Purpose Lock and Heere (2017) argued that two different theories of social identity theory(SIT) and role identity theory have been used in previous studies of team identification. However, they failed to provide why such phenomenon existed in the literature of team identification. Thus, the first purpose of the study is to provide the possible reasons why the two theories were used as the ground of team identification in the previous literature. In addition, the current study examined whether team identification was properly developed from SIT by incorporating the cases of organizational identification and consumer-company identification in business literature. Results & Conclusion There are two possible explanations on why the two theories have been used in team identification studies. First, in the initial studies of team identification, theoretical ground of team identification was lacking. Thus, without a firm theoretical guidelines, authors might have used the two theories as the ground of team identification. Second, as previous literature noted, the two theories are like the two different sides of a single theory. Thus, authors may have not recognized the need of differentiating the two theories and used the two theories as the ground of team identification. This study also examined whether team identification was properly developed from SIT. The social category in team identification includes two different social identities(team members and fans), which is quite different from a social category with single identity in it. The locus of social category of team was arbitrarily expanded to include fans in the same category. This case is quite similar with consumer-company identification in marketing literature. Future study needs to examine whether the locus of social category can be expanded to include two different social identities.
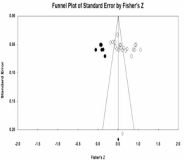
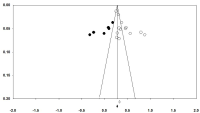
[Purpose] The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect size of the relationship between team identification and their intention to attend sport events and intention to purchase licensed team merchandise using a Meta-analysis. [Methods] To accomplish the purpose of the study, multiple databases were visited (e.g., RISS, KISS, Library of National Assembly) and studies were collected using the keyword of team identification. Through the search process, total of 92 studies were identified, among which 20 studies provided Pearson correlation coefficients between team identification and intention to attend and 13 studies between team identification and intention to purchase licensed team merchandise. The 33 studies were analyzed using Comprehensive a Meta Analysis(CMA) program. The analyses were done using random effect model assuming there were significant heterogeneity among the studies included. [Results] The overall effect size between team identification and intention to attend sport games was .567 and .403 for between team identification and intention to purchase licensed team merchandise, which can be classified as large effect size(Cohen, 2013). Sub-group analyses were done using types of publication(journal article vs. thesis). The results of the sub-group analyses indicated that the effect size differences were statistically insignificant. [Conclusions] As indicated in many previous studies, team identification was found to be a significant predictor of sport consumers’ behaviors. However, future studies need to find the reasons of heterogeneity in effect sizes.

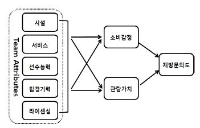
The purpose of this study was to provide managers and owners of Korea professional baseball teams with the necessary information for improving managerial performance by fan acquisition and retention. This paper chose LG, Nexen, and SK fans over the age of 17 as population of this study who visited at least twice home games held in the Jamsil, Mokdong, and Munhak baseball stadium. For the analysis of data, 413 questionnaires were used using SPSS 15.0 Windows and Amos 7.0. To examine respondents demographics traits, frequency analysis was processed and reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis and correlation analysis for relationship among the variables were conducted. Also, convergent validity analysis and discriminant validity analysis were made. Finally, path analysis was made for the verification of model suitability and of research hypotheses through structure equation modeling. The research results are as per the below. First, team attributes like physical facilities, team performance and licensing had significantly positive influence on consumption emotion. Second, team attributes like service and team performance significantly positive impact on viewing value. Third, consumption emotion had significantly positive impact on revisit intention. Fourth, viewing value had significantly positive impact on revisit intention.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the role of trust on sport fan behavior following the favored team’s loss. Methods Online survey modes were employed to collect the data. A total of 300 individuals participated in the study, of which 288 were valid and therefore analyzed. To test the hypotheses, structural equation modeling was conducted using Mplus 8. Results The findings are as follows. First, cognitive trust had a significant effect(+) on future viewing intention. Second, affective trust had a significant effect(+) on future viewing intention. Third, cognitive trust had a significant effect(-) on switching behavior. Fourth, affective trust had no significant effect on switching behavior. Fifth, team identification moderated the relationship between affective trust and switching behavior. Conclusions The results of this study suggest that sport fans’ trust affects fan behavior following a team’s loss. Therefore, professional sport teams should seek to establish strong affective trust and cognitive trust.

The purpose of this study was twofold: 1) to investigate the structural relationship among the variables interested, and 2) provide rationale for professional sport team parent companies for operating and managing professional sport teams. Using convenience sampling method, data was collected at a professional soccer match held in Suwon World Cup Stadium through survey distribution. Collected data were analyzed using SPSS 20 and AMOS 20. The results derived through multiple steps of data analysis displayed that community attachment and team image significantly affected team identification. Moreover, team identification affected parent company image, parent company image affected parent company product image, and parent company product image affected purchase and WOM intention. As a result it was found that for parent companies, operating and managing a professional sport team not only provide intangible benefits such as brand awareness and brand image, but also economical benefits such as increase in product sales through improved company product image.
