of topic modeling is explained and the analysis procedure is summarized step by step by text preprocessing, text formatting, and topic number determination. The application cases were selected from 274 news articles about dementia-related physical activities reported in 13 major daily newspapers from 2000 to 2018. Results When the number of topics is 3, the Coherence Score figure is the highest. Topic 1 is about welfare services for dementia patients, Topic 2 is about prevention of dementia, and Topic 3 is about dementia research. The ratio by each subject is Topic 2 (46.0%), Topic 3 (33.2%) and Topic 1 (20.8%) in order of high ratio. Conclusion Topic modeling is an effective methodology to extract potential information excluding subjectivity of researchers. It is expected to be used when searching for information in massive texts in the field of physical education.



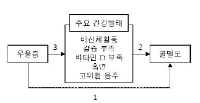
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between depression and bone mineral density in Korean elder men (55+), and test mediating role of health behaviors. Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2006-2011 data were analyzed. Bone mineral density was measured using DXA. Depression was measured by whether a participant had diagnosed depression, depressed mood lasted longer than 2 weeks, and/or suicidal thinking. Mediating health behaviors were serum vitamine D, calcium intake, high-risk drinking, endurance physical actiity, and resistance exercise. The associations among depression, health behaviors, and bone mineral density with demographic covariates were tested by linear regression, logistic regression, and path analysis. Diagnosed depression was not significantly associated with bone mineral density. Men who experienced substantial depressed mood and suicidal thinking has significantly lower bone mineral density than non-experienced counterparts. The effect of suicidal thinking on bone mineral density was mediated by endurance physical activity only. This study results suggest that elder men who experienced severely depressed mood and suicidal thinking were at-risk population for osteopenia. Also, physical activity intervention seems to be a priority to prevent osteoporosis comorbidity in depressed people.