PURPOSE This study aimed to verify the criterion validity of the two-minute step test in older Korean adults, develop an equation for predicting VO2max, and verify cross-validation. METHODS A submaximal exercise test and the two-minute walk test were performed on 150 older adults (74 males and 74 females) aged 65 years or older. Correlation analysis was performed to confirm criterion validity. An equation for estimating VO2max was developed through multiple regression analysis, and cross-validation was confirmed by performing a correlation analysis between measured and predicted values of VO2max. RESULTS The correlation coefficient between VO2max and the two-minute step test was 0.457 (p<.001). The adjusted R2 of the developed VO2max prediction equation was 0.430 (p<.001), and the explanatory variables finally selected were sex, age, number of steps in the two-minute step test, and percentage of body fat. The correlation coefficient between the measured VO2max (19.08±4.36) and the predicted VO2max (19.73±3.36) was 0.654 (p<.001). CONCLUSIONS This study confirmed the criterion validity of the two-minute step test in older Korean adults, and the cross-validation of the developed VO2max prediction formula was verified. The explanatory variables of the prediction equation will be easy to apply in the field, and more meaningful results will be derived if the validity of the prediction equation developed for a larger number of participants is verified.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to explore the process of change in parallel bar Skills over the last 20 years and to suggest the Skills to learn. Methods This study targeted on 48 finalists in parallel bar from 5 Olympic Games from 2000 to 2016 and 2019 World Championship over the last 20 years and explored the process of change in difficulty elements, each element group, and salto and arm hang. Results First, Element Group I preferred healy to support the most and performed it for 41 times. Also, percentage of salto and arm hang got lower and got substituted by Swing forward with 3/4turn and 3/4 healy to support and following a swing element to handstand on 1 rail, Healy to support. Secondly, Element Group III performed underswing frequently while performing salto and arm hang less frequently. Element Group III changed their skills to Moy piked with straddle backward to handstand, Swing forward straddle cut backward, and regrasp with straight body at horizontal. Third, Element Group IV preferred double salto backward pike the most in the past. However, the skill changed to double salto forward tuck with 1/2turn starting from 2016 Olympics. Conclusions Parallel bar is regarded as a weak gymnastics event. In response, this study result is expected to be used as the base data for growing the strength in parallel bar and winning the medals in main international competitions by suggesting the parallel bar Skills that Korean athletes need to learn.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of training methods on body composition, isokinetic strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function, and anaerobic power in female judo players. Methods Subjects performed weight training (n=10) and circuit weight training (n=10) consisting of 10 sports items for 12 weeks. In order to analyze the effects of training, body composition, isokinetic strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function, and anaerobic power were measured and the effect of training was verified. Results First, the comparison of body composition between WT and CWT groups showed that significant interaction effect between group and period was found in all variables (weight: F=1082.694, p=.001, body fat mass F=199.999, p=.001; skeletal muscle mass F=2481.698, p=.001, and percentage body fat: F=496.246, p=.001). Second, there was a significant interaction effect between group and duration in shoulder muscle strength and knee endurance (EPTL: F=6.598, p=.019; EAPL: F=12.860, p=.002). Conclusions The result of this study showed that the interaction effect between period and group was not significant according to the training method but the overall effect of the circuit weight training group was more positive than the weight training group. Therefore, it can be concluded that the 12 weeks circuit weight training can contribute to improve the performance of female Judo players by improving body composition, strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function and anaerobic power.

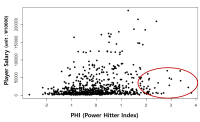
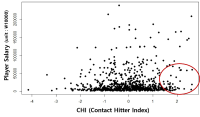
Purpose The main purpose of this current study is two-fold. Firstly, it attempts to develop a model to determine the true market value of Korean professional baseball players (hitters only) solely based on their athletic performances on the field. Secondly, it is to provide the evidential data for the market value of baseball players in Korea. Methods The statistical data and performance information were obtained from baseball almanac from KBO from 1997 to 2016. Seven hundred and ninety three players were included for data analysis. Principal component factor analysis was utilized to eliminate multicollinearity among 12 sabermetrics indices (OPS, GPA, SECA, TA, RC, RC/27, XR, ISO, PSN, sOBA, %OW, BABIP) and increase power of explanation of the proposed model with KMO(=0.77), p<0.001. Results The proposed model was successfully developed with YSalary = Years of Experience*921.5 + FA (free agent)*53528.9 + PHI(Power Hitter Index)*7313 + CHI(Contact Hitter Index)*5893.6. Furthermore, the proposed model explained 64.5% of variances of the market value for the Korean professional baseball players and proved to be statistically valid. Conclusions The newly developed model in this study was very helpful for us to identify the variables that affect the true market value of baseball players. It is expected that this model could make an important contribution in determining true market value of the baseball players in Korea.

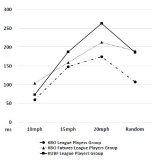
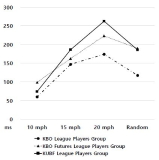
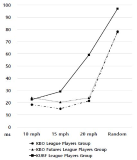
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to investigate effects of baseball expertise and stimulus speeds on coincidence-anticipation timing accuracy of batting. [Methods] Participants were 21 baseball batters, 7 of Korea Baseball Organization(KBO) League, 7 of Korea Baseball Organization Futures League, and 7 of Korea University Baseball Federation(KUBF) League. All of the participants were asked to swing the bat exactly at the time when the light arrived the target point of the runway. The Bassin Anticipation Timer was used to present stimulus with stimulus speed of 10, 15, and 20mph. Participants performed 10, 15, 20mph trials (3 kinds of speed per 5 times) and random trials (3 kinds of speed per 3 times randomly). The timing error of coincidence anticipation task was recorded and raw scores were transformed to constant error(CE), absolute error(AE) and variable error(VE). For data analysis, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures were used. And post-hoc test (Tukey HDS) were conducted. [Results] Results indicated a significant interaction on expertise and stimulus speeds for CE, AE and VE. The KBO League players group showed more accurate and consistent performance than the KBO Futures League players group and the KUBF League players group in baseball batting timing. [Conclusion] This findings revealed that coincidence-anticipation timing accuracy batting in baseball can be used as a factor to distinguish the ability of the other.

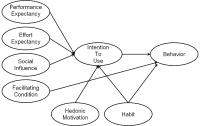
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the factor that influence the using behavior of online sport media by university students applying Unified theory of acceptance and use of technology 2(UTAUT 2). Methods The study performed a research survey using convenient sampling method. The sample was 235 university students who had experience with online sport media. The data were analyzed through frequency analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, and structural equation model using SPSS Windows ver . 20.0 and AMOS 20.0. Results The results showed that, firstly, performance expectancy and effort expectancy had a positive effect on intention to use, however, no significant influence on social effect on intention to use. Secondly, facilitating condition had positive effect on usage behavior. Thirdly, hedonic motivation had positive effect on intention to use. Fourthly, Habit had positive effect on the intention to use and usage behavior. Lastly, intention to use had positive effect on usage behavior. Conclusion Based on the conclusion of this study, online sports media companies should provide useful and convenient viewing experience by providing personalized services, and should apply various attraction strategies to habitually use sports online media.

PURPOSE Inclusive leadership has become increasingly important in sport organizations. Accordingly, this study examines interorganizational inclusive leadership effects on organizational trust and affiliated organizations’ employees depending on power distance. METHODS A total of 250 affiliated sport organization employees participated, and latent moderated structural equation modeling with a bifactor structural model was employed to test the hypotheses. RESULTS The results indicated that macro inclusive leadership as well as its two components significantly enhance organizational trust. Interestingly, power distance positively moderated the macro effect of interorganizational inclusive leadership on organizational trust. Lastly, organizational trust enhanced job performance and well-being, and reduced turnover intention. CONCLUSIONS The results provide meaningful insight into the relationship between lead and affiliated organizations in the context of highly competitive and collaborative sport organizations.

Vertical jumping is one of basic skills in many sports activities. Maximizing vertical jumping performance requires large “power”, which implies that one should generate force against the ground in a short period of time. In order to gain better understandings of how human musculo-skeletal system mechanically functions to achieve maximal power in vertical jumping, the proposed “dynamic catch” mechanism, one of “power amplification” mechanisms through the role of muscle-tendon interaction, was specifically reviewed base on the morphological and mechanical characteristics of lower limb muscle-tendon complex. By understanding basic structural and functional features of human muscle-tendon interaction, this review aims to provide basic scientific information for training and rehabilitation and promote convergence researches in related areas, such as sports biomechanics, mechanical engineering, and sports medicine.


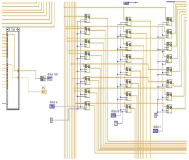
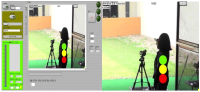
This study was to develop and to apply real-time neurofeedback system for psychological self-regulation of shooters. Neurofeedback system was developed with expert meetings consisting of 8 sport psychology, EEG, and sport engineering experts based on Labview program. Developed neurofeedback system was applied to 4 college shooters for 10 sessions(1 session/week, 30 mins/session). Collected EEG wave data were analyzed by paired sample t-test and independent sample t-test. The results were as follows: Firstly, based on user experience concept neurofeedback system was developed which easily perceived neurofeedback information as traffic lights with minimizing visual search activities. Secondly, after neurofeedback system application right brain activation level of shooters(except one shooter) were increased compared to left brain activation. Based on the results of this study, neurofeedback system can apply various sports and contribute to help athletes’ self-regulation and athletic performance enhancement in sport field.



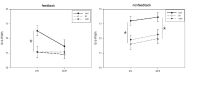
[Purpose] Perception plays an important role in understanding the environment or related objects in order for humans to perform physical movements more effectively. Sometimes they create different movements with different perceptions. Especially, visual perception errors that occur in sports situations can have a considerable effect on performance. Accurate knowledge of the environment in this process of perception is important in performing movements or actions. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of learning formation on perception using Muller-Liar illusion diagrams. To measure this, we compared the feedback group that induced knowledge learning and the control group that did not provide knowledge To see if there is a difference. Therefore, in this study, we have provided a visual feedback that can establish the cognitive awareness of the actual stimuli length to subjects, and investigated the changes in their matching action responses. [Methods] A total of 32 young and healthy subjects were randomly divided into two groups (Feedback and Non-Feedback groups). Subjects were asked to match the stimulus size with their index fingers and thumbs. Initially (pre-test), three different visual stimuli (inward, outward, and no arrows) were randomly presented 60 times (20 times each) and the grip sizes were recorded using the Liberty Motion Analysis System (Polhemus Co., America). Then, video clips of two lines merging each other were presented as feedbacks. Post-test protocol was identical to the pre-test protocol. The data were analyzed using the 3-way ANOVA with one RM factor (2 x 3 x 2). [Results] Results showed a significant 2-way interaction effect. Post-hoc results showed significant interaction between stimulus shape and pre/post-tests only in the experimental group. There was a significant decrease in the grip size after feedback in the OUT condition of experimental group. However, in the control group, there was no interaction between stimulus shape and pre/post-tests. [Conclusion] Overall, current results indicates that, while visual illusion can affect the action, the provision of visual feedback can establish the awareness of actual stimulus size and suppress the influence of illusion on action.