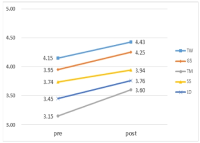
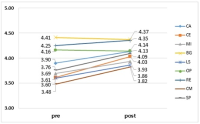
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of National Fitness Award program group exercise classes on daily fitness and balance-confidence among the elderly participants(n=496, 80.2% women). This study investigated body composition, daily fitness, and balance-confidence, and quality of life among the subjects who participated in the combined exercise program of improving physical fitness class for 8-week in the 10 national physical fitness certification centers by the demonstration project for the elderly of 2013 Korean National Fitness 100 project. Body composition and physical fitness for daily living were defined by Korean National Fitness 100 project for elderly, also the balance-confidence and health-related questionnaires were added. The following results were obtained by comparing the pre-test and post-test. In body composition body weight (p<.05), body mass index (p<.05), fat mass (p<.01), and percent body fat (p<.05) were significantly decreased, but muscle mass was not. Except for walking-around-two-cones-in-a-figure 8, all other daily fitness items such as relative grip strength (p<.001), chair sit to stand, two minutes place to walk, and sit-and-reach significantly increased (p<.01), and timed up and go were significantly decreased (p<.01). In balance confidence rating ABC tests (p<.001) were shown significantly increased. Although, quality of life measured by EQ-5D was not significantly improved, self-health status measured by EQ-VAS (p<.001) showed significant increase. Therefore, the group exercises of National Fitness Award program improved body composition, daily fitness and balance confidence in Korean elderly participants.
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the effects of motion analysis and image training using self-modeling with visual cues on the skill performance, imagery, and sports confidence of adolescent female soccer players. METHODS The participants were elite soccer players from two girls’ high school soccer teams divided into an experimental group (D girls’ high school, n=16) and a control group (I girls’ high school, n=13). The experimental group underwent motion analysis and image training when performing penalty kicks, short kicks, and long kicks using self-modeling with visual cues, while the control group underwent training using self-modeling videos without visual cues. Before and after the training, the evaluation score was calculated according to kick performance, and the imagery and sports confidence factors were measured. For the statistical analysis of all collected data, descriptive statistics, the Friedman test, the Mann-Whitney U test, and two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance were used. RESULTS First, on the motion analysis using self-modeling with visual cues, the experimental group’s penalty kick and short kick scores were improved and differed significantly, but no significant change was noted in long kick score. Second, as a result of image training using self-modeling with visual cues, all visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability factors of the experimental group improved except for the auditory factor, and the interaction effect was confirmed. In addition, the stated sports confidence of the experimental group was improved and the interaction effect confirmed. CONCLUSIONS The analysis of kick motion using self-modeling with visual cues was effective for the penalty kicks and short kicks of adolescent female soccer players. Moreover, this study confirmed that the analysis of kick motion improved the visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability sub-factors of imagery and significantly affected the players’ stated sports confidence.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to verify their effectiveness as we develop and apply worksheets for improving life skills and resilience of collegiate Taekwondo athletes. Methods The study went through three stages: developing, applying, and evaluating. In the developing stage, literature review, expert meeting, and pilot test (n=25) were conducted to develop the worksheets. In the applying stage, 37 athletes participated in life skills program using the worksheets. Data were collected by survey and in-depth interview. In the evaluating stage, paired t-test, word cloud analysis, and inductive content analysis used to identify the effect of worksheets. Results First, the worksheets were composed of 3 stages (plan, acquisition, implementation) and 15 sessions including 12 factors of life skills. Second, the worksheets were applied in each phases such as planning, acquiring, and implementing. In the planning phase, they understood life skills knowledge and set goals. In the acquisition phase, students learned specific life skills’ strategies. In the practice phase, the acquired life skills were applied and practiced in real life and relationships. Third, the result of paired t-test showed that all the factors of life skills and 6 factors of resilience were significantly improved. In addition, word cloud and in-depth interviews revealed that the participants' cognitive and psychological changes were most prominent. Conclusions The life skills worksheets consists of 12 factors in 15 sessions and can be considered as an effective intervention tool for improving the resilience and life skills of collegiate Taekwondo athletes.











Purpose The purpose of this study was to further understand how out-of-school adolescents’ self-esteem and interpersonal relations have changed in a peer mentoring basketball program and what they have experienced for the program It was action research of qualitative research method. Methods 4 out-of-school adolescents in the adolescents Center of C-si were selected as the participant. The data was collected by in-depth interviews, participant observation, and research journal. The collected data was then analyzed by an inductive categorical system. Results The findings were summarized as follows: the out-of-school adolescents showed somewhat low self-esteem and difficulties of interpersonal relations at an early stage participating in the peer mentoring basketball program. However, their self-esteem and interpersonal relations have been gradually changed during the program. First, they participated in various mentoring activities and self-expression activities. Their self-esteem has been improved as they found their real values, communicated with others, and lived with their confidence. Second, they overcame personal relations with fear and indifference of others, extended personal relations, and sympathized with others to solve the problem that they had as interpersonal relations. Conclusions The out-of-school adolescents has positively changed their self-esteem and interpersonal relations through the peer mentoring basketball program. We expect that out-of-school adolescents could overcome their difficulty and live well their life in the future.



Purpose This study was conducted to investigate the appropriateness of the concept of condition for athletes and to conceptualize condition in a way suitable for field and then to produce a tool to test condition that reflects usability. Methods 30 college athletes and national athletes with more than 5 years of experience were selected. In the conceptual review stage, the appropriateness of the concept of condition was verified. In the conditional element collection stage, the condition concept reflecting usability was extracted. In the development stage of the conditional questionnaire, a condition questionnaire was developed in consultation with the data provider to reflect usability. Results Previous studies on the condition of athletes were complicated and the necessity for consideration of usability was raised. As a result of conceptualization with consideration of the application to the sport scene, condition in a scene is summarized into both physical and psychological states. As a result of the appropriateness evaluation of the tool that produced the condition inspection tool reflecting the condition element based on universality and peculiarity of conditionality, the athletes evaluated that the condition inspection tool properly reflects condition, is easy to apply and can be used for condition control. Conclusion The development and application of psychological testing instruments reflecting usability will accelerate the application of sports psychology in the appropriate direction. The reflection of usability will contribute not only to the reliability and validity of the psychological testing tools used in the field of sports psychology, but also to the improvement of the possibility of intervention by leaders and athletes, the convenience of development procedures, and the utility of response results.

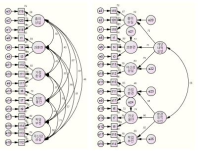
This study was to identify the structure of sports drop-out of athletes considering cognition, emotion and situational motivation, and to develop the measurement of sport drop-out motivation. For this, the validity of internal structure and relationship with overall drop-out intention were examined by targeting 689 individuals and team athletes. The results were as follows: Sports drop-out motivation was verified two hierarchical structure. One is individual internal factor including loss of interest, overtraining, loss of confidence, the other is environmental external factor including home environment, career anxiety, academic slump. The female players have higher drop-out motivation level than male players, and the drop-out motivation was shown the difference by level of school. Also, loss of interest and confidence weres to predict overall drop-out intention well. Therefore, this study was found this measurement was able to reliably predict drop-out motivation among players.

PURPOSE This study aimed to develop and implement a customized mental plan program to facilitate an optimal psychological state and peak performance among para shooting athletes. It also sought to empirically verify this program’s psychological effects by focusing on improvements in concentration, confidence, and relaxation. METHODS A total of six para shooting athletes who had earned medals in the Paralympic Games underwent six program sessions that were designed and implemented based on attention-related psychological factors identified through open-ended surveys and in-depth interviews. RESULTS The athletes’ attention was facilitated by task-focused behavior, breathing control, performance routines, and physical condition management. Meanwhile, their concentration was hindered by task-irrelevant thoughts, negative physical states, and external distractions. These factors were further categorized according to competition phase: the day before, precompetition, and during competition. Based on the statistical analysis, significant improvements were observed in the athletes’ concentration, confidence, and relaxation. CONCLUSIONS The custom program was practically effective as an intervention for psychological skills tailored to experienced para shooting athletes’ individual needs. The findings offer valuable insights for developing strategies supporting the psychological states of athletes in disabled sports.
PURPOSE This study identifies girls with learned helplessness in middle school physical education coping mechanism and growth process. METHODS Eight female 9th graders who previously experienced learned helplessness in physical education were purposely selected with their physical education teachers’ recommendation. After individual in-depth interviews, data were analyzed using inducted data analysis. RESULTS Findings show that the girls could overcome learned helplessness through their own will and with support of peers and physical education teachers. Moreover, they have undergone various growth processes after coping with learned helplessness. Recently, they have self-confidence in physical education classes and desire to learn physical education. Additionally, results showed that the girls’ learning will in physical education influenced other subject matters, which helped them overcome new challenges in their school and daily lives. CONCLUSIONS Results can be used as practical guidelines to develop educational programs and create policies for girls with learned helplessness.
PURPOSE This study aimed to extract football coaches’ categories of performance evaluation factors (PEF) and examine the reflective characteristics of the football coaches’ player and casting judgments. METHODS PEF were extracted through an open-ended questionnaire and categorization from 80 AFC C or higher football coaches. Reflection was calculated in player and casting judgments through an analytic hierarchy process. The difference between the football coaches’ player and casting judgments was examined using SPSS 21.0. RESULTS First, the PEF of football coaches were categorized into four general categories: physical intelligence, psychological intelligence, growth potential, and competition intelligence. Second, the importance of football coaches’ player judgments were reflected by the PEF as football intelligence, situation judgment, football talent, tactical understanding, tactical operation, etc. The importance of the casting judgment were reflected by the PEF as tactical understanding, mediative skills, fitness, tactical operation, situation judgment, etc. Third, a statistically significant difference was noted between player and casting judgments. Football coaches tended to value growth potential and talent as sub-factors in the player evaluations. Football coaches’ PEF were aligned with the importance of player and casting judgments in psychological and competition intelligence as sub-factors such as skills, physical, attitude, passion, etc., but differed from physical intelligence and growth potential as sub-factors including mediative skills, physical, football talent, and tactical understanding. CONCLUSIONS In the football coaches’ player evaluations, the idealistic principle centered on growth potential. However, in the casting evaluation, the realistic principle centered on victory takes effect.
Purpose The purpose of this studied to improve athletes’ performance through sports psychological skills training and counseling of a male canoe player in high school. Methods One male high school athlete in J area was interviewed for sports psychological skills training and counseling, and interviewed athletes and coaches diagnosed the potential psychological problems of athletes. Through this process, the athlete gained the ability to control anxiety about the game and strengthened the attention-focused ability to increase his confidence and set a goal for improving concentration. For effective training, sports psychological counselors, athletes, and coaches met once a week to create a routine. and participated in direct training on a boat with the coach every week. Sports psychological skills, anxiety about competition, and self-management of athletes were measured before and after to confirm the effectiveness of training of athletes' psychological skills. Results As a result, athletes' psychological skills and anxiety decreased, their confidence increased, and their concentration, which was diagnosed as an urgent problem of athletes, improved. Conclusions psychological skills of athletes, psychological shortcomings of players were reinforced, thus enhancing the athletes' performance. This suggests the effectiveness and necessity of training in sports psychological skills. It is hoped that continued support will serve as an opportunity to diagnose potential psychological problems of student athletes and apply them to training to contribute to improving their performance.