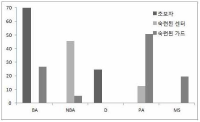
PURPOSE In this study, in-depth interviews were conducted with track-and-field athletes and leaders who participated in the Tokyo Olympics. The study aimed to present practical measures for the development of Korean track and field, which people at the forefront of Korean track and field thought. METHODS In-depth interviews were conducted using semi-structured questions for a total of five track-and-field national athletes and four track and field coaches. RESULTS A total of 39 subcategories and 104 concepts were derived with regard to four research questions: the process up to the Tokyo Olympics, the actual condition of Korean track and field, a comparison with track-and-field power nation, and practical measures for becoming track-and-field power nation. CONCLUSIONS Practical measures are needed to improve and develop the competitiveness of Korean track and field, which is expected to improve its competitiveness and help develop Korean track and field in the future.

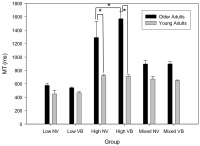
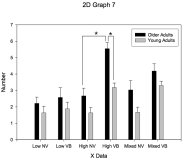
Purpose The present study was to investigate to extent that effects of sensory information distortion by muscle vibration on continuous limb movement in aging and accuracy constraint. Methods Young adult group (n=11) and older adult group (n=11) were divided. All participant were instructed to perform repetitive aiming movement to specified targets under three-accuracy constraints (i.e., low, high, and mixed accuracy constraints) in the vibration and no-vibration conditions. Kinematic data was collected by movement time and movement error frequence. Results The results showed that compared with young adult, older adult increased movement time when accuracy constraint was high under vibration condition. Older adult also was a high degree of movement errors than young adults when accuracy constraint was high under vibration condition. Conclusion The muscle vibration stimulation may influence considerably on the continuous limb movement probably due to degeneration in sensory information processing by aging.

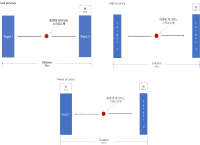

Researchers and teachers in physical education have emphasized sportsmenship in sport education setting. However, how to teach sportsmenship in physical education is not proposed yet. The purpose of this study was (1) to develop an instructional program for teaching and learning sportsmanship and (2) to examine its effects on sportsmenship. Participants were 7th middle school students(N=95). Data were collected using Sportsmanship Test(Park, 2014), open-ended questionnaire and in-depth interviews with students. The data were analyzed through paired samples t-test and qualitative content analysis. Results showed that significant difference was observed in students' sportsmanship test scores after instruction. Analysis of interview data showed that students experience the value of utmost effort, respect for opponents, respect for teammates, acknowledging results, respect for judgment, and valuable lessons related to character education. Implications for sportsmanship education using instructional program were discussed.



The objective of this study was to examine the relationships among preferred and perceived leadership behavior, their congruence, and satisfaction with leadership based on Chelladurai's(1978) Multidimensional Model of Leadership(MML). To achieve the study objective, 210 professional dancers from 6 professional dance teams located in Seoul and the suburbs participated in this study. For hypotheses testing, descriptive statistics, hierarchical multiple regression analyses, and a confirmatory factor analysis using SPSS and AMOS were used. Results showed that the congruence between preferred and perceived leadership behavior did not have statistically significant influence on dancers satisfaction. The results of the study were inconsistent with what MML suggested. However, the results were quite consistent with empirical evidences of previous studies that investigated the influence of the congruence between preferred and perceived leadership on satisfaction.
This study aimed to compare professional sport consumers on the basis of their ideology, spectator motivation, and message framing. In order to answer the research questions, the study first examined whether message framing effects existed across the designated variables. The study also assessed whether there were any differences in progressive-conservative ideology and motivation across respondent groups. The participants were spectators of two professional sports, soccer and baseball, sourced from 9 stadiums. Data were collected by the researcher and 33 survey assistants, from May to August 2013. The results of a chi-square test, MANOVA, and MANCOVA indicated that significant effects in message framing existed across the two variables. The findings also showed differences in ideology and motivation across major variables (e.g., age, gender, sports, and choice of newspaper). Some issues including media communication strategies were discussed based on the results of this study.
PURPOSE This study investigated the effects of moderate-intensity continuous exercise (MICE) and high-intensity interval exercise (HIIE), performed postprandially, on blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lactate levels in men aged 40–50 with prediabetes and prehypertension. METHODS Twelve men with prediabetes and prehypertension were selected. After consuming a liquid meal, the participants participated in three trials: MICE, HIIE, and a non-exercise condition, with a one-week washout period between each trial. The trials were conducted in a counter-balanced manner to ensure equal energy expenditure across conditions. The intensity of the MICE trial was set at 70% of the heart rate reserve (HRR), whereas the HIIE trial alternated between 50% and 90% of HRR for 30 minutes. Blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lactate levels were measured at various time points during each trial, and a two-way repeated-measures ANOVA was used for analysis. RESULTS 1) In the MICE trial, significant reductions were observed in blood glucose (at 15 and 30 minutes during exercise), systolic blood pressure (SBP) (at 50 minutes post-exercise), and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (at 20, 40, 50, and 60 minutes post-exercise). 2) In the HIIE trial, significant reductions in blood glucose (at 15 and 30 minutes during exercise), SBP (at 40 minutes post-exercise), and DBP (at 40 minutes post-exercise) were observed. Blood lactate levels significantly increased. 3) When comparing the two exercise trials, blood glucose in the HIIE trials showed a recovery trend post-exercise, and blood lactate levels increased to a greater extent. CONCLUSIONS These findings suggest that both MICE and HIIE effectively lower blood glucose during exercise, but HIIE causes a more rapid post-exercise increase in blood glucose compared to MICE. In addition, MICE results in a smaller rise in blood lactate. Therefore, MICE is recommended for improving prediabetes and prehypertension. Future research should compare these effects in healthy individuals and examine long-term adaptations to repeated exercise.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of an 8-week online yoga training on body composition, muscle activity, flexibility, and balance in males (n=7) and females (n=15). METHODS Twenty-two participants were recruited and divided into two groups (Exercise group, n=11 and control group, n=11). All participants had two visits. During the visits, body composition, muscle activity for forward and back-bending poses, flexibility for sitting-forward and back-bending poses, and balance for one-leg standing were determined. After 8-week yoga training, all measurements were re-performed. An independent t-test was performed to determine the difference between the exercise and control groups. A two-way repeated measures of ANOVA was used to assess the interaction effects (group*time). All values were represented as mean ± standard deviation. An α level was set at 0.05 for all analyses. RESULTS First, the height significantly increased (F=16.573, p=0.001) and body fat mass (F=7.109, p=0.015) and body fat percent (F=7.667, p=0.012) were significantly decreased after the 8-week online yoga training. Second, the muscle activity for vatus lateralis doing a back-bending pose (F=6.140, p=0.022) significantly increased after the 8-week online yoga training. Third, the flexibility on sitting-forward bending pose (F=4.661, p=0.043) and back-bending pose (F=11.650, p=0.003) were statistically increased after the 8-week online yoga training. Lastly, balance on the Center Of Pressure (COP) X (F=5.769, p=0.026) and the Center Of Pressure (COP) Y (F=4.365, p=0.05) significantly increased after the 8-week online yoga training. CONCLUSIONS This study will provide scientific evidence on improving exercise programs using online yoga training on physical activity.
Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of a single corrective exercise (CEX) and corrective kinesio taping (CKT) on gait patterns, plantar pressure, balance, and pain in 20~30s female patients with moderate hallux valgus. Methods Twenty-one participants (age: 30.1±5.1 yrs; height: 164.1±4.8 cm; body weight: 56.7±6.8 kg; body mass index: 21.2±5.7 kg·m-2; hallux valgus angle: 27.2±6.1°) with hallux valgus was recruited and participated in three trials, i.e., CEX trial, CKT trial, and combined CEX and CKT (CEX+CKT) trial, repeatedly in a counter-balanced order. One week of wash-out period was placed between the trials to minimize the effect of the previous treatment on the next treatment. Variables related to gait pattern, plantar pressure, balance, and pain were measured during each treatment. We carried out repeated two way ANOVA on measured variables. Results 1) Regarding gait patterns, CEX treatment and CEX+CKT treatments showed significant increases in the length of patients strides, the single support line during the stance phase, and significant reduction of the cadence. 2) Regarding gait cycle, CEX treatment and CEX+CKT treatments showed significant reductions in the contact times of forefoot, midfoot, and heel. There was a significant reduction of double stance phase in CEX treatment. 3) Regarding foot pressure on gait, CEX+CKT treatments significantly increased the maximum pressure of midfoot and heel. CEX treatments significantly increased the maximum pressure of forefoot. 4) Regarding balance, CEX treatment and CKT treatments significantly increased one leg standing with eyes closed. 5) Pain was significantly reduced in CKT treatment and CEX+CKT treatments. Conclusions According to the aforementioned results, it was concluded that a single CKT treatment was effective in reducing pain when walking and that plantar pressure, gait pattern, gait cycle, and balance were improved through a single bout of CEX treatments. Therefore, treatments by stage, starting with CKT treatments to reduce the pain, and then treating CEX to improve the gait pattern, gait cycle, foot pressure when walking, and balance ability, would be effective. Future research is warranted to identify the effects of long-term treatments.
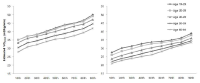
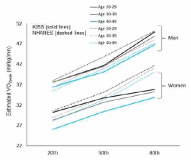
To provide the distribution of cardiorespiratory fitness including Bruce treadmill exercise time and estimated peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) and investigate association with cardiorespiratory fitness and metabolic syndrome, sedentary lifestyle, or education level among Korean adults. Analysis of data on 2,006 adults (19-64 yr) who had completed a maximal grade treadmill exercise test, from the Sports Institute of Sports Science Fitness Standards (KISS FitS) project 2014-2015. The mean maximal exercise time was 11’26’‘, 11’18’‘, 11’06’‘, 10’03’‘ and 8’51’‘ (minutes and seconds) for men 19-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59 and 60-64 years of age, respectively, for women, it was 9’49’‘, 9’09’‘, 8’42’‘, 8’01’‘ and 7’33’‘ for the corresponding age groups. The mean peak oxygen uptake was estimated as 42.3, 41.8, 41.2, 37.6 and 33.6 ml/kg/minute for men 19-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59 and 60-64 years of age, respectively, For women, it was 34.0, 31.8, 30.3, 28.0 and 26.4 ml/kg/minute for the corresponding age groups. A positive association between cardiorespiratory fitness level and education level was observed for both men and women. Furthermore, participants with sedentary lifestyle had a significantly lower cardiorespiratory fitness than participants with activity lifestyle. Finally, Men with moderate and high fitness level had 50% and 87% lower odds for the metabolic syndrome, and women had 48% and 50% lower odds for the metabolic syndrome, respectively, than the ones with low fitness level after adjustment for age, smoking, alcohol intake, and sedentary lifestyle. These results can be used to track future Korean assessments and to evaluated interventions. The differences in fitness status by education level, sedentary lifestyle or metabolic syndrome can also be used to develop health policies, program and educational services.

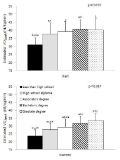

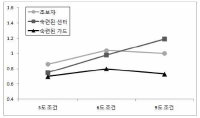
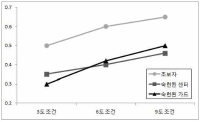
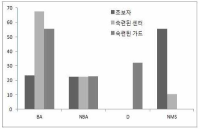
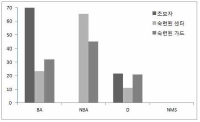
The purpose of this research was to investigate the difference in decision making and perceived eye-focus location on peripheral vision and attacker's expertise in basketball tactical game. A total of twenty four subjects who were expert guard players (n=8), expert basketball center players (n=8), and novices (n=8), participated in this experiment. All subjects participated two tasks. The first task was to anticipate the attack direction after viewing a sequence of basketball tactic film. These films simulated three situations including offensive patterns. The three situations were consist of 3, 6, 9 degree peripheral vision. The second task was to express the level of confidence on their anticipation and to verbalize the perceived visual cues immediately after responding. For this research, an Eyelink eye movement system, an equipment for measuring anticipating, basketball tactic film were used. The variables on anticipation of attack direction were speed, accuracy, and the level of confidence. The acquiring process of advanced visual cues was examined through analyzing visual search strategies and perceived eye-focus location. In order to examine the difference in visual search, in decision making, and in perceived eye-focus locations as a function of expertise, data were analyzed through descriptive statistics, two-way ANOVA, and two-way MANOVA. This research had the following results. First, there was a significant difference on the search rate among the three groups. But, on the other hand, expert guard and center exhibited more fixations of shorter duration than the novices in the 6 and 9 degree condition. Second, results from the ratio of fixation time allotted to areas in the 3 degree condition revealed that experts spent more time fixating the ball-attacker(BA) than novices. The results from the ratio of fixation time allotted to areas in the 6 and 9 degree condition revealed that expert guard and center spent more time fixating the non-ball attacker(NBA) than novices. Expert guard also fixated longer on the pass attacker(PA) and meaning space(MS) than novices. Finally, experts paid attention to two or three locations simultaneously, whereas novices did to only one location such as the ball, attacker, defender, non-meaning space in all condition.