Purpose : The purpose of this study was to investigate coaching information with which coaches provided players during badminton competition. Methods : To this end, we generated an open-ended questions and presented it to 88 high school athletes registered in the Badminton Korea Association. The survey was conducted during a tournament and immediately after the tournament to collect the data. The collected data were categorized through inductive content analysis. Results : As a result of this study, a total of 480 raw data points collected through the open-ended survey were categorized into four general areas: psychological information, technical information, tactical information, and game operation information. Specifically, psychological information was divided into six subdivisions: concentration, confidence, relaxation/stabilization, mental toughness, play thought, and passion; technical information was broken into four subdivisions: strokes, footwork, swing and posture, and position preparation; tactical information had four subdivisions: coping to opponents, play changes, rotation, and manipulation of opponents; and, game operation information was divided into two subdivisions: taking the lead in a game and changing atmosphere. Conclusions : In other words, in badminton competition, the coaches strengthened psychological skills that promote psychological stability to attain the athletes’ peak performance and modified the athletes’ motion into the action necessary for achieving accurate techniques. Furthermore, they provided a variety of coaching information so that the athletes will respond appropriately to their opponents’ play, take the lead in games and induce a positive mood. The psychological, technical, tactical and game operation information offered by badminton coaches are the main factors influencing the performance of badminton players and suggest a need for the proper management and control of the coaches as well as athletes for the peak performance.
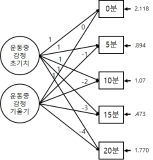
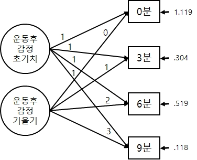
Recent research on exercise and affect has examined participants` affective changes during and after exercise with a longitudinal approach. With regard to this viewpoint, a theoretical model (Dual Mode model) has been presented to explain the different change of affect in an exercise setting and the model identified the impact of psychological factors on the affective changes. However, not only there is little empirical studies on the dual-mode model, but some relevant research has used an inappropriate statistical method (ANOVA), which cannot effectively explain the overall trends in affective change during and after exercise. Exiting research has a limitation to generalize the DM model examining only a certain gender such as active male or inactive female participants. Thus, the aim of present study was to investigate the effect of intrinsic motivation on affective change during and after exercise in participants who do not take part in regular exercise considering gender based difference. 51 inactive university students (M: 36, F: 15) responded a survey measuring intrinsic motivation for running activity and participated in moderate-intensity running exercise to examine affective change during exercise. Therefore, present study examined the influence of intrinsic motivation as a psychological variable on the trend of affective changes during and after exercise based on the dual mode model. Results from the latent curve model analysis revealed that there were decreasing trends of affect during exercise and the trends were individually different. Importantly, the decreasing trends were weaker in the participants with higher intrinsic motivation[FL=-.34, p=.000]. Additionally, participants` affective responses were positively changed after the exercise in general, but the changes were not influenced by intrinsic motivation. Therefore, the decreasing trend of affective change during exercise was weaker in the participants with higher intrinsic motivation, and the positive change in affect after exercise was not influenced by intrinsic motivation.

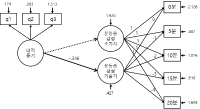
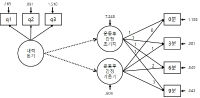
Drawing on the studies of implicit ways of teaching (Choi, 2002; Fenstermacher, 1990; Hasen, 2001; Oakeshott, 1989; van Manen, 1991), the aim of this study is to examine the educational effects of indirect teaching behavior (ITB), a new approach of researching teacher behavior, in order to better understand well-rounded education in the field of physical education. An ethnographically informed case study based on participant observation (eight months, 8th grade two co-ed physical education classes) was employed to produce a thick description of the ITB. Participant observation was supported by video recordings of classes, photos of students, questionnaires and interview, and teacher's self-report. Through inductive analysis of the data, we found that ITB had a powerful influence on forming a positive classroom atmosphere in relation to fun, active and moral. The positive atmosphere played a pivotal role in encouraging students' social and moral development including respecting their teacher, cooperating with other friends, learning the intrinsic value of physical education, and reflecting themselves. An understanding of ITB will help expand the way in which educators view teaching methods and studies in physical education beyond the dominant approach to techniques-oriented teaching in that ITB can be seen as essential content for holistic development of students. In this sense, this paper suggested that researchers and teacher educators need to re-examine the power of ITB in regard to teacher's professional competence in physical education and teacher education (PETE). For future research of ITB, it is necessary to explore what and how key personal and social-cultural factors impact teachers' ITB as is currently being conducted in the realm of teaching.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to find out the physical characteristics of Wushu athletes by comparing the differences on the results of physical fitness between the male athletes of the Wushu national team Taolu and the Sanda group. Methods Measurement of basic and professional fitness based on muscle function, targeting 37 men Wushu national team players (24 taolu, 13 Sanda) in the selection and evaluation contests twice in 2018 and 2019. Body composition, isometric muscle strength, flexibility and equilibrium, anaerobic power, and isokinetic muscle strength. The fitness factors were divided into two groups, Taolu and Sanda. Results First, body fat rate of the Sanda athlete group was significantly lower than that of the taolu athlete group (p<.01). Second, in the isometric muscle strength category(back muscle strength, grip strength), the Sanda athlete group had higher muscle strength than Taolu athlete group, but there was a statistically significant difference only in the left grip strength (p<.01). Third, in terms of flexibility and equilibrium, the taolu players were significantly higher in all items(p<.001). Fourth, in the anaerobic power, the taolu athlete group had higher both the peak power and the mean power, and there were a significant differences(peak power: p<.01, mean power: p<.001). Fifth, isokinetic muscle strength was significantly higher in the right knee flexion of the taolu athlete group (p<.01), and lumbar extensor muscle was significantly higher in the Sanda athlete group (p<.05). Sixth, in the isokinetic strength ratio, the knee flexion ratio of the Sanda athlete group were significantly higher on the left and right knee flexion and extensor ratios (p<.05). In addition, in the lumbar flexor and extensor ratios, the group of Sanda athlete group were significantly higher on the lumbar extensor(p<.05). Seventh, there was no significant difference between two groups in isokinetic muscle power. Conclusions The results of this study can be used as basic data to improve the efficiency of technical and physical training through the analysis of the characteristics of Taolu and Sanda. The effectiveness of this training will help to improve the performance.