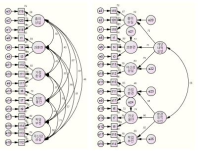
This study was to identify the structure of sports drop-out of athletes considering cognition, emotion and situational motivation, and to develop the measurement of sport drop-out motivation. For this, the validity of internal structure and relationship with overall drop-out intention were examined by targeting 689 individuals and team athletes. The results were as follows: Sports drop-out motivation was verified two hierarchical structure. One is individual internal factor including loss of interest, overtraining, loss of confidence, the other is environmental external factor including home environment, career anxiety, academic slump. The female players have higher drop-out motivation level than male players, and the drop-out motivation was shown the difference by level of school. Also, loss of interest and confidence weres to predict overall drop-out intention well. Therefore, this study was found this measurement was able to reliably predict drop-out motivation among players.

Purpose This study seeks to explore the process where drop-out elite athletes collect their life skills obtained during their sports career and transfer them to their daily lives. Methods An open-ended questionnaire survey was conducted on a total of ninety retired elite athletes and the responses were analyzed. Based on the results of inductive analysis, five subjects were selected for a follow-up in-depth interview. The responses to the open-ended questionnaire were analyzed by the inductive content analysis method and the results from in-depth interviews by the deductive content analysis method. Results A total of 478 life skills were collected from the drop-out elite athletes and structuralized into four general categories: psychological skill, social skill, self-management skill, and goal-setting skill. The results of this study have revealed that life skills positively transferred to their future courses of lives and daily lives. Conclusion It is believed that the results of this study will be helpful to understanding the concept of sports life skills, studying the possibility of transfer, and provide the basic data for helping drop-out elite athletes with re-socialization and positive adaptation.
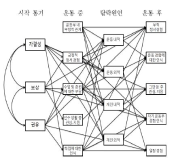
The purpose of this study is to explore the drop-out process of student-athletes and propose valuable policy ideas related to interscholastic sports. For this purpose, we surveyed 560 middle and high school drop-out student athlete's in 13 areas and finally 400 completed surveys were used for the study. To set the scales used for the study and test the reliability and validity of the scales, factor-analyses, Cronbach's alpha, and interfactor correlations were conducted using SPSS. For the main test, the paths analyses were carried out with AMOS program. As a result, we found two paths which had major effects on the drop-out process of student-athletes, self-efficacy path at the point of starting athletic career and negative relation path during athletic experiences. Based on these results, the following policy ideas were proposed. First, student-athletes should be able to join and leave athletic teams voluntarily. Second, the comfortable environments were provided to promote student-athletes' positive emotion toward athletic teams.

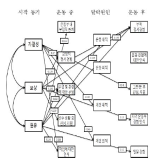



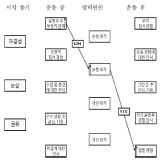
PURPOSE This study aimed to explore the re-socialization process of college soccer players who rejoin college soccer clubs after dropping out. METHODS A case study approach was employed, and participants were selected using the snowball sampling method. Data were collected through in-depth interviews, participant observation, and literature reviews. The authenticity of the data was validated through triangulation, member checking, and peer debriefing. All research procedures were conducted following approval from the institutional review board. RESULTS The study revealed several key findings. First, participants faced numerous challenges during the re-socialization process into sports, including interpersonal, academic, and emotional difficulties. Second, distinctive features of the re-socialization process emerged, including the determination and effort required for adapting to university life, support from socialization agents within the university, and rapid re-socialization following dropout. Third, experiences within collegiate soccer clubs indicated low barriers to entry for former athletes, academic success through complementary relationships, a hierarchical culture familiar to student-athletes, and enhanced satisfaction in interpersonal relationships and a sense of belonging. CONCLUSIONS This study underscores the importance of institutional support that enables college athletes to participate in sports clubs, facilitating the successful re-socialization of athletes who have dropped out.
This study was to explore and confirm factors of sport psychology counseling needs in Korean elite coaches. In order to achieve this purpose, 56 elite coaches in Korean Olympic training center at Taereung and Jincheon responded on open-questionnaire and 260 coaches responded on survey. Open-ended questionnaire responses were analyzed by inductive content analysis and collected survey data were analyzed by exploratory factor analysis and confirmatory analysis. The results were as follows: Firstly, sport psychology counseling needs of elite coaches were competition preparation, negative athlete-coach relationship, athlete private problems, performance degradation, pressure on performance result, injury management, team cohesion degradation, motivation, training management, different gender athlete control, athletes drop out, pressure from outside, conflicts with colleagues, neglecting from athletes, feeling of incompetence, emotional control problem, and so on. Secondly, based on these responses, closed-ended questionnaire was developed, surveyed, and analyzed. Exploratory factor analysis illustrated that sports counseling needs of coaches were performance enhancement strategies, unreasonable pressure, negligence on training, coaching stress, competition result stress, conflicts with athletes. Finally, confirmatory factor analysis showed that construct of sport counseling needs illustrated appropriate fit indices values. The results of this study contributed to provide fundamental information on coaching education program and sport psychology counseling program development and application. Consequently, it will help coaches to control their mind at coaching in training and competitions.

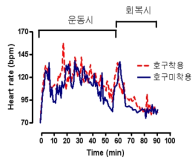
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of wearing of safeguard devices on various blood ions (i.e., Na+, K+, Ca2+) concentrations, gas parameters (PO2, PCO2, hematocrit [Hct], hemoglobin [Hb], Saturated [Sat] O2), and energy substrates (i.e., glucose, free fatty acid [FFA], lactate) concentrations during Kumdo training. Research scope extended to examine the heart rate changes during each exercise sessions. In order to achieve the research goal, 10 male elite Kumdo players, who play for G city in Gyeongsangbuk-do, were participated, and their mean maximum oxygen uptake level was 51.2(±6.1)mL· kg-1min-1. All subjects undertook Kumdo training sessions twice, which carefully pre-planned and consisted of routinely carrying out exercise program. Training period for each session was 80 min long including 10 min each for warm-up and warm-down period, but the conditions with wearing body protection devices were different following either with wearing complete set of safeguard devices or without wearing any safeguard devices except general training cloth. Heart rate was measured by every minute interval. K+ and Ca2+ showed interaction effect between the conditions with wearing safeguard devices and conditions with time of Kumdo training. Hct and Hb level significantly increased after 60 min Kumdo exercise regardless of wearing safeguard devices. Kumdo training induced dropping of blood pH independently with wearing safeguard device conditions, however the values and/or concentrations of PO2, Na+, glucose, lactate, Sat O2were significantly increased. Heart rate was maintained marginally higher values throughout exercise period when safeguard devices were worn. Based on these results, it was concluded that wearing the safeguard devices could possibly be causing a physiological metabolic changes, and this may be drawn by increased body fluid loss and energy expenditure. Further study should be undertaken to examine the effects of wearing safeguard devices on hitting intensity and hormone secretion and concentrations, that closely associated with body fluid and ion balance during Kumdo exercise and/or training.
