
Purpose The purpose of this study was (1) to analyze judges’ evaluation on rhythmic gymnastics performance by applying generalizability theory and (2) to suggest recommendations to improve judges' rating. Methods Data were 34 players’ scores from Senior Part at 29th KGA President’s Cup National Rhythmic Gymnastics Championship in Korea. Difficulty and execution scores in ball, clubs, hoop and ribbon event were analyzed. Analysis models containing components of area and reputation rank were designed and multivariate generalizability theory were used for analysis. Results The G-study results showed (1) that the error source about players has more significant impact to evaluation than other error sources in analysis model containing components of only player and judge, (2) that the error source about players has more significant impact to evaluation than other error sources in analysis model adding components of area, but the error source about area has more significant impact to evaluation of clubs event than other error sources, (3) that the error source about players has more significant impact to evaluation than other error sources in analysis model adding components of reputation rank, but the error source about reputation rank has more significant impact to evaluation of hoop event than other error sources in analysis model adding components of area. The D-study results showed generalizability coefficient was stable in analysis model without components of area and reputation rank, but generalizability coefficient in analysis model containing components of area and reputation rank not stable in some event. Conclusion Recommendations for improving judging were discussed.


The purpose of this study was to investigate the level of factors associated with points and the difference among weight categories after the revision of wrestling competition rules from video images. Factors associated with points were average point per a game, average points according to playing type, the occurring frequency of point according to the skills, the frequency and successful ratio of Parter, and the time zone of points occurred. The video contents were concerned on athletes ranked in 1 - 5 (6 person) at 59, 66, 75 Kg categories of Greco-Roman style in the 2014, 2015 World Wrestling Championship. The analysis was done by watching TV monitor several times. Five quantitative factors were tested between weight categories. As the results, no significant difference was found in average obtained point, but significant difference was found in average lost point (p<.05). Average obtained point showed significant difference in cross effect of the type of game and weight category. And average lost point showed significant difference in the type of game (p<.01) and weight category (p<.05), too. The frequency of point by skills of stand and ground wrestling showed significant difference in weight category (p<.001). However, no significant difference was found in frequency of point by time zone among weight categories. In conclusion, the point obtained and lost and the frequency of it are associated with the type of game and skills included in it of Greco-Roman style wrestling. New training program focused on enforcing the correct type of game and skills in it might be useful for developing the performance.
The aim of this study was to evaluate gender differences of expert and non-expert in match playing time, moving distance, energy consumption and heart rate (average, maximal) during 16 simulated badminton matches in male (n = 16) and female (n = 16) national elite players. The players had perform three sets on same day, and this time observed the playing time, moving distance, energy consumption and heart rate (resting, average, maximal) level during badminton match. Analyses of variance with repeated measures were used to test any significant time×group interaction effects on the measured variables. Statistical significances were tested at p = 0.05 with spss-pc (version 18.0). As a result, male's player had significantly difference between expert and non-expert in moving distance (p=.012), energy consumption (p=.003), average heart rate (p=.002) and maximum heart rate (p=.002). Female's players showed significant difference between expert and non-expert in moving distance (p=.001) and energy consumption (p=.012). In conclusion, there seemed to be an increased playing intensity (i.e., moving distance, energy consumption, average heart rate and maximum heart rate) from expert than non-expert in gender differences. These results suggest that men male's players with expert performed the game at a higher intensity than compared to non-expert, on the other hand female's player with non-expert showed that more activity and energy consumption was unclear during the game
The purpose of this study is to investigate the further direction of molecular biological studies, the advantages and limitations of assaying samples, and variables in figuring out the details of domestic and overseas studies verified through cell and molecular biological analysis in order to analyze the effect of concurrent training. The analysis study was limited to domestic and overseas literature, which investigated the effect of combined training using molecular biological analysis among studies to date. The study was reclassified by specialty, composed of professors of physical education and doctors of exercise physiology. The final selected study analyzed the subject and the trend of studies in terms of comprehensive perspectives. In detail, it analyzed hormonal and enzymatic changes in criteria such as leptin, 5-HT, ACTH(adrenocorticotropic hormone), cortisol, testosterone, GH(growth hormone), LDH(lactate dehydrogenase), CPK(creatine phosphokinase), antioxidants in blood samples and protein, and enzymatic and morphologic changes in for CRP, VEGF(vascular endothelial growth factor), PAI-1(plasminogen activator inhibitor-1), MAD(malondialdehyde), carnosin, and SDH(succinate dehydrogenase), the area of muscle fibers, ratio of type Ⅰ/Ⅱ muscle fiber and capillary proportion per muscle fiber in the extracted muscle by biopsy, for example. Finally, urine samples, and hormonal changes (like cortisol), were analyzed. The results of the analysis of domestic and overseas studies according to combined training has shown that this training has more varied effects than single training and lower improvement by interference effect or magnifying the effect of one type of training amongst the combined training types appears, rather than higher improvement through combined trainings. Therefore, it should be investigated in view of performance improvements relating to the characteristic of sports.

The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of running economy and energy return in lower extremities according to the increase of bending stiffness of the shoes, furthermore to investigate the relationship between running economy and energy return for the improvement of sports performance. Subjects employed for this study were 10 healthy male college students who have not had the experiences in lower extremities injuries. Four different kinds of shoes in bending stiffness as with 0.56 N/mm, 0.74 N/mm, 0.96 N/mm, 1.21N/mm were used respectively. 3-D cinematography and pulmonary gas analyzer were utilized for energy return and energy consumption data during running according to the increase of bending stiffness of the shoes to obtain the following results. As the bending stiffness of running shoes increased, the statistical significance were not founded, however, the tendency of decrease in max. flexion moment and power, increase in max. extension moment and power in lower extremity joint were showed. Joints energy showed no statistical significance in phase 1, however, the tendency of lesser absorbtion as the bending stiffness of running shoes increased were showed. More energy were generated as the bending stiffness of running shoes increased in phase 2 with no statistical significance. Energy economy increased according to the increase of bending stiffness of running shoes. Negative correlation were showed between flexion moment of hip joint and energy consumption(p<0.05). Slightly higher degree of correlation between max. flexion power of hip and ankle joint and energy consumption were showed without statistical significance. Negative correlation were showed between joints energy and energy consumption for ankle joint in phase 1(p<0.05).


PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of regular moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise on body composition, resting metabolic rate, and blood lipid profile in normal-weight obese women. METHODS The participants in the study were normal-weight obese women in their 20’s, divided into moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise (VIAE) groups. Aerobic exercise was performed three times a week for 8 weeks. To verify the exercise effect, pre- and post- body composition, resting metabolic rate, and blood lipid profile were analyzed. RESULTS Weight and body fat decreased in both groups, and lean body mass and resting metabolic rate increased in the VIAE group. Blood TC, TG, and LDL-C decreased in both groups and HDL-C increased in the VIAE group. CONCLUSIONS In normal-weight obese women, vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise is more effective than moderate intensity aerobic exercise for improving body composition, resting metabolic rate and blood lipid profile.
PURPOSE This study examined whether K-league fans’ responses to game outcomes align with reference-dependent preference and loss aversion principles. METHODS We collected user comments from the 2023 K-league game highlights videos on YouTube. We identified each user’s supporting team and excluded neutral fans’ comments. Sentiment analysis using KoBERT was applied, and estimated sentiment scores served as dependent variables. We performed panel regression to test whether unexpected wins and losses generate positive and negative comments. RESULTS First, an unexpected win generates more positive comments, and an unexpected loss generates more negative comments; a reference-dependent preference exists. Second, the difference between the coefficient on upset win and the absolute value of the coefficient on upset loss is not statistically different; loss aversion does not exist. CONCLUSIONS The findings derive a deeper understanding of sports viewership and explain the difference between domestic and overseas sports fans. Also, the findings provide insights into the domestic professional sports business.
PURPOSE This study developed and tested a theoretical research model delineating the relationships between sports consumers’ team identity and their response to regional identity, sense of community, and community contributions. METHODS To achieve the purpose of this study, a total of 1,196 spectators who attended professional baseball games were surveyed. For the data analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, convergent validity, discriminate validity, and composite reliability were performed to confirm the validity and reliability of the scale through AMOS 24.0. Research model and hypothesis testing were conducted using structural equation modeling, which used data from ten different professional baseball team area contexts. RESULTS The results provide empirical evidence of the positive influence of sports consumers’ regional identity and sense of community on team identity toward community contributions in sporting event area contexts. CONCLUSIONS This study confirmed the role of regional identity and sense of community in building professional sports team identities and community contributions.

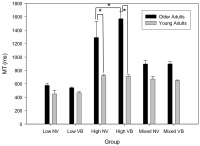
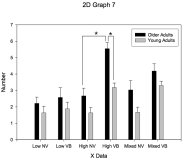
Purpose The present study was to investigate to extent that effects of sensory information distortion by muscle vibration on continuous limb movement in aging and accuracy constraint. Methods Young adult group (n=11) and older adult group (n=11) were divided. All participant were instructed to perform repetitive aiming movement to specified targets under three-accuracy constraints (i.e., low, high, and mixed accuracy constraints) in the vibration and no-vibration conditions. Kinematic data was collected by movement time and movement error frequence. Results The results showed that compared with young adult, older adult increased movement time when accuracy constraint was high under vibration condition. Older adult also was a high degree of movement errors than young adults when accuracy constraint was high under vibration condition. Conclusion The muscle vibration stimulation may influence considerably on the continuous limb movement probably due to degeneration in sensory information processing by aging.


Purpose This study was to explore construct of fear and courage behavior overcoming the fear and relationship between fear and courage in competition. Methods Total 65 national athletes of combat sports(Judo, Boxing, Taekwondo, Fencing) responded to open questionnaire about fear and courage behavior in competition. The data was analyzed by triangle verification and content analysis. Results Firstly, the fear of combat sports athletes consisted of five factors, which were negative consequences, lack of preparation for a game, concerns of performing one’s best, expectation of significant others, and internalized ego threat. Secondly, courage behaviors to overcome fear were self-effort, self-suggestion, self-conviction, selfish self-regulation, social self-control, self-analysis, and acceptance of experience. Finally, there were the relationship between fear and courage in competition. Conclusion These results will contribute to provide useful information for combat sport athletes and coaches in different level to cope with competition fear.
