PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the decision-making process for consumers participating in sports centers based on an extended goal-directed behavior model (EMGB), and to provide empirical data for establishing effective operation strategies for sports centers, including additional risk perception of consumers during pandemic. METHODS A total of 446 surveys were used as the final sample. For data analysis, SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 were used for frequency analysis, correlation analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, and structural equation model analysis. RESULTS Except for hypothesis 2 and 9, all of the hypothesis were chosen. CONCLUSIONS The findings suggested that extended goal-oriented behavior models can increase consumers' cognitive and emotional factors through emotional aspirations, suggesting that a lower risk perception of COVID19 increases their desire to participate in sports centers, and provides academic fundamental data on how to increase and activate sports centers.
PURPOSE This study aimed to verify the differences in anticipated regret and gambling discontinuance intent based on the fear appeal type and source similarity in different types of horse-racing gamblers. METHODS Using convenience sampling, 172 responses were collected from horse-racing participants who bought horseracing tickets within the last 6 months. After eliminating 30 insincere responses, descriptive, correlation, reliability, and two-way multivariate covariance analyses were conducted using SPSS Ver. 26.0. RESULTS Anticipated regret and discontinuance intent were higher under fear appeal using social compared with financial risk. Compared to recreational gamblers, problem gamblers had higher anticipated regret and discontinuance intent under fear appeal using social compared with financial risk. There were no differential impacts of source similarity on anticipated regret and discontinuance intent in both types of gambler. CONCLUSIONS Practitioners in charge of conducting messaging campaign to prevent addiction to horse-racing gambling may cause problem gamblers to expect regret and quit gambling by delivering preventive messages with relatively unfamiliar risks such as social risks, rather than familiar risks such as financial ones.
PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze the moderating effect of physical fitness on the relationship between abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome (MetS) in older women. METHODS A total of 190 participants were categorized based on waisthip ratio (WHR) into high (50%) and low (50%) groups, as well as based on Z-score of fitness into high (25%; high fit), moderate (50%; moderate fit), and low (25%; low fit) groups. Logistic regression was used to assess the relative risk of MetS based on abdominal obesity and fitness levels, and moderation analysis using the Process macro was conducted to explore the moderating effect of fitness on the relationship between abdominal obesity and MetS risk factors. RESULTS After adjusting forcovariates, logistic regression showed that high WHR (odds ratio (OR)=2.721, p=0.004) led to a significantly higher risk of MetS compared with low WHR; the high fit group (OR=0.360, p=0.044) had a significantly lower risk of MetS compared wih the low fit group. Moderation analysis revealed that the impact of abdominal obesity on MetS risk factors varied depending on the level of fitness (β=-0.495, p=0.037), and the results remained significant after covariate adjustment (β=-0.458, p=0.049). CONCLUSIONS This study suggests that the risk of MetS from abdominal obesity can be mitigated by higher levels of physical fitness. These findings highlight the need for participation in regular physical activity to maintain a high level of fitness, along with proper nutritional intake, to prevent MetS in older women.
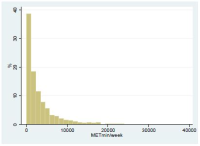
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the associations between accelerometer-measured physical activity and both cardiometabolic disease risk factors and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. METHODS We performed a retrospective cohort study with age-sex matched case-control using data from the 2014-2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, which was administered to South Korean adults (n=320). Individuals were categorized into quartiles based on accelerometer-measured moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA). Demographic and physical characteristics, waist circumference, visceral adiposity index, blood pressure, lipid profiles, and TG/HDL-C were observed. The associations between MVPA status and cardiometabolic disease risk factors as well as metabolic syndrome were determined using multiple logistic regression. RESULTS For the waist circumference, SBP, DBP, MBP, visceral adiposity, triglyceride, and a surrogate estimate of insulin resistance, the Q1 and Q2 groups had higher means compared with the Q3 and Q4 groups. HDL-C was higher in the Q3 and Q4 groups compared to the Q1 and Q2 groups. Odds ratios for cardiometabolic disease risk factors and metabolic syndrome decreased in a curvilinear manner with the increasing quartile of MVPA. CONCLUSIONS Adults with higher MVPA participation were strongly associated with cardiometabolic disease risk factors and metabolic syndrome.
PURPOSE This study aimed to identify movement pattern differences in the running of youth soccer players with and without lateral ankle sprain (LAS) histories. METHODS A total of 12 participants were recruited and assigned to the LAS group or the control group. All participants were assessed for anthropometric data, and they filled in the subjective ankle function questionnaires. Then, reflective markers were attached to their bodies, and they were instructed to run at the preferred speed on the 9-m runway thrice. 3D joint angles for ankle, knee, and hip joints were exported, and their mean values and 95% confidence intervals were calculated. Ensemble curve analysis was conducted to compare running kinematics between the groups. RESULTS The LAS group exhibited fewer dorsiflexion angles and more inversion angles compared to the control group. Excluding the dorsiflexion deficits and more inverted ankles, there were no significant differences between the groups. CONCLUSIONS Although the ankle kinematic patterns found in this paper are not considered LAS risk factors, it will be able to identify precise LAS risk factors with prospective design (e.g., lower extremity movement patterns) as well as intrinsic risk factors.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between depression and bone mineral density in Korean elder men (55+), and test mediating role of health behaviors. Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2006-2011 data were analyzed. Bone mineral density was measured using DXA. Depression was measured by whether a participant had diagnosed depression, depressed mood lasted longer than 2 weeks, and/or suicidal thinking. Mediating health behaviors were serum vitamine D, calcium intake, high-risk drinking, endurance physical actiity, and resistance exercise. The associations among depression, health behaviors, and bone mineral density with demographic covariates were tested by linear regression, logistic regression, and path analysis. Diagnosed depression was not significantly associated with bone mineral density. Men who experienced substantial depressed mood and suicidal thinking has significantly lower bone mineral density than non-experienced counterparts. The effect of suicidal thinking on bone mineral density was mediated by endurance physical activity only. This study results suggest that elder men who experienced severely depressed mood and suicidal thinking were at-risk population for osteopenia. Also, physical activity intervention seems to be a priority to prevent osteoporosis comorbidity in depressed people.

PURPOSE This study analyzed the difference in lower extremity joint angle and shock absorption patterns at the point of maximum ground reaction force during single-leg drop landing with or without anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR). METHODS Forty adult males were recruited for this study, with 19 in the ACLR group (age: 20.52±1.43years, height: 179.26±5.18cm, weight: 74.91±6.29kg) and 21 in the control group (age: 21.42±1.61years, height: 174.97±6.83cm, weight: 69.27±7.56kg). Participants performed single-leg landings on a 30cm tall box. An independent sample t-test was used to analyze the difference in kinetics variables at the point of maximum ground reaction force upon landing, with significance set at p=0.05. RESULTS The lower limb joint angle showed significant differences in hip flexion, hip abduction, knee flexion, and knee valgus (p<0.05) between groups. There was no significant difference between the groups in terms of the results of kinetics variables during single-leg landing (maximum ground reaction force, lower extremity stiffness, and shock absorption time). CONCLUSIONS The ACLR group showed a clear difference in kinematics compared to the control group, but no significant difference in kinetic results was found. The two groups compensated for the same impact with different movements, though movements in the ACLR group may increase the risk of ACL re-injury. Those with ACLR should strive to reduce the risk of re-injury by training to use correct movements.
PURPOSE This study identified a company sports club’s dual characteristics— both for leisure activity and as an extension of work—to provide comprehensive interpretation and understanding of such clubs. METHODS A qualitative case study design was employed, incorporating in-depth interviews, nonparticipant observation, and supplementary data collection from 25 office workers who had participated in an in-house sports club for at least one year. RESULTS Participants reported a wide spectrum of motivations, from voluntary motives such as stress relief and health improvement to more obligatory or organizationally driven motives, including pressure from supervisors or colleagues and expectations related to performance evaluations. The club offered both team sports—which fostered teamwork and a sense of belonging—and individual sports—which offered personal development opportunities. However, some participants experienced blurring of work–leisure boundaries and reemergence of hierarchical organizational culture, leading to conflict and fatigue. CONCLUSIONS Overall, Although company sports clubs have become a welfare program that provides employees with opportunities for leisure and self-development and promote inter-departmental communication and collaboration, they also carry the latent risk of imposing additional burdens and pressures on employees. These findings underscore the need for refined operational strategies and institutional improvements to mitigate negative outcomes and maximize such programs’ original intent.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the occurrence of sports injuries among badminton national team candidates during training camps and to identify appropriate measures for players to effectively manage and respond to such injuries in the future. METHODS The participants consisted of 123 individuals who took part in national team candidate training camps for badminton in 2022 and 2023. Record sheets were utilized to document the athletes' thoughts and opinions related to exercise injuries during the training period. RESULTS Badminton national team candidates experienced exercise-related injuries in various areas, including the ankles, thighs, knees, hips, shoulders, and back. Female players had a higher incidence of lower body injuries compared to their male counterparts. Through interviews with players about these injuries, individualized approaches involving appropriate rest and training adjustments were found to be necessary; additionally, educating the players about rehabilitation strategies for exercise injuries is essential. CONCLUSIONS When conducting recreational training activities, it is important to avoid fostering excessive competitive attitudes. Additionally, if potential risks are present within the exercise environment, it is crucial to assess and address these with the utmost caution.
PURPOSE This study analyzed the effect of dynamic lumbar kyphosis on the biomechnical factors affecting the lumbar joints during deep squats. METHODS Thirty adults in their 20s who had experienced weight training for more than one year participated in this study (age: 23.4±3.5years old, height: 175.3±4.3cm, weight: 75.8±6.5kg, squat single repetition maximum (1RM) weight: 115.3±19.5kg). Under both restricted dynamic lumbar kyphosis (RDLK) and dynamic lumbar kyphosis (DLK), subjects completed one repetition of deep squats at a load of 70% of their 1-RM weight. To verify the consistency of deep squat movements performed under DLK and RDLK conditions, intra-rater reliability was analyzed using intra-class correlation . The biomechnical variables of the lumbar joint were calculated during DLK and RDLK deep squats. Paired sample t-tests (IBM SPSS 27.0, Armonk, New York, USA) were used for statistical verification. RESULTS During the deep squat movement performed in DLK and RDLK conditions, the peak angles of the ankle, knee, and hip joints, the minimum height of the pelvis, and the time and tempo showed statistically high reliability, confirming the accuracy of the movement. The peak flexion angle and moment, left flexion moment, left rotation moment, and compression force factors of the lumbar joint during deep squat were significantly lower in RDLK than in DLK. CONCLUSIONS Restricting lumbar dynamic kyphosis during deep squats is essential for decreasing the risk of lumbar joint injury.