Purpose The purpose of this study is to review the governance of the 2018 Pyeong Chang Winter Olympic Organizing Committee (POCOG), and to suggest potential governance models for the next mega sport event organizing committee. Methods For this study, In-depth Interview was conducted on 5 subjects who were involved in the process of organizing Pyeong Chang Olympic Games internally and also externally. Throughout the interviews, the subjects were asked to answer questions about the leadership of POCOG management, working relationships among the staff members, and improvement plans for the next mega event. Results The results of the study are as follows: First, POCOG sat up a governmental system and then tried to blend government officials and people from private sector to run the committee; Second, POCOG leadership was not an effective to run an Olympic Organizing Committee; Third, there were not effective working relationships among the staff members in the committee; Lastly, the subjects proposed the future organizing committee to hire more experts, to establish some kind of system that can prevent the turnover, and to go for privatization with the limited involvement from the government. Conclusions Therefore, this study suggests that the future mega sport event organizing committee should implement effective governance in bring more experts, and keeping them from the beginning to the end of the event. Also the organizing committee should consider implementing corporate governance to run the committee with entrepreneurial mindset, and to create cooperative working environment among the committee members.
This study was designed to examine the effects of 12 weeks of resistance exercise training on physique, body composition, insulin resistance, and blood lipid profiles in 20s normal weight obese females. Sixteen females were randomized into one of following two groups: resistance training group (RT group; n=8) and control group (CON group; n=8). Subjects in RT group completed 12 weeks of resistance exercise training for three times/wk, and subjects in CON group were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same intervention period. Data were analyzed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post hoc test. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Body weight, BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, WHR, and WHtR decreased significantly in RT group. 2) All variables regarding body composition did not change in both groups; however, fat mass was tended to decrease more in RT group than CON group. 3) Fasting plasma glucose decreased significantly in both groups, whereas other variables regarding insulin resistance did not change significantly in both groups. 4) All variables regarding blood lipids did not change significantly in both groups. Results indicate that 12 weeks of resistance exercise training was beneficial in physique and body composition; however, it was not beneficial in insulin resistance and blood lipid profiles in 20s normal weight obese females. Future research including normal weight obese subjects with higher age would be warranted to elucidate more clearly the effects of resistance exercise training on metabolic status.
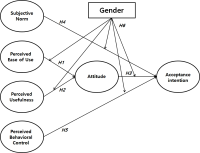
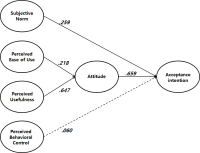
Purpose The current study was aimed to examine acceptance intention of sports wearable smart device using the Technology Acceptance Model and Theory of Planned Behavior. Methods Data were drawn from 357 consumers who had experience purchasing sports products. Data were analyzed through frequency analysis, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling using SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 program. Results First, perceived ease of use had a positive effect on attitude. Second, perceived usefulness had a positive effect on attitude. Third, attitude had a positive effect on acceptance intention. Fourth, subjective norm had a positive effect on acceptance intention. Fifth, perceived behavioral control did not affect acceptance intention. Sixth, differences of path coefficients between attitude and acceptance intention, subjective norm and acceptance intention were significant according to gender. Conclusion The significance of this research is to provide the basis of positioning strategy for domestic companies of sports wearable smart device.


This study was designed to investigate the effects of increment of physical activity for 12 weeks through aerobic exercise training or change from own vehicle to public transportation for commuting on physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function in middle-aged men. Forty-four subjects, aged 30-50 yrs, were randomly assigned to either one of three groups, i.e., aerobic exercise training group (TR: n=14), change to public transportation group (PT: n=15), or control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR performed aerobic exercise for 30 min per sessions, three sessions per week, subjects in PT changed from their own vehicle to public transportation for commuting, and subjects in CON maintained their life patterns during the same intervention period. Physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function were measured at pre- and post-test, and the data were analyzed by repeated two-way ANOVA. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables related to physical fitness improved significantly in TR. Right grip strength, standing long jump, side step test, and sit-and-reach improved significantly in PT. 2) Although there were no significant changes in all variables related to insulin resistance, the variables tended to be improved in TR and PT. 3) TNF-α decreased significantly in TR and PT. IL-6 and CRP tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. 4) ALT decreased significantly in PT. AST and γ-GT tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. It was concluded that the 12 weeks of change to public transportation as well as aerobic exercise training would be beneficial for physical fitness and inflammatory markers. These interventions also would be possible to improve insulin resistance and liver function. The increment of physical activity through change from own vehicle to public transportation was found to be equally beneficial for health promotion compared to aerobic exercise.

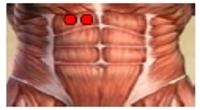
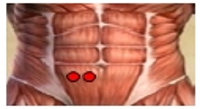
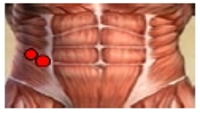
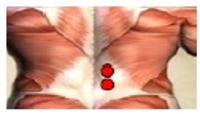
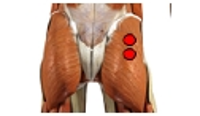
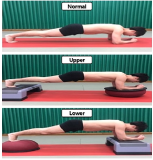
Purpose This study was to analyze and compare series of muscle activities during plank exercises with use of togu-jumper. Methods Ten male subjects (age 26.9±1.7 yrs, height 172.2±5.7 cm, weight 66.5±7.5 kg) who have no musculoskeletal disorder with one's upper or lower limb were selected as subjects. To analyze and compare series of muscle activity, five of surface EMG electrodes were attached to the upper rectus abdominis (URA), lower rectus abdominis (LRA), external abdominal oblique (EO), erector spinae (ES) and gluteus maximus (GM). Each subject did plank exercise on stable support surfaces (normal surfaces) and unstable support surfaces with the togu-jumper. For each dependent variable, one-way ANOVA with repeated measures were performed with significance level p<.05. Contrasts were performed to execute post tests for results with statistical significance. Results The study showed that the average IEMG values of URA and LRA increased in Upper (Togu-jumper used upper limb) compared to normal surfaces. This is perhaps because the effects of URA more than any other muscles for body stability. Furthermore, the peak IEMG values of LRA increased in Upper and Lower (Togu-jumper used lower limb) compared to normal surfaces. In addition, peak IEMG values of EO increased in Upper compared to Normal. This may have resulted due to momentary strong muscle activity in LRA and EO to correct body posture and balance. Therefore, using Togu-jumper on upper limb maximizes the performance of core training in plank exercise. Conclusions The study may be further applied to a method for effective training. It is considered that research and analysis has to be further done on modified plank exercise. Additionally, it is necessary to analyze not only global muscle but also local muscle, as a comprehensive research, to suggest ideal method for plank exercise.



Purpose The study was designed to investigate the effects of 12 weeks of circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation on physical fitness and metabolic syndrome. Methods Forty-one menopausal women were randomly assigned to one of three groups. i.e., combined circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation group (CT+T: n=14), L-tryptophan supplementation group (T: n=14), and control group (CON: n=13). The subjects in CT+T exercised three sessions per week and took 3g of L-tryptophan per day for 12 weeks. The subjects in T took 3g of L-tryptophan per day for 12 weeks. The subjects in CON were asked to maintain their life pattern for the same period of intervention. Physical fitness and metabolic syndrome-related variables were measured at pre- and post-test. The data were compared by utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. Results Main results of the study were as follows: 1) Standing long jump, one leg standing with eyes closed, sit-and-reach, sit-up, and maximal oxygen uptake increased significantly in CT+T. 2) Body weight, body mass index, waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, fat mass, and percent body fat decreased significantly in CT+T. 3) Total cholesterol decreased significantly in CT+T. 4) Fasting plasma glucose (FPG), fasting plasma insulin, and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in CT+T. FPG and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in T. 5) Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and rate pressure product decreased significantly in CT+T. DBP and MAP decreased significantly in T. 6) Number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased significantly in CT+T and T. Conclusion It was concluded that the circuit training and L-tryptophan supplementation would have positive effects on physical fitness and metabolic syndrome, and that L-Tryptophan supplementation would have positive effects on metabolic syndrome by improving insulin resistance and hypertension in menopausal women.
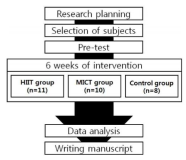
The primary purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 6 weeks of high-intensity intermittent training (HIIT) and moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) under relatively equal energy expenditure on body composition, aerobic capacity, cardiovascular function, insulin resistance, and blood lipid profiles in 20s overweight males. Twenty-nine males were randomized into one of the following groups: HIIT group (n=11), MICT group (n=10), and control group(n=8). Subjects in HIIT group completed 6 weeks of training for 25 min/sessions, three times/wk, and subjects in MICT group exercised for 33 min/session to equalize the energy expenditure with HIIT group. Subjects in control group were asked to maintain their normal life pattern during the same intervention period. Data were analyzed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post hoc test. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Body weight, BMI, fat mass, and WHR decreased significantly in HIIT group. 2) VO2max, VEmax, and time to exhaustion increased significantly in HIT group. 3) SBP decreased significantly in HIIT group and HRrest was tended to decrease in HIIT. 4) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR were tended to decrease in HIIT, but the changes failed to reach the statistically significant level. 5) HDL-C and TG were tended to improve in HIIT, but the changes failed to reach the statistically significant level. Results indicate that high intensity intermittent exercise training is more beneficial in aerobic capacity and cardiovascular function. It was also suggested that 6 weeks of aerobic exercise training in either high intensity intermittent or moderate intensity continuous was not sufficient enough to induce changes in body composition, insulin resistance and blood lipid profiles.

The purpose of the study is to find the impact of social and economic factors in physical activity of children and youth. This study utilized the data from 4th Korean Children and Youth Panel Study(KCYPS), and the analysis were carried out based on the starting sample of 2,009 from ‘the elementary 4 panel’ and 1,978 from the ‘middle school 1 panel’ and 1,984 from the ‘high school 1 panel’, 5,971 full data were used in the final analysis. Data were processed using hierarchical regression analysis and it was statistically validated at the significance level of 0.05. First, Pearson r and Spearman ρ showed that all variables are statistically significant correlations. Second, among the first factors of personal and family characteristics, household income level(B=.113), family composition(B=-.049) and parental education (B=.060) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, parental education (B=.027) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Third, among the second factors of community-level characteristics, Gini coefficient (B=-.810), wealth concentrating (B=.120) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, the Gini coefficient (B=-0.315) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Additional factors that determine the coefficient of variation in the level 2 were found to be 0.623 and 0.001 respectively. Therefore, second factors of community-level characteristics are added such as Gini coefficient, wealth concentrating were explained to children and youth exercise time during physical activity 62.3%(p<.01) and subjective evaluation of physical education in grades 0.1%(p<.01). predictive power to
The purpose of the study was to investigate the relationship between the different kinematical variables with respect to the records and techniques performed by the participants during the 2011 Daegu IAAF World Championships Men's Pole Vault Event. Subjects chosen for the study were 8 male athletes who were selected for men's pole vault finals (highly skilled group) and 7 athletes who scored lowest record (skilled group) from the men's pole vault qualifying round. Personal best record of the each subjects were chosen to perform two dimensional (2D) and three dimensional (3D) video analyses. The data were obtained at 60 Hz with the use of five video cameras and digitizing was performed. Kinematical variables were calculated after smoothing the data using 2nd order Low-Pass Butterworth filter at cut-off frequency of 10 Hz and Independent samples t-test was performed to test any differences between two subject groups. The results: during the run-up stage, the horizontal velocity rate of the number of steps and run-up phase was obtained higher in highly skilled group than skilled group. During the take-off phase, deceleration in the horizontal velocity rate was observed in highly skilled group than skilled group. Distinct technical characteristics of distant and lower take-off of the take-off angle (angle of pole support) were also observed in highly skilled group than skilled group. During the pole bending and releasing phase, horizontal velocity was generally higher in highly skilled group than skilled group. It is considered that highly skilled group was able to jump higher as the vertical velocity during the pole bending as well as release phase was much higher in comparison to the skilled group.

It has been known that β-alanine supplementation induce the increment of carnosine in vivo and was effective in delaying fatigue by buffering the hydrogen which was formed during exercise. This study was designed to investigate the effects of 4 weeks of β-alanine supplementation on physical fitness and blood lactate concentration in middle school soccer players. Nineteen middle school soccer players were randomly assigned to either one of two groups, i.e., β-alanine group (n=10) and placebo group (n=9). Subjects in β-alanine group consumed β-alanine 2 g/day during 1st and 2nd week, as well as 3 g/day during 3rd and 4th week, whereas subjects in placebo group consumed maltodextrin in the same manner. All subjects ate same menu and trained same amount at the same training camp during the intervention period. Body composition, aerobic capacity, anaerobic capacity, isokinetic function, and blood lactate concentration during maximal GXT were measured at pre- and post-test. Main results of the present test were as follows: 1) Fat mass and percent body fat decreased significantly in β-alanine group. 2) No significant changes were found in variables related to aerobic capacity in both groups. 3) Average power increased significantly in β-alanine group. 4) Isokinetic muscular endurance increased significantly in β-alanine group. 5) Blood lactate concentration did not change in eithet group; however, blood lactate concentration immediately after maximal GXT in β-alanine group tended to be increased more than placebo group. It was concluded that β-alanine supplementation would have positive effects for improvement of body composition, anaerobic capacity, and muscular endurance in middle school soccer players.