PURPOSE This study assessed Taekwondo’s impact on functional fitness and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in older women from South Korean multicultural families. METHODS Through purposive sampling, 16 participants were divided into an experimental group that underwent a 12-week Taekwondo training program and a control group without this intervention. RESULTS Pre- and post-intervention assessments showed that the Taekwondo group experienced significant improvements in both functional fitness and HRQoL. These findings suggest that Taekwondo could be an effective physical activity for enhancing the well-being of older women in multicultural families, advocating for inclusion of culturally sensitive physical activities in health promotion programs targeting this demographic. CONCLUSIONS This study contributes to the growing body of evidence supporting physical activity’s benefits for elderly populations, particularly in multicultural family dynamics.

Purpose This study has been conducted to explore the factors that ignite the mental toughness of Taekwondo players and to compare report ratios concerning the explored factors between training and competition. Methods An open-ended questionnaire conducted 123 Taekwondo players offered raw data that stemmed the from 379 training and 369 competition situation. The raw data was categorized by an inductive approach, and the report ratios of both general and specific domain mental toughness in training and competition were compared. Results The results of this categorization were as follows. First, the mental toughness ignition factors of Taekwondo players are commonly categorized as willing to goal, external pressure, reward expectation, challenge, and social support. Second, factors were prioritized into reward expectation, challenge, willing to goal, social support, and external pressure. Third, willing to goal and external pressure were often reported in training, while reward expectation and challenge were more often reported in a competition. Social support showed similar ratios in both settings. Conclusion This study is expected to offer interesting results in the context of the ignition of mental toughness, while being utilized as a fundamental database for the development of mental social support strategies the help Taekwondo players ignite their mental toughness in competition.



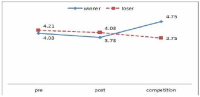
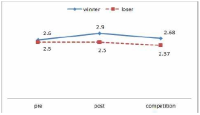
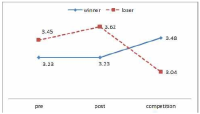
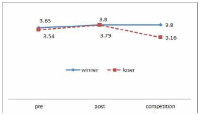
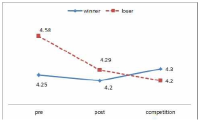
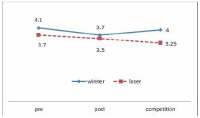
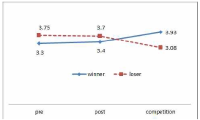
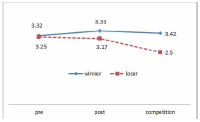
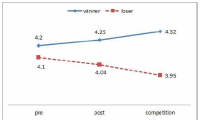
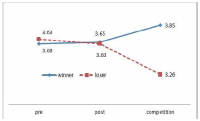
The purpose of this study was to confirm the differences between winner and loser groups of national team participated in the World Taekwondo Championships statistically and trends of psychological status according to applying mental coaching. In order to achieve the purpose it was the selection of 16 national members participated in the 2013 World Taekwondo Championships in Puebla. Data was selected by TOPS(test of performance strategy). The survey was conducted before and after applying the mental coaching and the game soon after. Data processing results were calculated utilizing Excel and SPSS 21.0 version. Based on the findings issue the conclusions were as follows. First, the psychological state of the winner and loser groups showed a different trend in the self-talk, emotion control, performed automatically, imagery, struggle, negative thinking, relaxation, condition factor. Winner group was shown maintenance or better trends of psychological state in the three times measurements on the other hand, loser group was shown decrease in the game soon after. Secondly, winner and loser groups are statistically significant differences in the psychological state of competition in self-talk, struggle, negative thinking, solving tension factors. In other words, The winner group had higher score in the four factors than loser group in the competition.

PURPOSE By analyzing trends in Taekwondo demonstrations, specifically in breaking and performances, to date, this study aims to offer timely insights and set the groundwork for future research. METHODS We used Korean abstracts from a total of 425 papers containing the keyword “Taekwondo demonstrations” spanning 20 years from April 2004 to April 2023. We employed Python 3.5.2 to conduct dynamic topic modeling (Latent Dirichlet Analysis, LDA) and to examine the correlation between the topic distribution by section and the publication year. RESULTS The main findings from the LDA are as follows. Topic 1 (10%): “The development of demonstrations: performance in culture and art, ” Topic 2 (11%): “The development of formalized rules and judgments in a demonstration event,” Topic 3 (08%): “A study on the educational courses and professionalism of Taekwondo coaches,” Topic 4 (11%): “Technical movements and kinematic characteristics,” Topic 5 (09%): “A study on marketing perspectives of demonstration performances,” and Topic 7 (33%): “Global exchange: the development and rise of internationalization.” In the correlation analysis between the topic share by section and the publication year, Topics 1 to 5 exhibited no statistically significant correlation. However, Topic 6, “A study on the attainment of events, training, and the psychological factors influencing athletes” and Topic 7, “Global exchange: the development and rise of internationalization,” also displayed a very statistically significant but negative correlation. CONCLUSIONS Future research should focus on studies on the psychological management of athletes during the performance of specific techniques and training methods. Further research considering the global characteristics of Taekwondo may be required.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to apply the Self-Assertiveness Training based on Solution-Focused to student-athletes caused by violence in sports. Methods Participants were five Taekwondo athletes in this study. They were consisted of offenders, a accuser, and a victim. The head coach of the team asked for counseling to resolve the conflict. Data was collected with quantitative, qualitative data, and group dynamics. The group counseling program was conducted for 90 minutes a week for eight weeks. Results The results are as follows. First, (application process) the 8-week Self-Assertiveness Training based on Solution-Focused was assessed to be applied step by step and systematically. Second, (qualitative evaluation) as a result of analyzing the observation journal and the interview data, the participants experienced the change of attitude and thought of group members in a short period of time by focusing on enhancing self-assertiveness. Third, (quantitative evaluation) self-assertiveness and attitude of school violence measured by questionnaires were higher in post-survey than pre-survey. In addition, participants' satisfaction with the program was found to be very positive. Discussions and Suggestions Self-Assertiveness Training based on Solution-Focused was found to have a significant effect on conflict resolution among the student-athletes who have experienced violence in sport. This programs was expected to increase the value of use in the sport field. Based on this case study, We suggested for future research.



Purpose This study was to investigate the systematic application of the life skills program and its effects in a sport setting. Methods Participants were 14 college students(8 males and 6 females) majoring in Taekwondo. Survey tools were utilized to measure items of life skills and journals. Data analyses were conducted by using Excel program and inductive content analysis. Results First, life skills in this study consisted of goal setting, self-talk, imagery, cognitive restructuring. Life skills program has undergone a procedure, such as the introduction, training, development, application, and evaluation. Second, the average scores of life skill variables have been changed according to measured points. Specifically, the average scores of goal setting and self-talk were highly increased over time and the average score of imagery indicated gradual rising line. The average score of negative thought was slightly reduced over time. Third, regarding effects of this program, participants’ responses were categorized into six components; performance enhancement, positive thoughts, chances of change, goal setting, struggling efforts, and motivation formation. Further, participants stated this program was a great opportunity to develop these components. Conclusion The application of life skills program in sport settings will contribute to participants’ life span developmental change in cognitions, emotions, and behavior.



This study aimed to explore elite taekwondo competitors’ imagery strategies . The study participants were 10 elite taekwondo athletes, who worked for S business team. Data were collected through open-ended questionnaires and in-depth interviews. The data were collected based on Gould et al. (1992)’s proposed qualitative research method. The inductive content analysis of the imagery was conducted following the imagery type of Paivio (1985) and Suinn (1996). The law data and case of imagery were separated by three specialists. The results were as follows. First, elite taekwondo competitors generally used the types of imagery proposed by Paivio (1985) and Suinn (1996). In particular, imagery of anxiety regulation appeared with the highest frequency among factors and ordered imagery of motivation, imagery of skills, imagery of mental skills, and imagery of competition. Second, elite taekwondo competitors mainly used imagery of skills before two weeks for competition. They mainly used imagery of anxiety regulation the day before a competition. They used imagery of anxiety regulation and imagery of motivation on the day of a competition. They used imagery of motivation after the competition. In sum, elite taekwondo competitors used individual strategies in terms of imagery in order to ensure effective training and peak performance in competition. The strategy of imagery was applied differently based on the juncture of the competition.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to examine the location, rate, cause, and types of injuries according to the injured area by age and sports in female athletes. Methods The subject of the study was 426 female athletes who were registered as combat sports(Judo, Taekwondo, Fencing) athletes at the Korean Sports & Olympic Committee. We collected the data via online questionnaires, and conducted a frequency analysis using R statistics program. Results As a result, 51.4% of athletes experienced injuries in the past year, and the highest injury rate was shown in Taekwondo-University(0.43) during competition and Taekwondo-Professional(5.55) during training. The cause of injuries during competition was mainly due to 'as a result of me or the opponent's hittings, skills, or fouls' among internal factors, and 'recurrent injuries' among external factors. Among internal factors during training except for torso area and professional athletes, most of the injuries were also caused by ‘as a result of me or the opponent's hittings, skills, or fouls’ and ‘recurrent injuries’ among external factors. The frequency of injury was the highest in the lower extremity area across all age groups. The most frequently injured area, in the case of Judo, is skin-bleeding in the head, skin-bruise, muscle-inflammation, bone-fracture, spondylopathy(disc, stenosis, etc.) in the torso, muscle-inflammation in the upper extremity, ligament-sprain, rupture in the lower extremity. Taekwondo athletes had skin-bruise in the head, upper and lower extremities, and muscle-inflammation in the torso area, as the frequent injury cases, and Fencing athletes had all skin-bruise regardless of injuries. Conclusions The results of this study will be used to take measures for preventing injuries or to change training programs.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to apply a life skills program to student-athletes and statistically verify the changes in life skills of the experimental and control group. METHODS Participants were 34 high school Taekwondo athletes (Mage=17.71). They were divided into 18 in the experimental group and 16 in the control group. For eight weeks, the experimental group participated in the life skills program after training and the control group participated in only training as usual. Data were collected by using Life Skills Scale for Student-Athletes (LSSSA), and the participants of two groups filled out the LSSSA before and after the program application. The collected data were analyzed by using repeated measure analysis of variance (ANOVA), and partial η2 (eta squared) was calculated to present the effect size. RESULTS The interaction between time and group was statistically significant in goal setting, coping with stress, positive thinking, and managing emotion among sub-factors of life skills. Partial η2 was interpreted as having a large effect size as it revealed the range of .22 to .51. Therefore, comparing before and after participating in the program, the life skills score of the experimental group among the two groups was significantly improved. CONCLUSIONS Student-athletes who participated in the program experienced positive changes in life skills than those who did not participate in the program.
The purpose of this research is to provide the information about sports injury by surveying and analyzing a result, and to lead analytic and scientific training among the subjects being elite summer sport athletes. All sports injuries are recorded on injury report form and the following results were obtained. In Cycle sport, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees were highest. and In Table tennis sport, the prevalence of injuries of the ankle was highest due to the chronic fatigue. The prevalence of injuries of the shoulder, low back were highest due to the overuse of joints. In Badminton sport, the prevalence of injuries of low back, knees, ankles were highest by overtraining. In Gymnastics, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees, ankles were highest. In Archery sport, there is a lot of injuries to the shoulder and neck. In Weight lifting sport, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees, and ankles were highest. In Golf sport, the prevalence of injuries of knees, low back were highest. In Hockey sport, the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees, low back were highest. In Boxing sport, the prevalence of injuries of hands, shoulder, the low back were highest, In Judo sport, there are overall damage occurred in parts of the whole body, but the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees, low back were highest. In Fencing sport, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees were highest. In Wrestling sport, although there is a difference slightly depending on freestyle and Greco-Roman, but the prevalence of injuries of knees, ankles, low back were highest. In Handball sport, the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees were highest. In Taekwondo, the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees, feet were highest.