
Sportscasting in Physical Education (Lee, 2011) is a class activity that students simulate sports broadcasting (e.g., students report, analyze, and comment on game play). It encourages problem solving (PS) learning for students. Scaffolding is the support with the intention of helping the student achieves his/her learning goals and contributes to problem solving. However, limited studies have examined if sportscasting with scaffolding is effective instructional strategies for PS. The purpose of this study was to examine effects of sportscasting with scaffolding on PS abilities, and on academic achievement. Participants were 46 college students. The static-group comparison design was used: an experiment group (N=26) with supportive scaffoldings (e.g., conceptual explanation, terminology dictionary, visual materials) and a control group (N=20) with reflective scaffoldings (e.g., organizing the environment, using appropriate cues to guide behaviors, and modeling). The results revealed that students in reflective scaffoldings had higher PS abilities than students in supportive scaffoldings. However, two groups were not statistically different in academic achievement. Sportscasting with instructional scaffolding promote a deeper level of cognitive skills and male students performed better than female students. The effective scaffolding types (Lewis, 2010) for sportscasting were discussed to help students to foster PS skills.


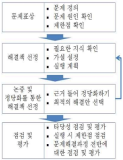
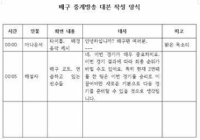
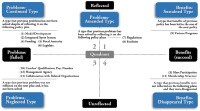
Purpose The purpose of this study is to identify policy learning in the government-led sport club policy and to analyze its type of the policy learning. Methods Sport club related documents such as policy plans, evaluation reports and journals published from 2004 to 2018 were analyzed by framework of this study. For identifying the policy learning, 12 items were determined by policy goals, policy means and policy targets. Each item was placed on four quadrants of the X-axis(benefits and problems) and the Y-axis(reflected and unreflected), and was categorized. Results This study found out the five types of policy learning. A 'benefit-sustained type' is the type that benefits of previous policy has been led to the benefits of next policy and a ‘problem-amended type’ is the type that previous problem is solved by reflecting on the following policy plans. A ‘problem-continued type’ is the type of problem that has not been solved. On the other hand, A ‘Benefit-diminished type’ and the ‘problem-neglected type’ are that previous results were not reflected. It indicates that those types have not performed the policy learning. Conclusions In order to expand the benefits of the sport club policy and to solve the problem, we should recognize the policy process and environment are not static and do policy learning. Furthermore, it suggests that there should do policy learning on what Korean sport club would be.


Purpose This study was to investigate the effect of various motor leaning techniques which were applied on the youth soccer training program. Methods 12 elementary soccer players and the director of R youth soccer team have participated in the study. The expertise level of youth soccer team were ranged from beginner to advance. To investigate the effect of new soccer training program we adopted a methodology of action research. We first analyzed the problems of original youth soccer program and reconstructed the training program considering of individualized characteristics. The 3 main problems of original soccer program (1. feedback provisions 2. difficulty of task level 3. time distribution of training) have been reconstructed by four motor learning experts. For the data analysis, several qualitative analyze techniques were conducted to observe player’s improvements. Results First, participants had a better understanding on proper motion of shooting and lifting skills from the guidance techniques. Second, utilizing the personal skills and team cohesion have been improved by the modified rules and space competition. Third, the ability of active problem solving have been improved from the self-learning environment. Forth, the player’s confidence level have been improved by eliminating performance outcome. Conclusions From the aspects of variety circumstances in sport education field, the comprehensive motor learning program should be developed and applied.

Purpose The purpose of this study is to explore the physical activity promotion plans for female student by revising and supplementing the SPARK program which is actively applied as a P.E physical activity improvement program recently. Methods To achieve this, this study followed the custom of action research and apprehended problem in female students' physical activity in SPARK soccer program(first action and examination), problem solving plan(replanning), execution and evaluation of replanned SPARK soccer program (second action and evaluation). The collection and analysis of data was conducted by sequential explanation strategy. Specifically, the study utilized 3 dimensional accelerometer to measure the physical activity in P.E class, and collected data which could apprehend the experience of students by utilizing qualitative study tools(observation, class note, interview). To analyze the collected data, the study utilized mixed-methods study analysis method developed by Greene(2007). Results The study results are as follows. As for the result of first action(October~November 2014), SPARK program increases the entire physical activity in P.E class, but the female students' activity was relatively lower than male students'. The reasons for lower physical activity of female students' were unmotivated class, burdensome class, alienated class. These were specified into teaching strategy to replan and execute the second action (May~June 2015). Compared to first action, the second action showed positive physical activity, and the MVPA of female students' showed statistical difference (<.01). As for the result of qualitative analysis, the positive grounds of second action are 1) motivative resource like "necessity", 2)hard but meaningful learning activity, and 3)kind P.E teacher. Conclusions In conclusion, the implementation of a soccer class with a modified supplement to the SPARK program can enhance physical activity of female middle school students.
Purpose The purpose of this research is to provide implications for the study of the physical education curriculum in Korea and China by comparatively analyzing the revised high school physical education curriculum in the two countries. Methods Using Bereday(1964)’s four steps of comparison model in education, this study focuses on the format and content of the general high school physical education curricula of Korea and China, each curriculum having been revised respectively in 2015 and 2017. Results First, in terms of format, both countries consider PE a necessity and share similarities in regard to course structure, credit allocation and document format. Nevertheless, though both countries are oriented toward competency-centered education, there are some differences with respect to official education curriculum documents, numbers of subjects and hours of study based on the reality and situation of each country. Second, in terms of content, both countries present various teaching methods and evaluation principles for the sake of acquiring core competence. However, the Korean curriculum prefers to advocate learning of the value of physical activity to achieve core competencies, while the Chinese curriculum prefers to focus on acquiring athletic skills and health knowledge for achieving core competencies. Conclusions After comparing physical education curriculum in both countries, two implications could be obtained. One is that the consistency problem in Korea should be solved between the core competency, the teaching and learning methods and evaluation standards. The other is that, in China, integrated value of physical education should be paid more attention and core competency as well as teaching and learning methods should be considered.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to understand student athletes coaches’ occupational challenges from the dual perspectives(social relationship-political system), to analyze the nature of the coping strategies for the challenges, and to provide implications for building a human rights-friendly student athletes club culture. Methods Five coaches(n=5, average career length= 19.2 years) were selected through purposeful sampling. Data were collected by semi-structured interviews with participants. The collected data were inductively analyzed(Patton, 2015). Results First, participants struggled with informal roles demanded by the interested parties(principals, athletic directors, parents, and university coaches). Second, the system for protecting student athletes’ learning rights, the 52-hour work system and the human rights system added difficulties to the coaches’ work environment. Third, the disharmony between interested parties’ demands and government agencies’ institutional ideals pushed participants to choose anti-institutional, un-ethical, un-educational coping strategies. Conclusion The findings suggest that the government, academia and the community should empower coaches as ‘the subject of reform’ who can solve the problem together rather than regarding them as ‘the object of reform.’ Furthermore, this conclusion is expected to provide implications to alleviate disharmony between interest parties’ demands and government agencies’ systems.’
PURPOSE This study aims to investigate the problems posed by the new “Health Exercise Managers” qualification system implemented in 2015 and suggest a reformation plan for the qualification definition, written test, and practical–oral test. METHODS Eleven experts working in the academia and the exercise prescription field were selected as research participants using purposive sampling method (professors=5, director of sport science division in national research and development institute=1, head of national/private organization that issue Health Exercise Managers certificates=2, and health exercise managers working at university hospitals =3). The results were collected, examined and classified following numerous discussions among the authors. RESULTS First, the qualification definition should be based on “course completion” in the short term and “department certification” in the long term. Second, the written test can be reformed by identifying the core courses related to health exercise management and merging similar or overlapped courses. Also, the grades should be calculated for each question based on the knowledge gained in related courses. Third, the practical–oral test questions should be publicly available in advance to help candidates better prepare and learn practical skills, rather than set the standards for elimination. CONCLUSIONS An overall reformation of the qualification definition, written test, and practical–oral test will solve the problems posed on the quality of the “health exercise managers” qualification system.